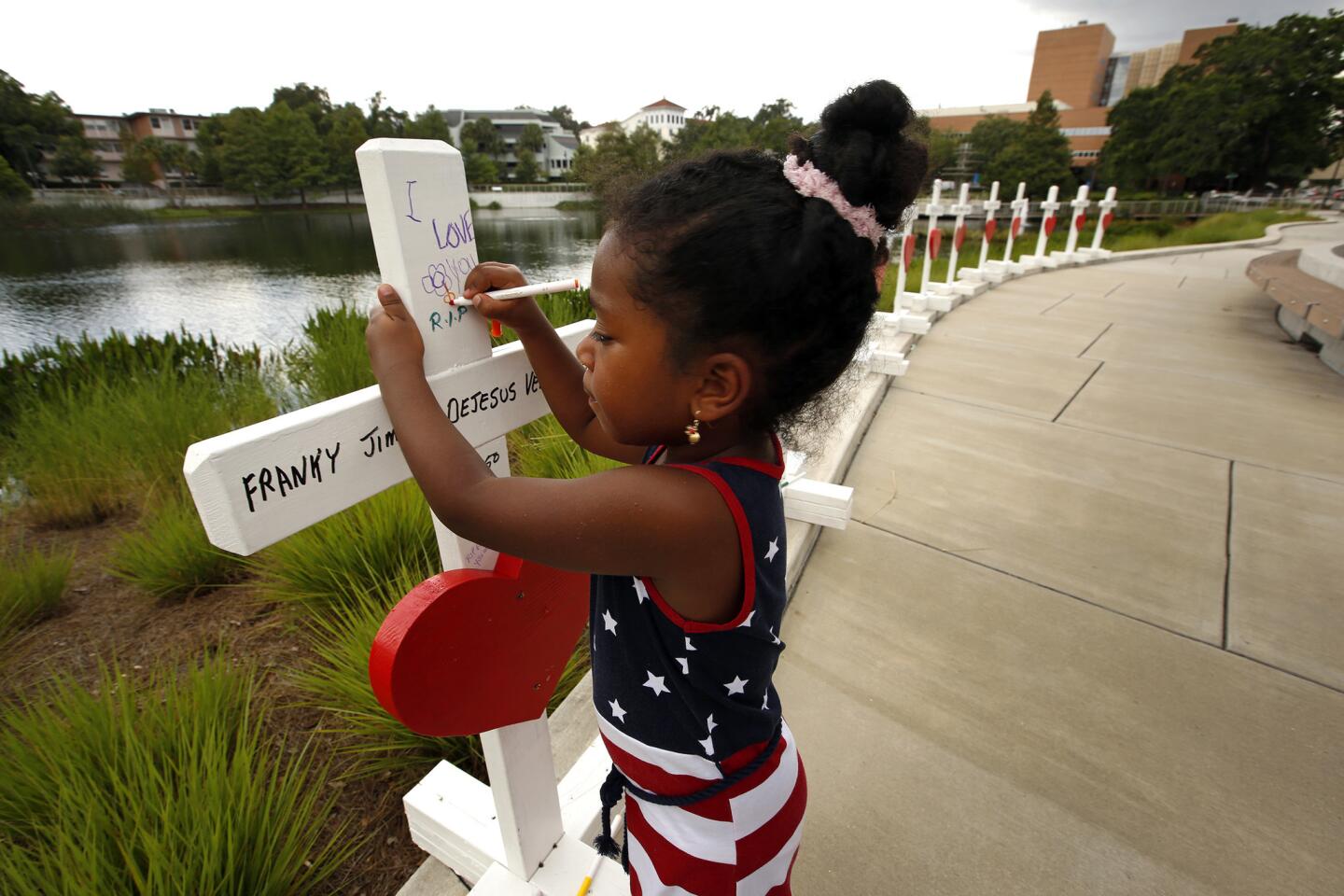
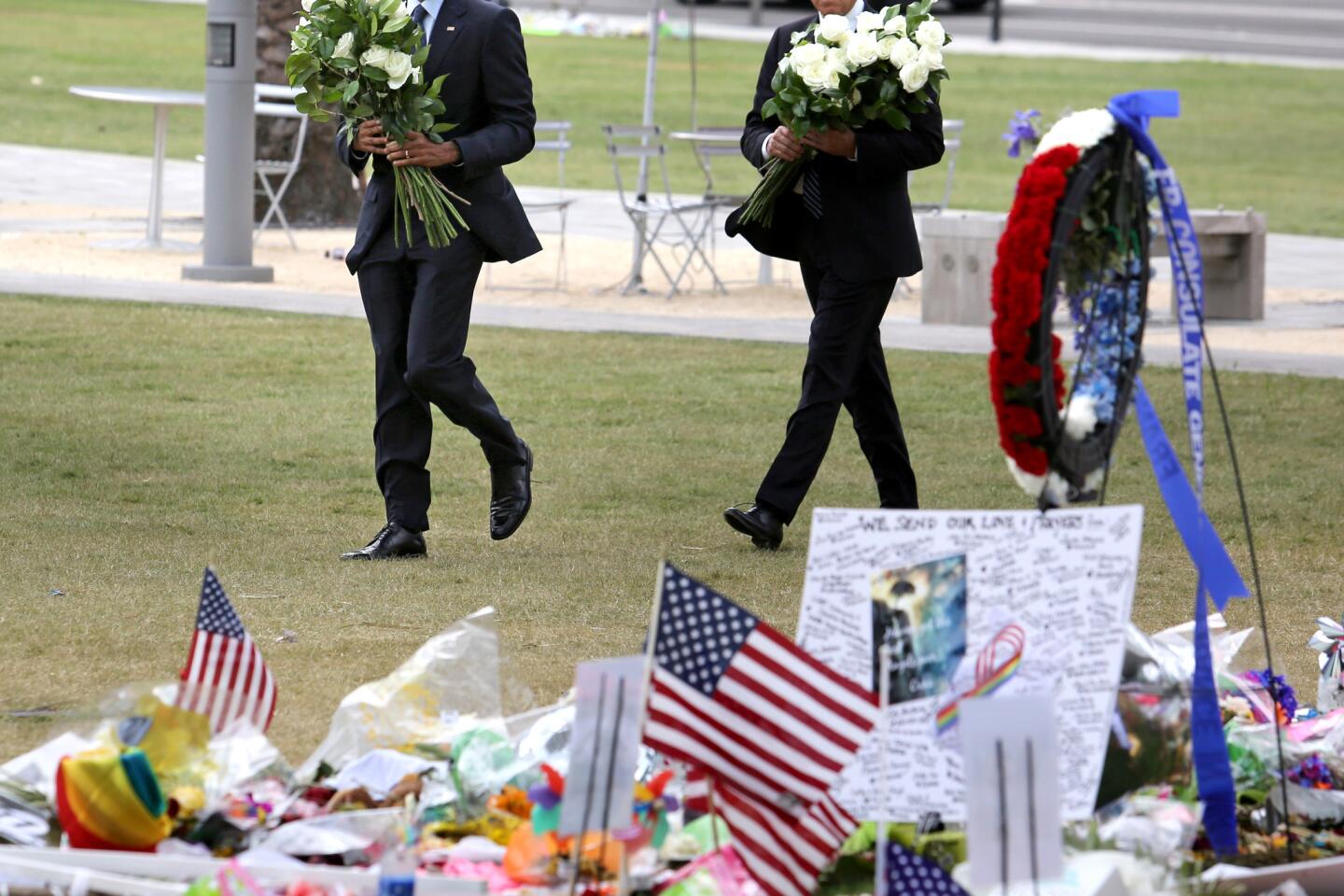
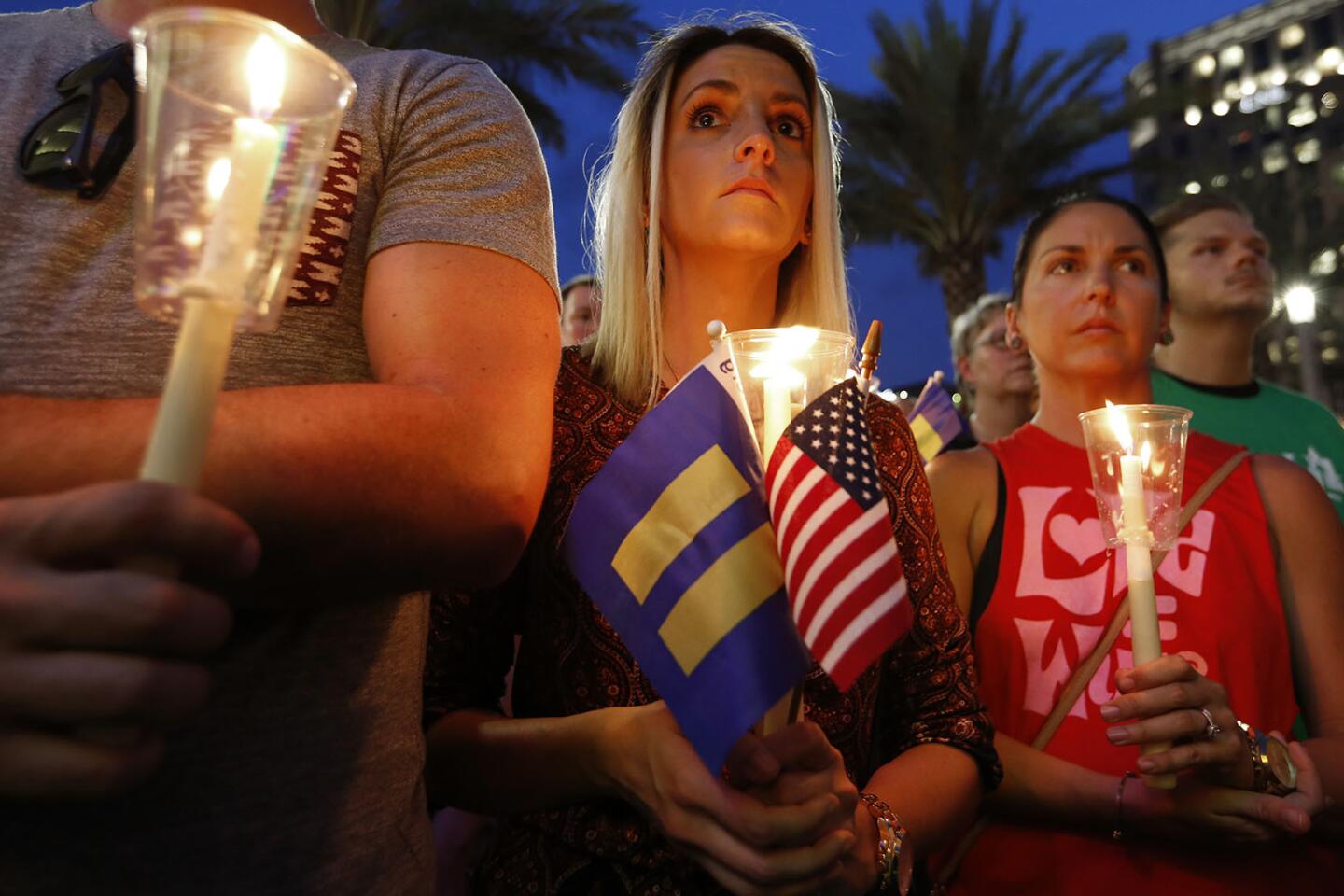
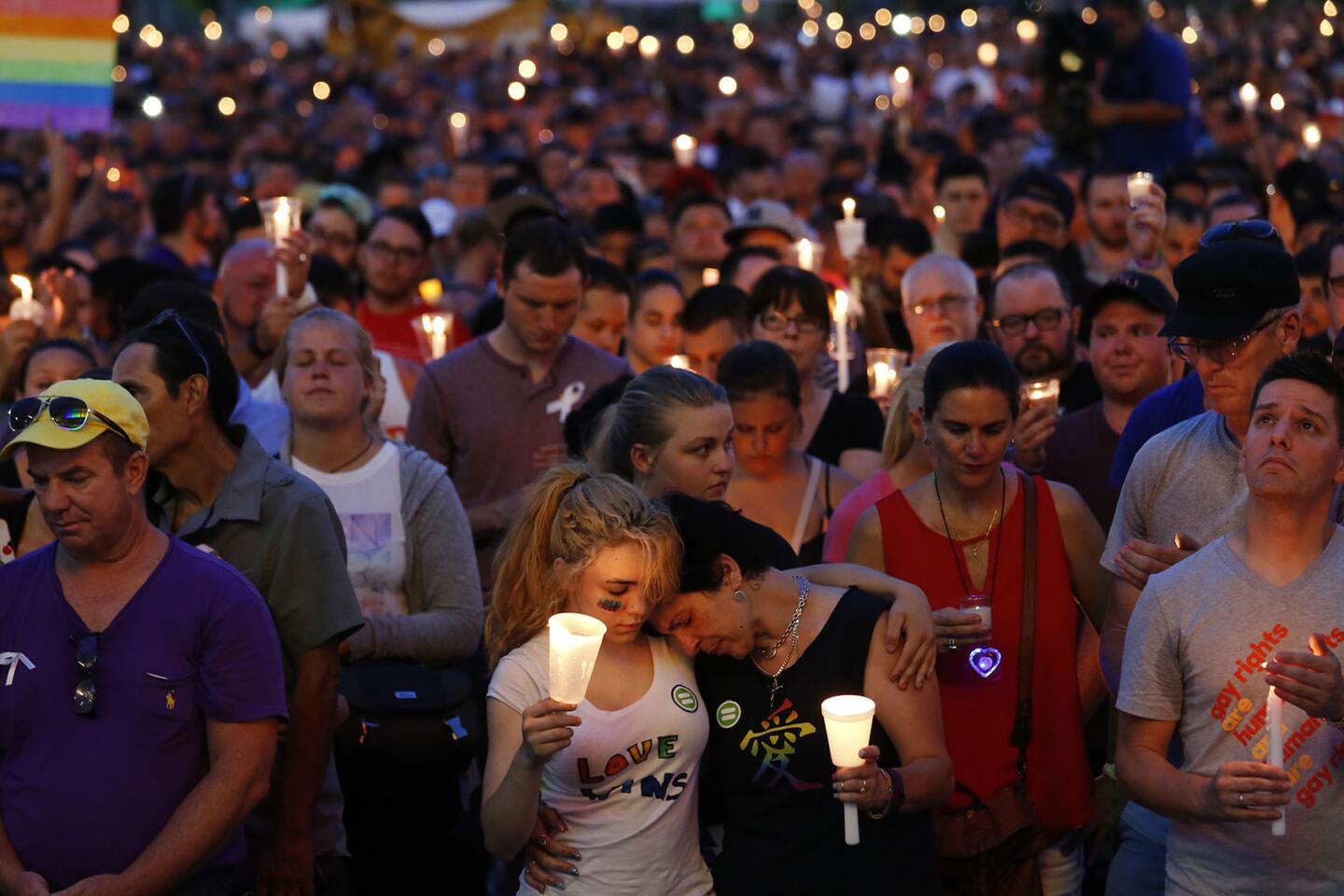
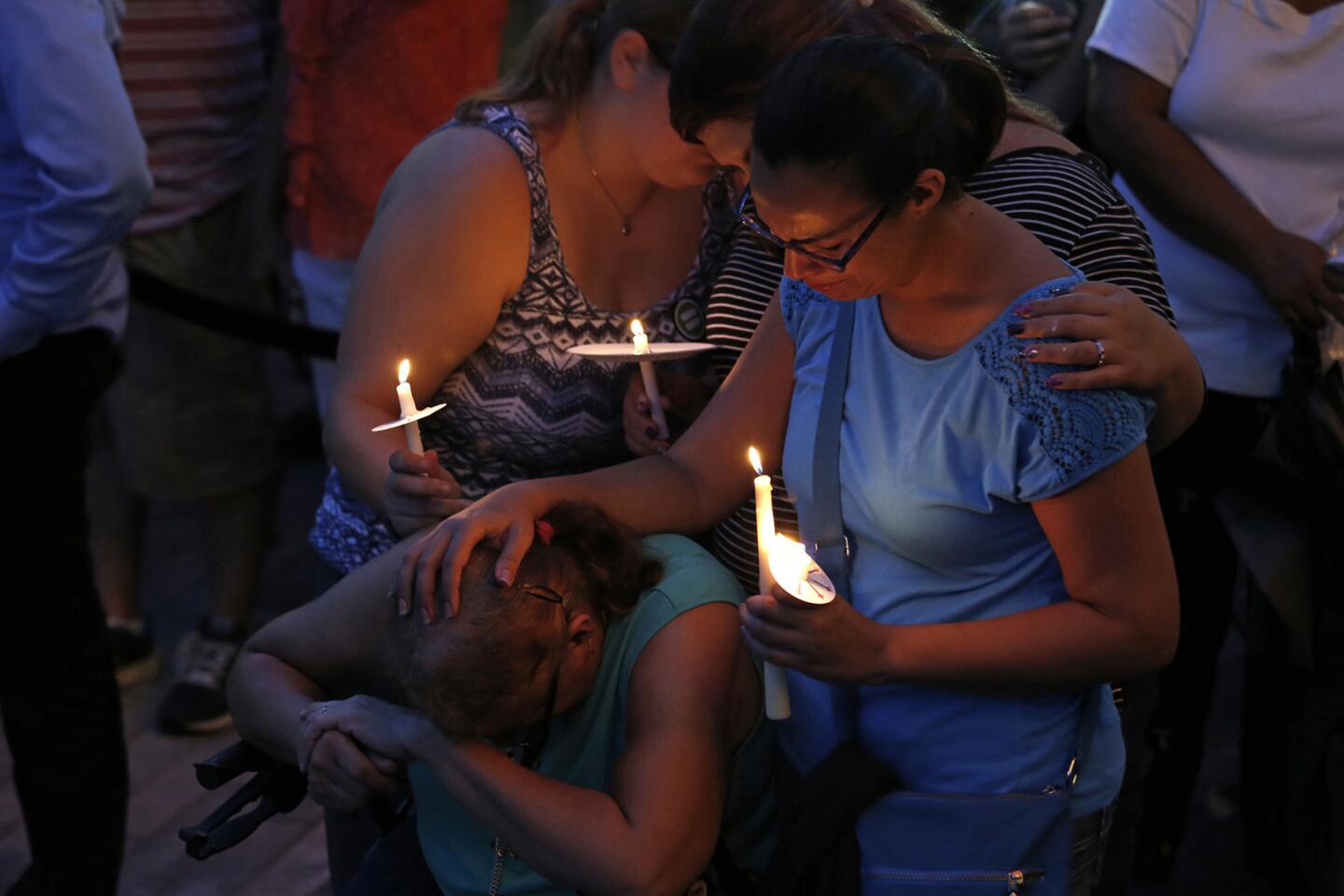
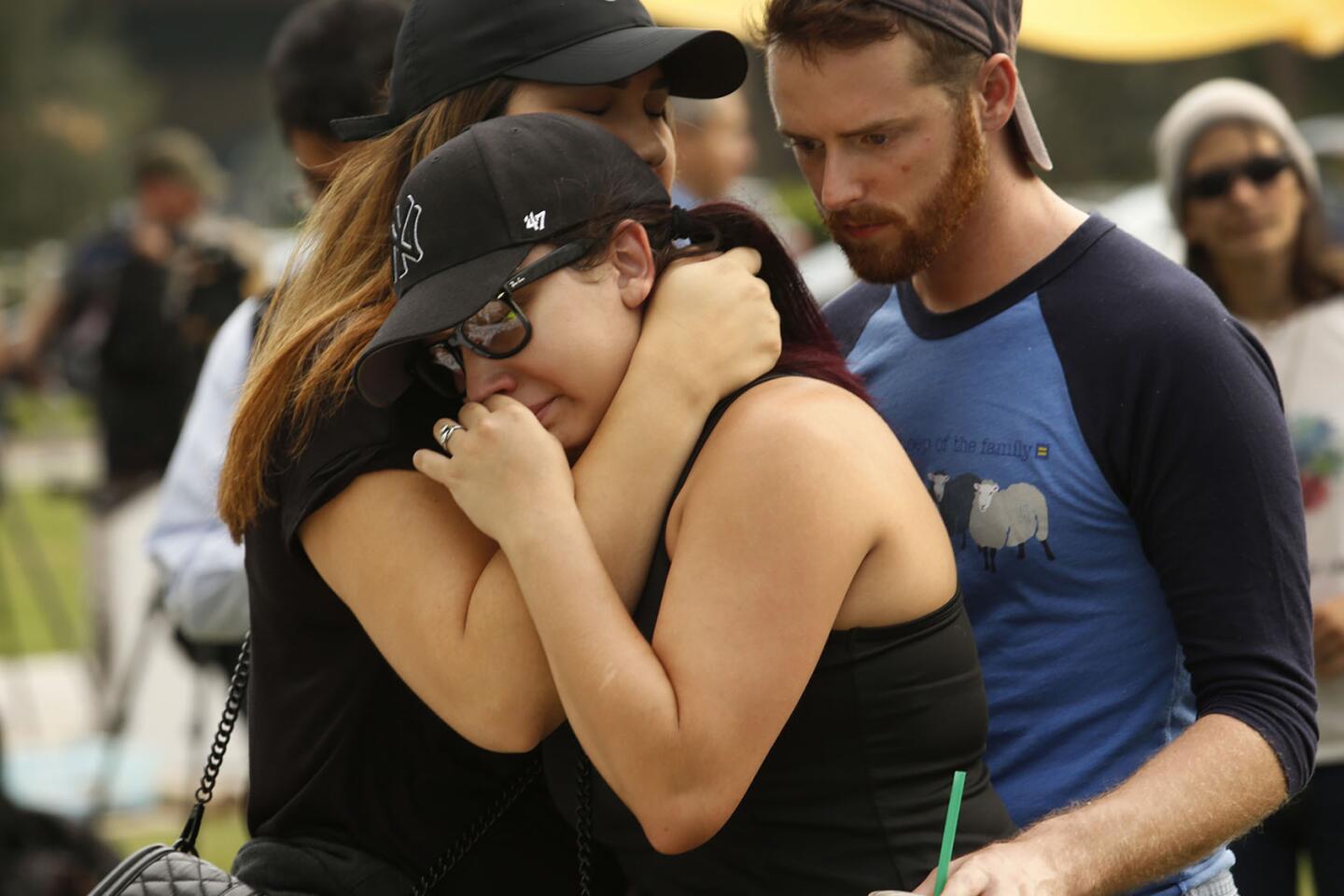
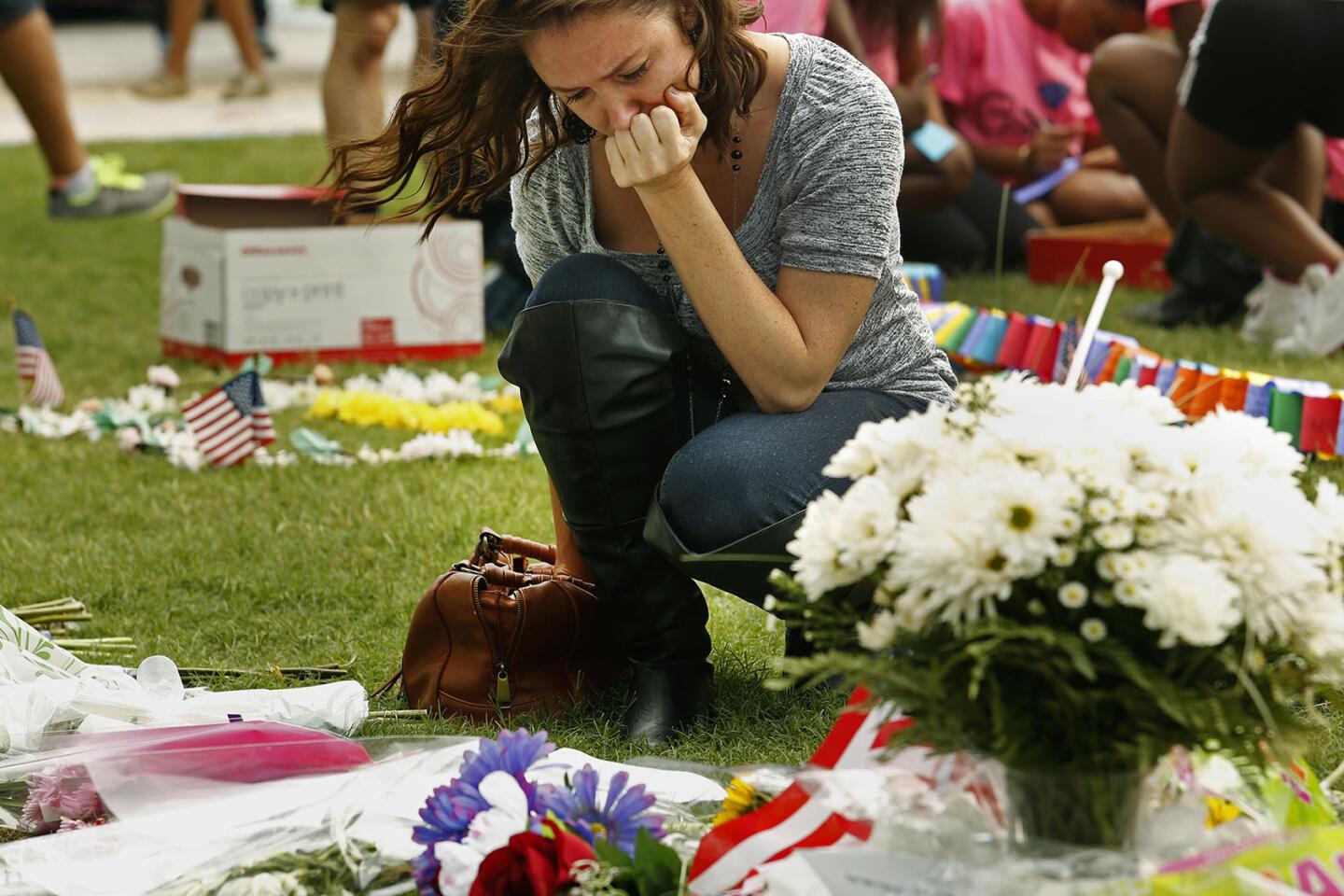
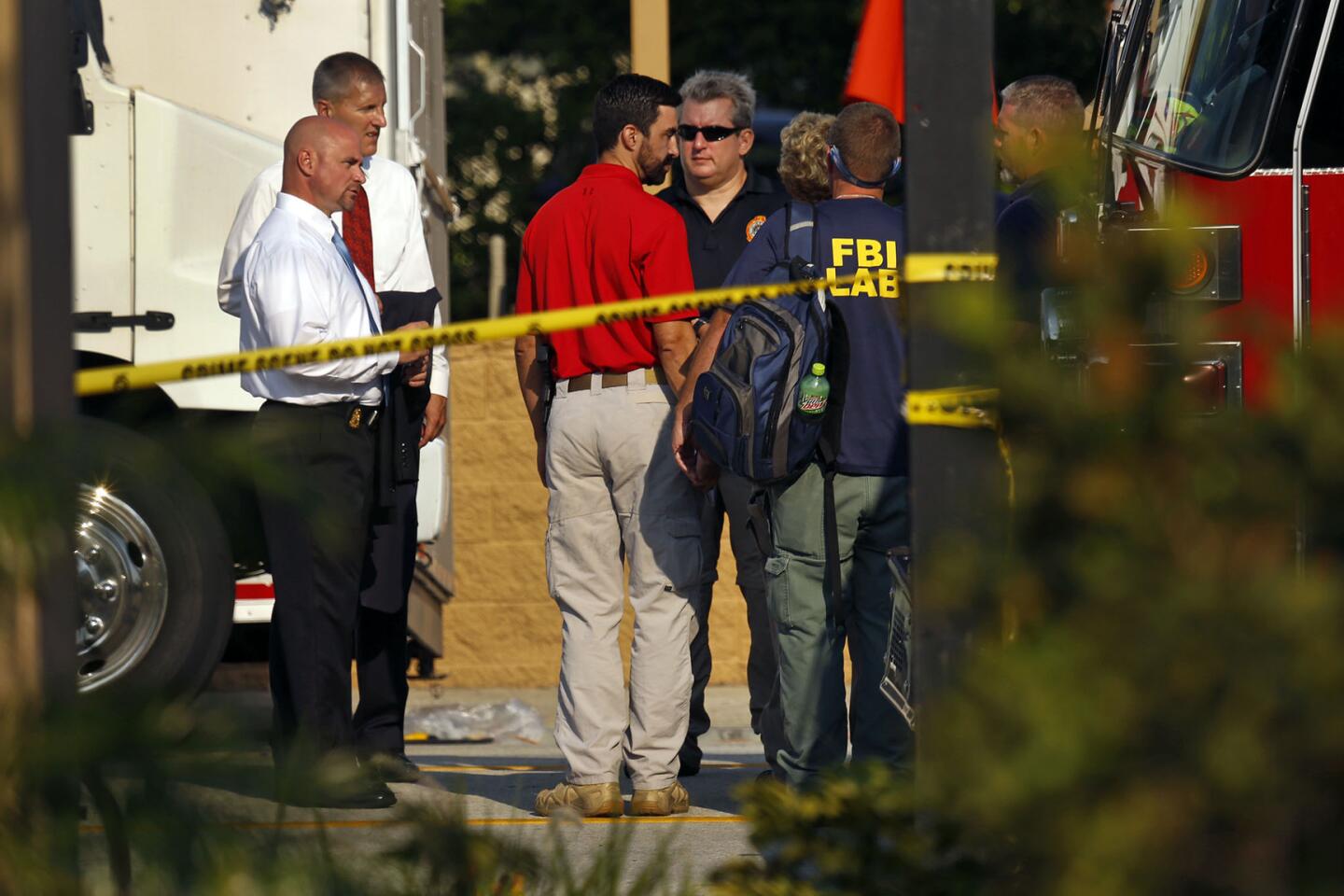
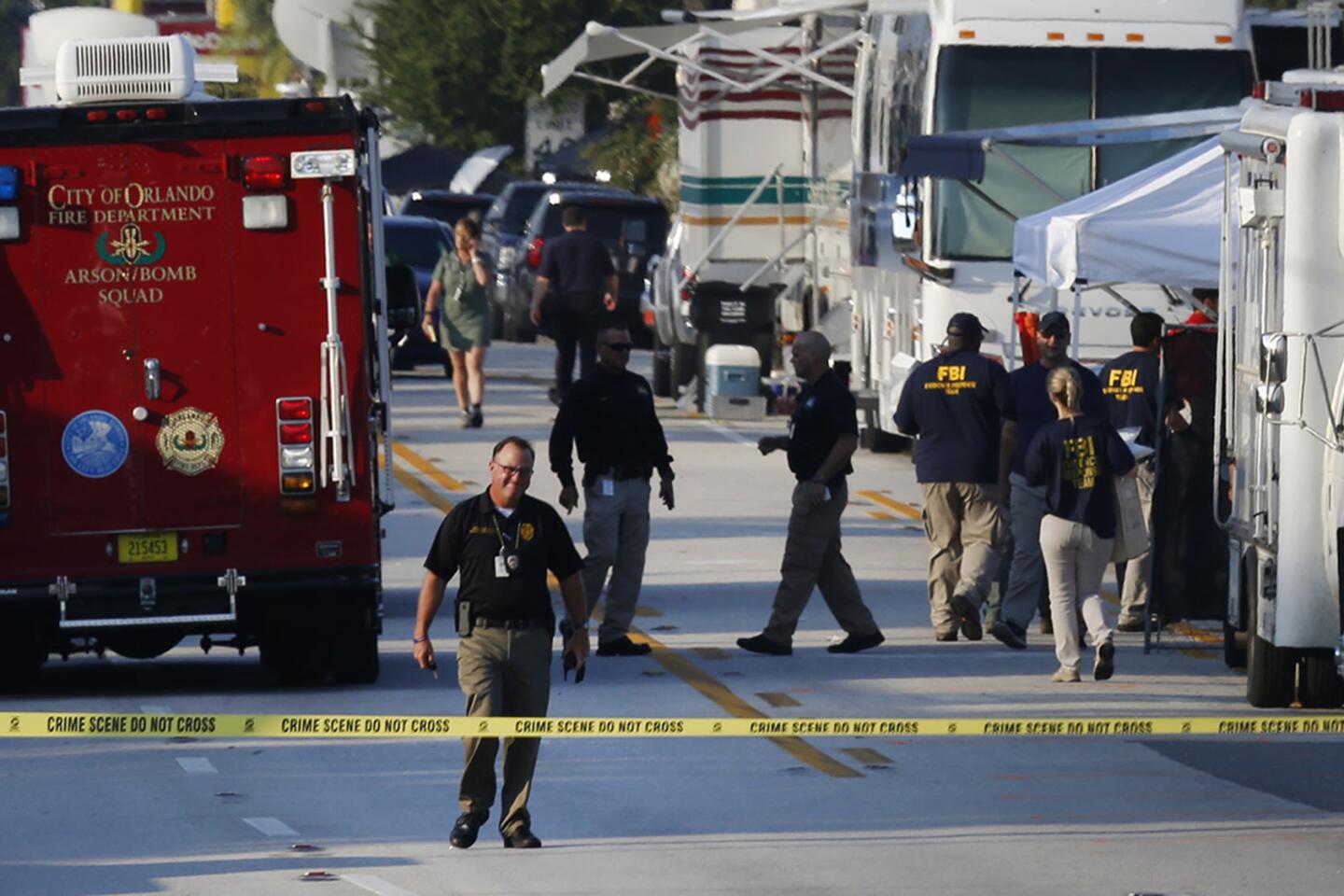
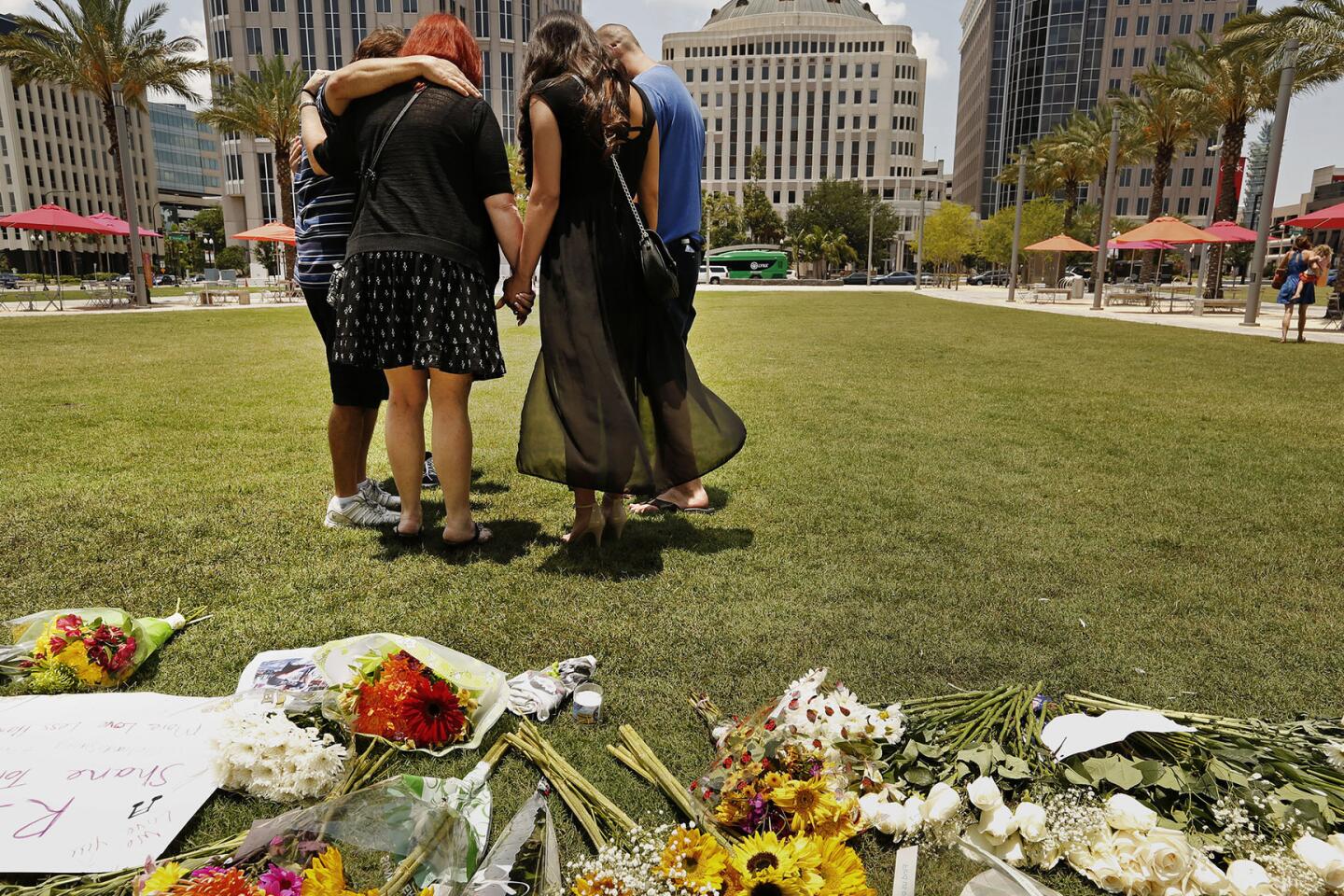
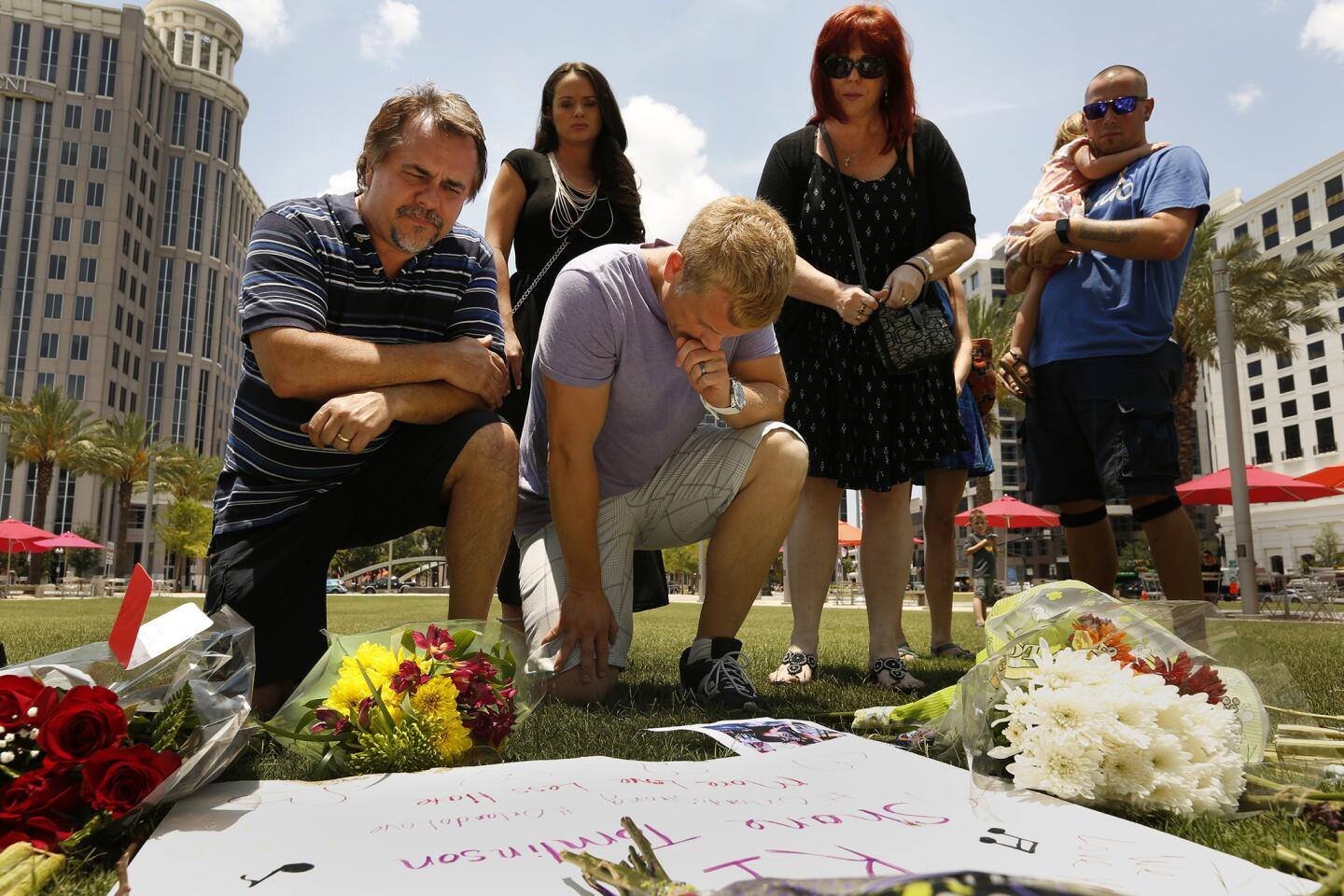
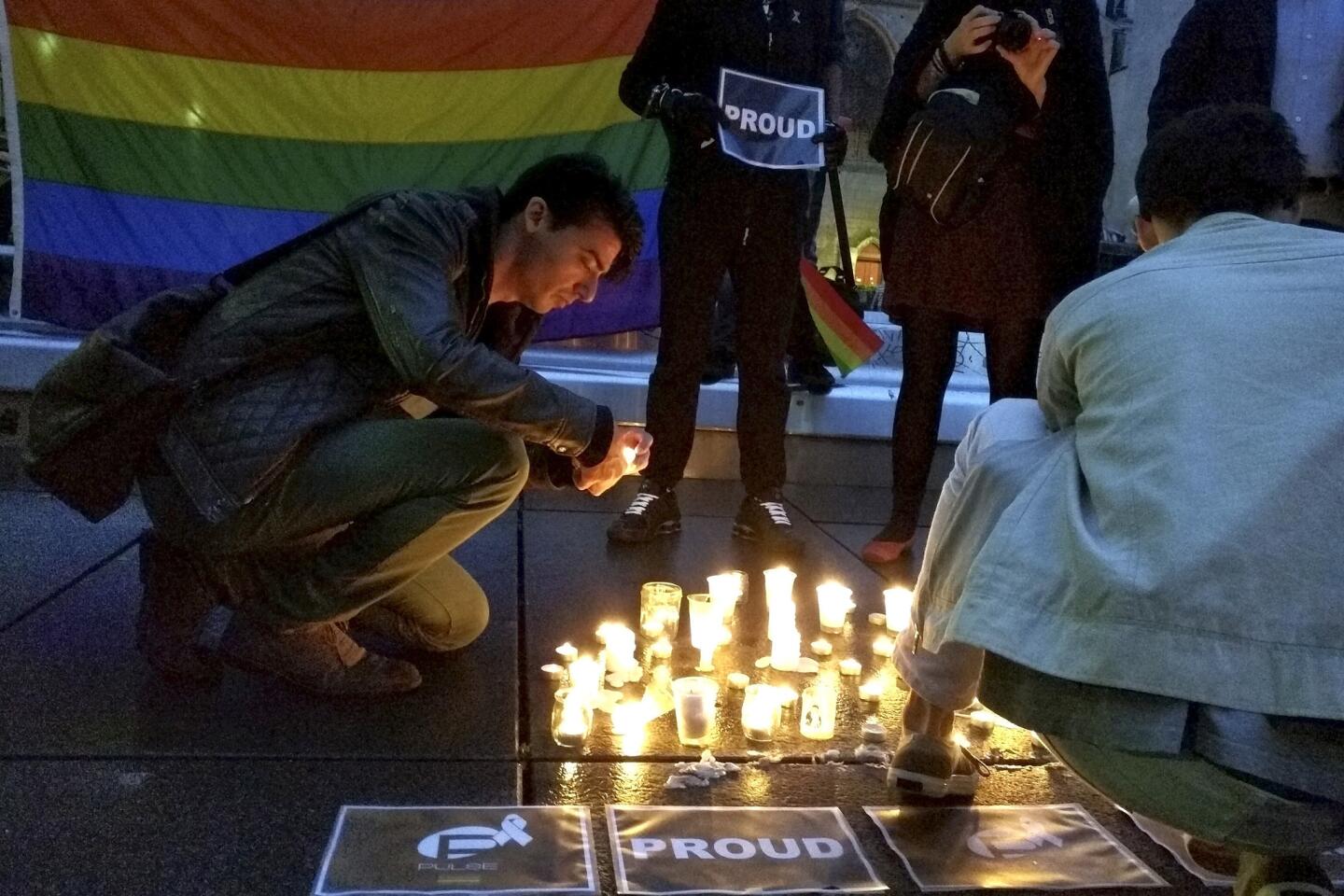
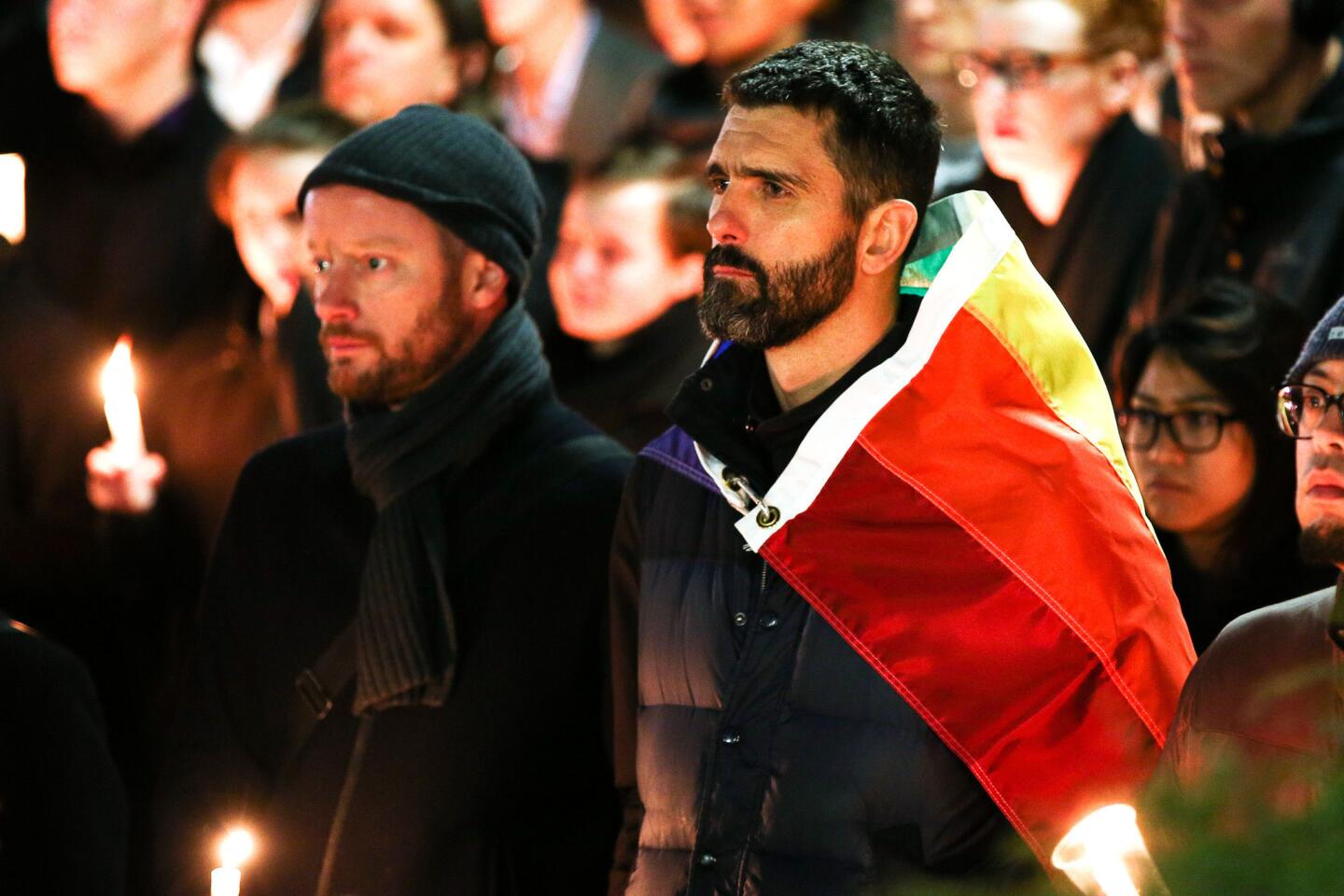
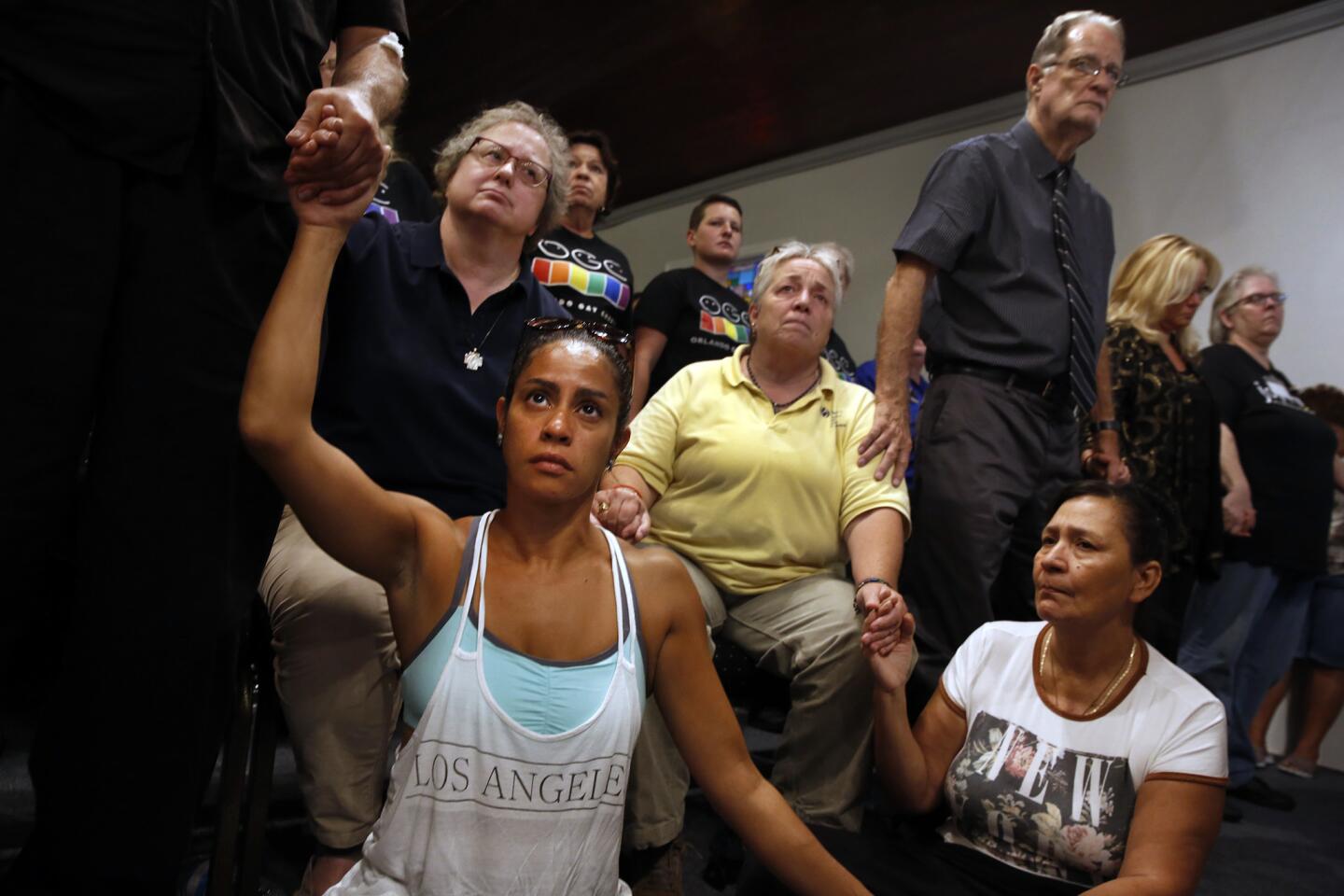
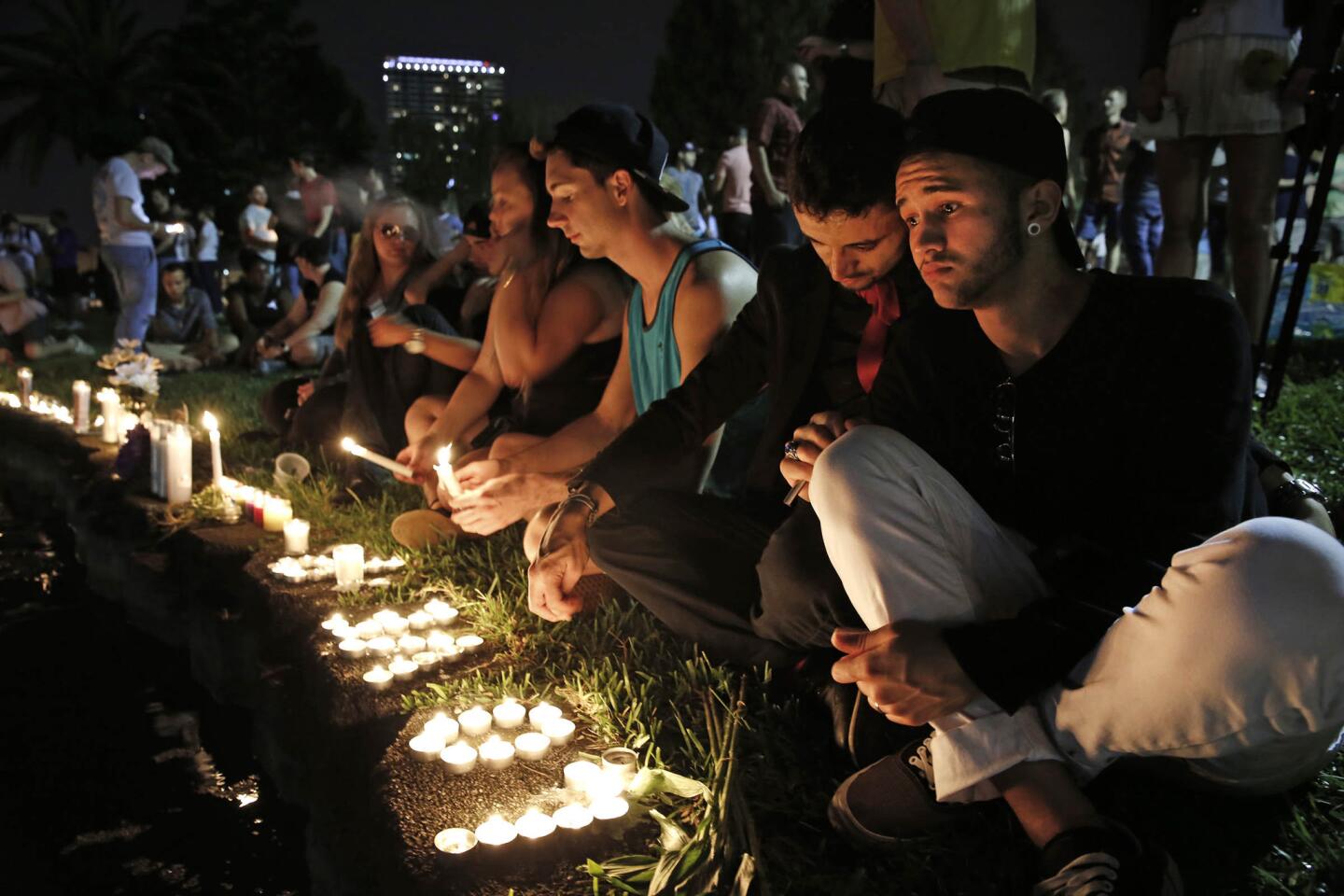
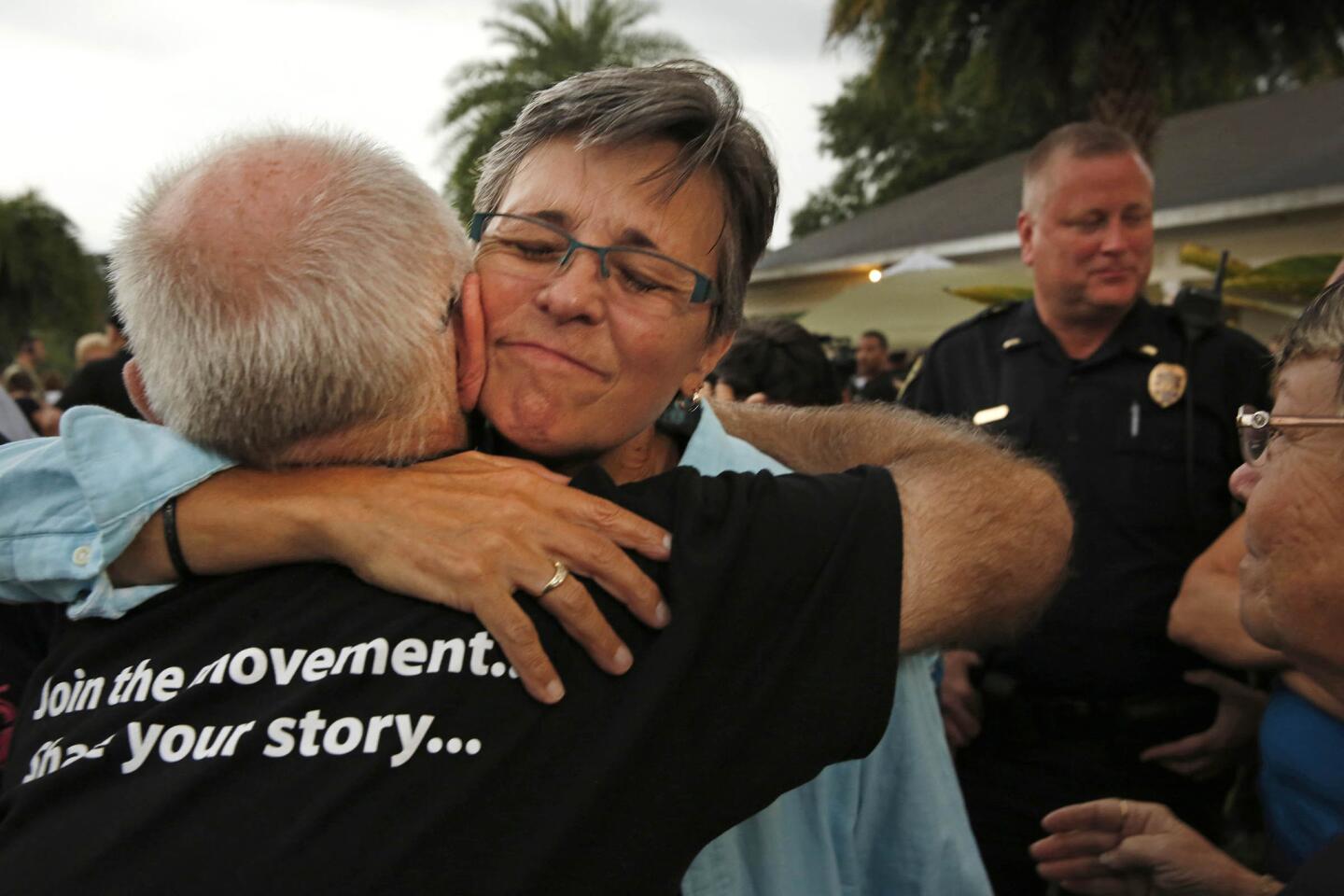
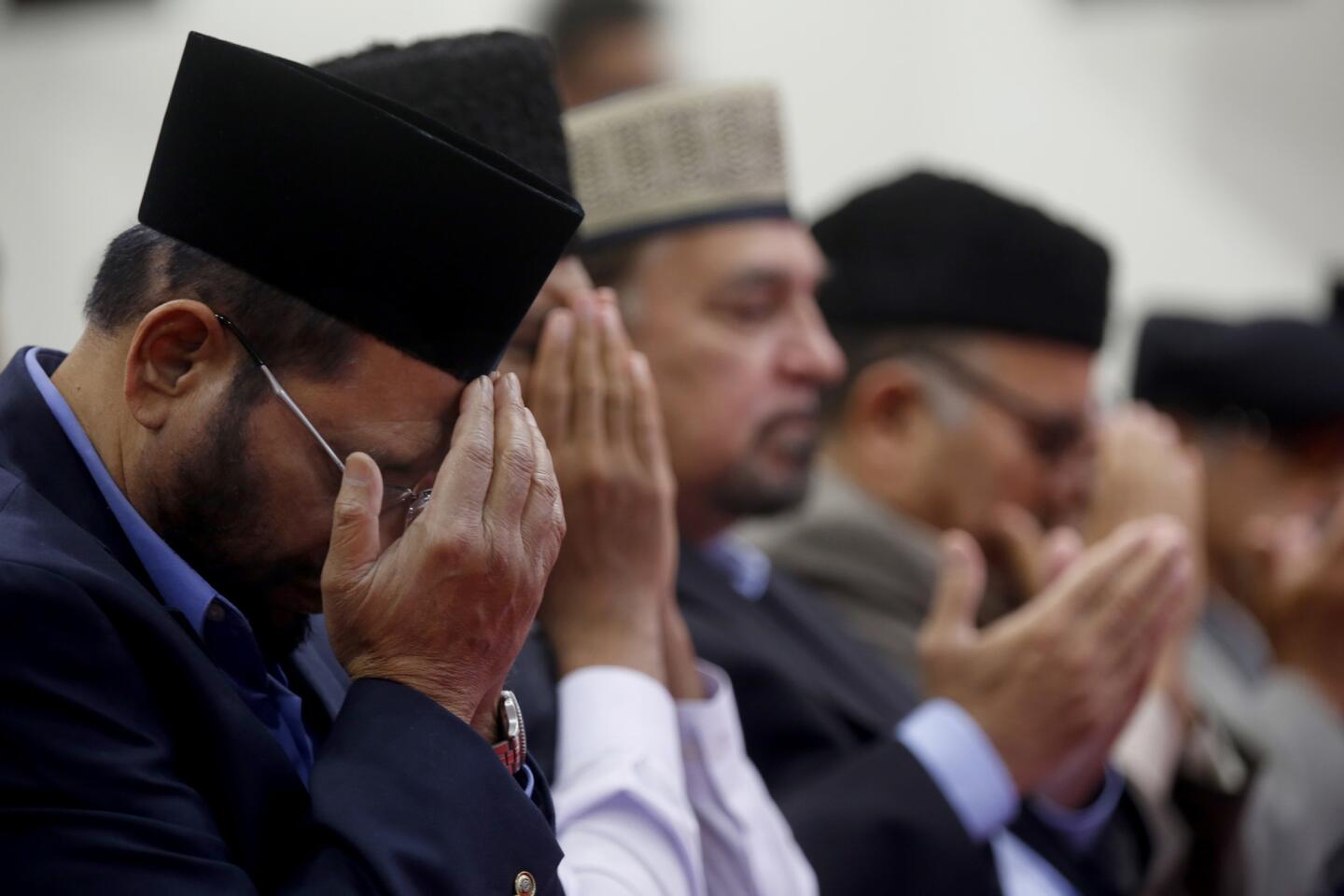
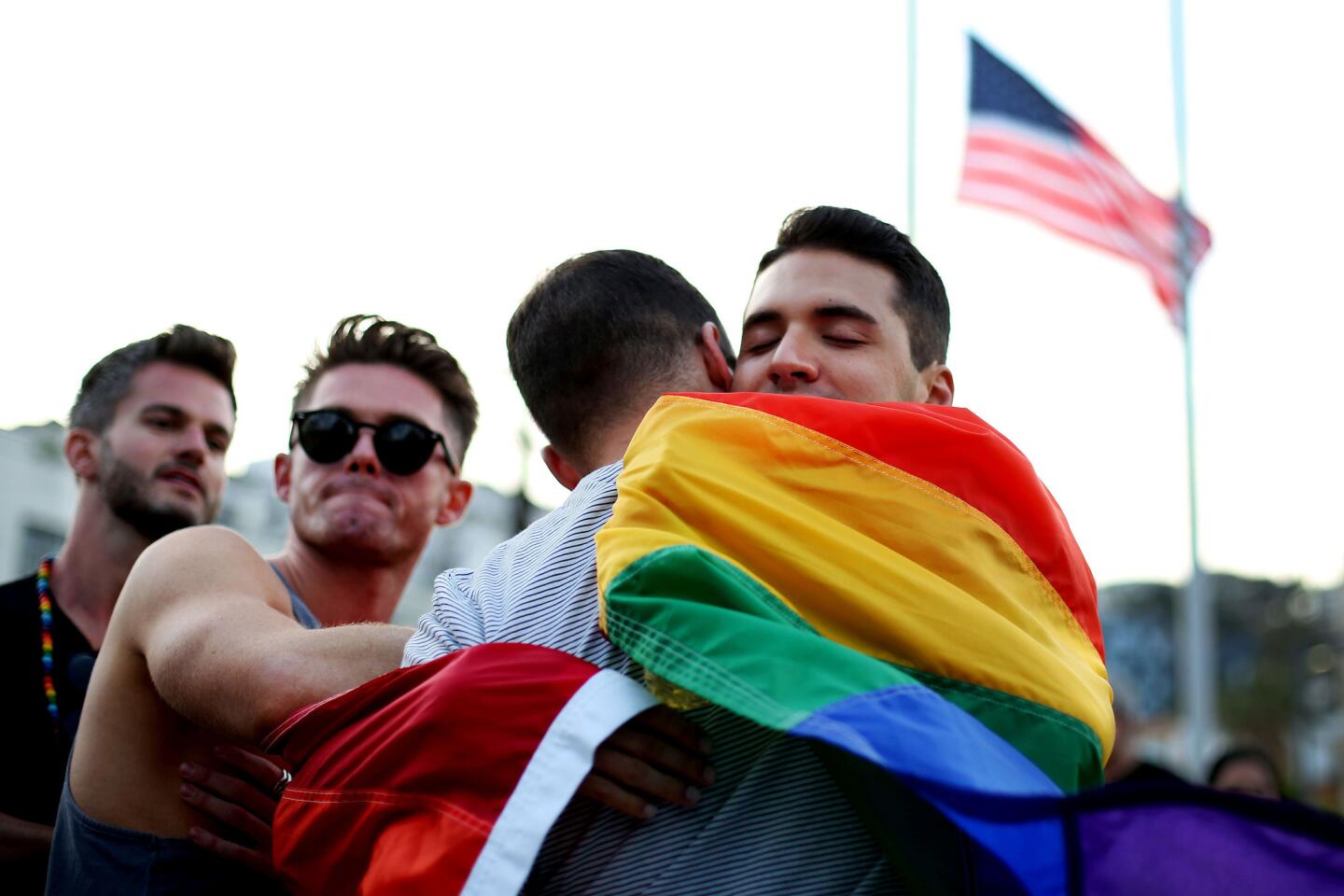
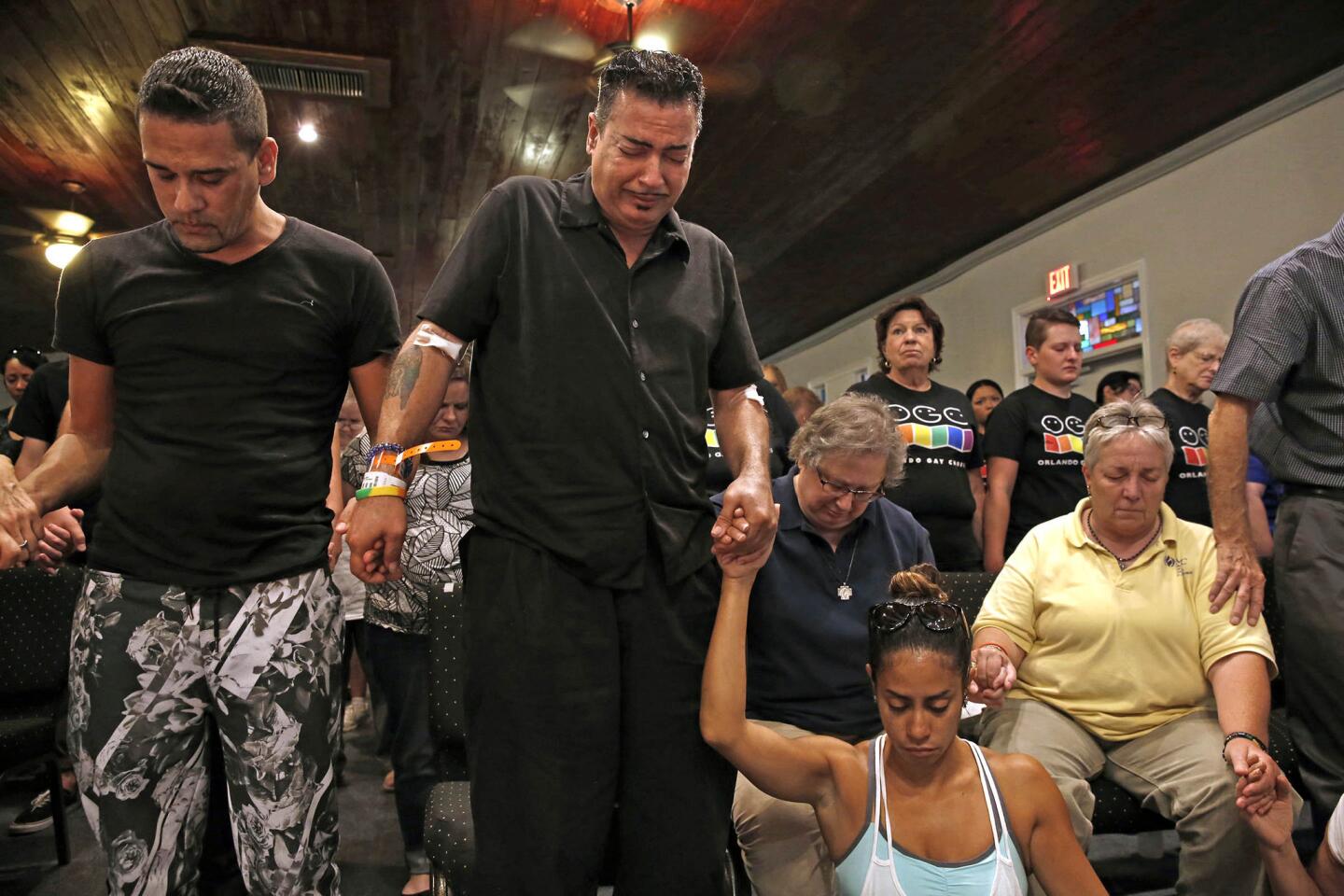
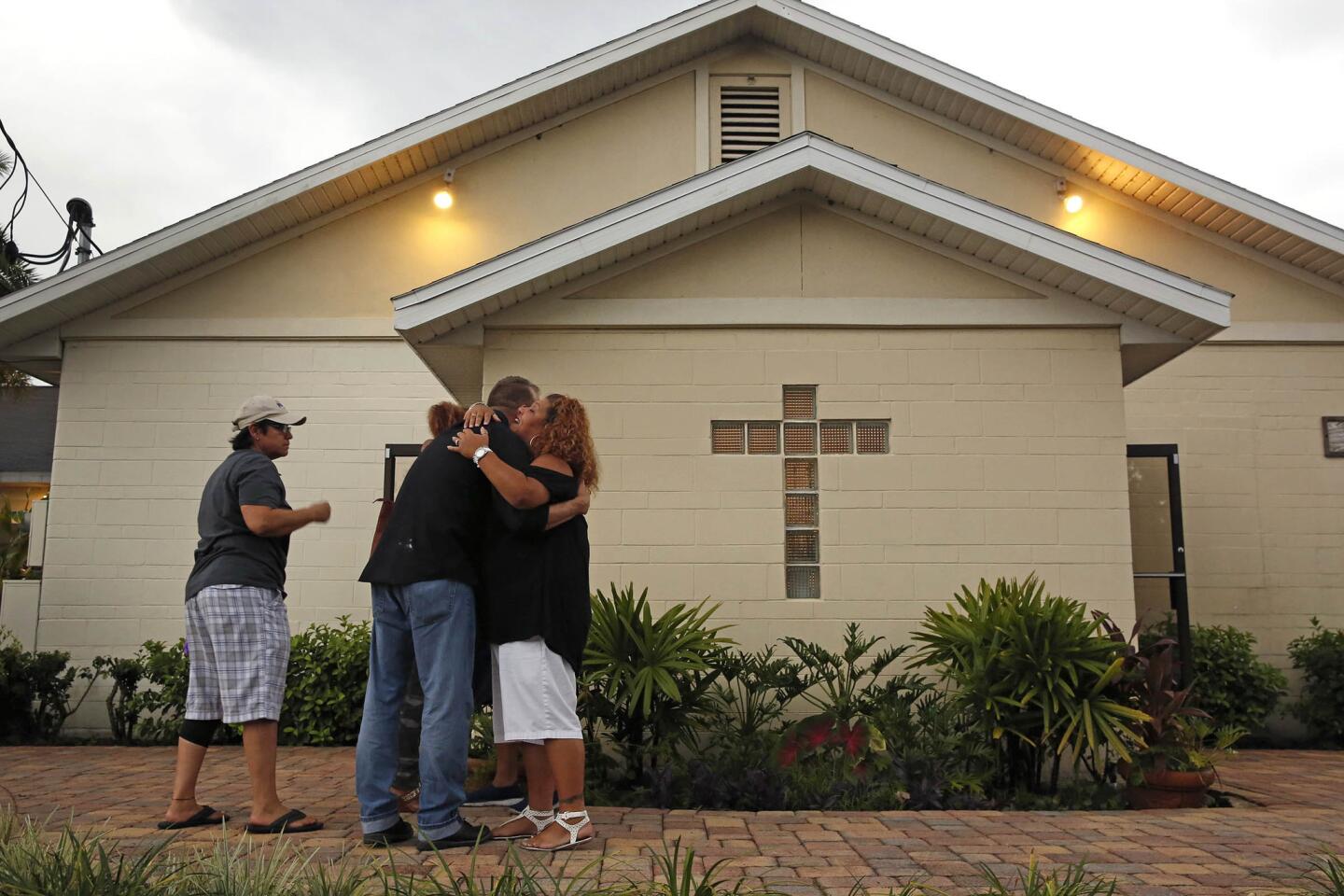
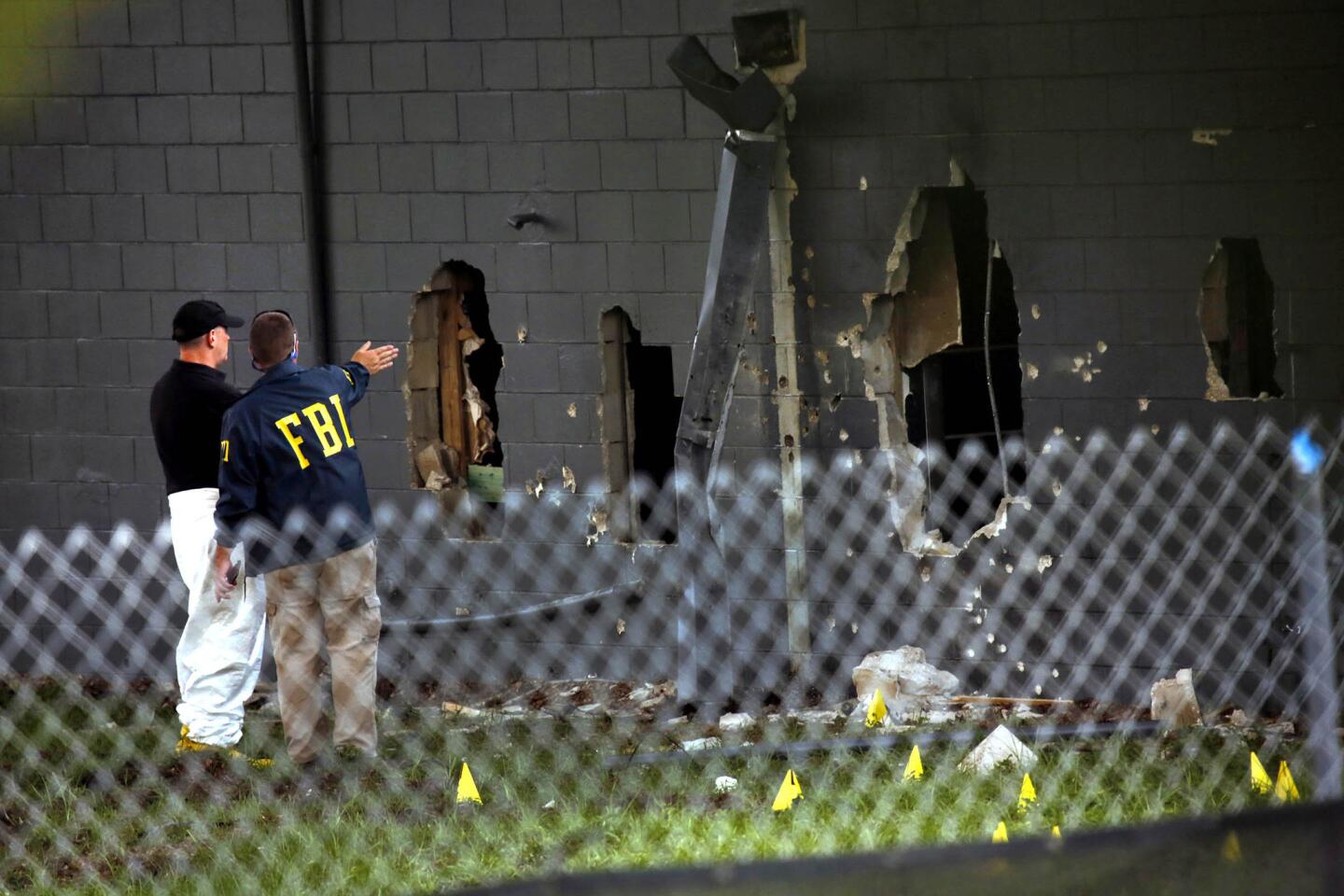
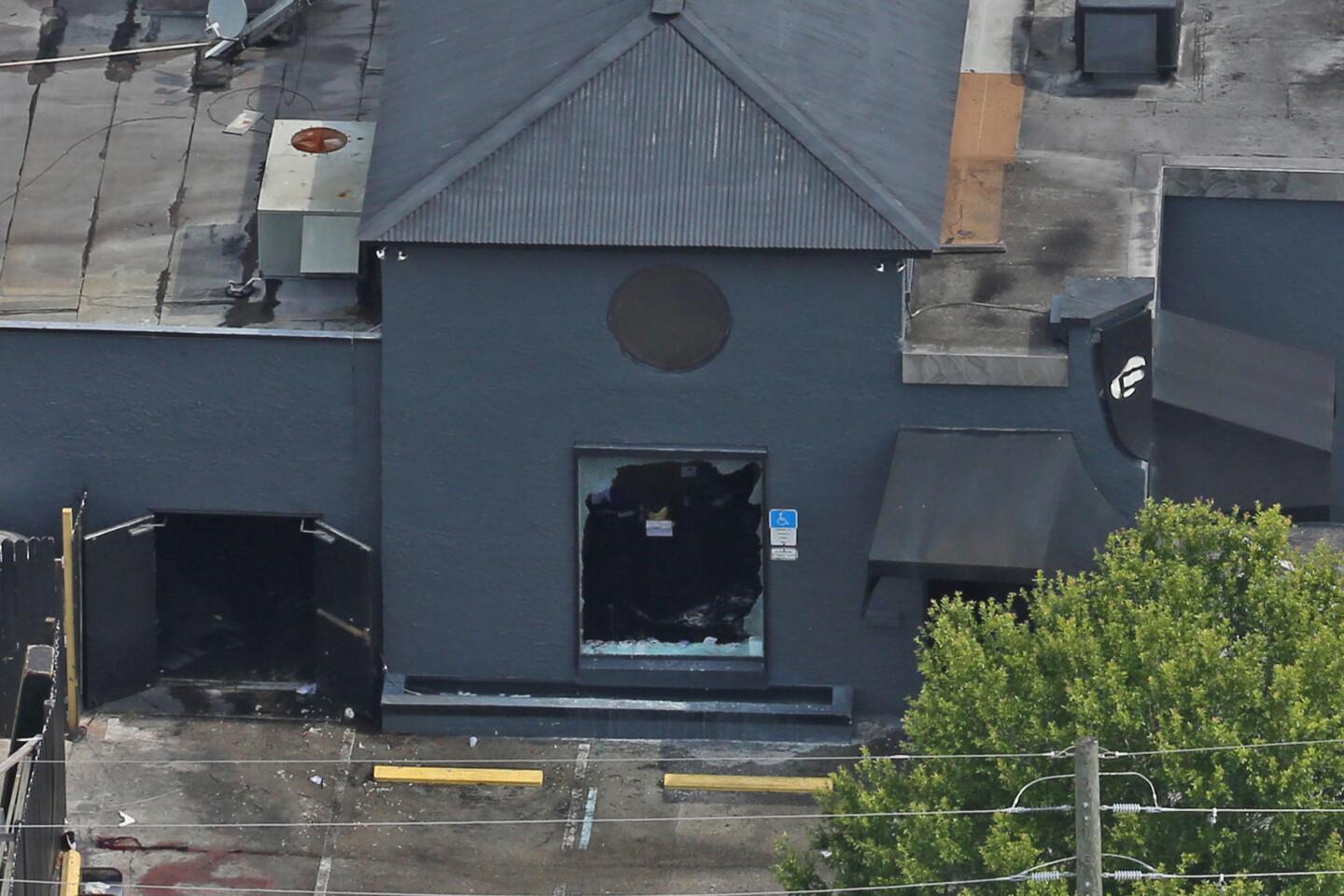
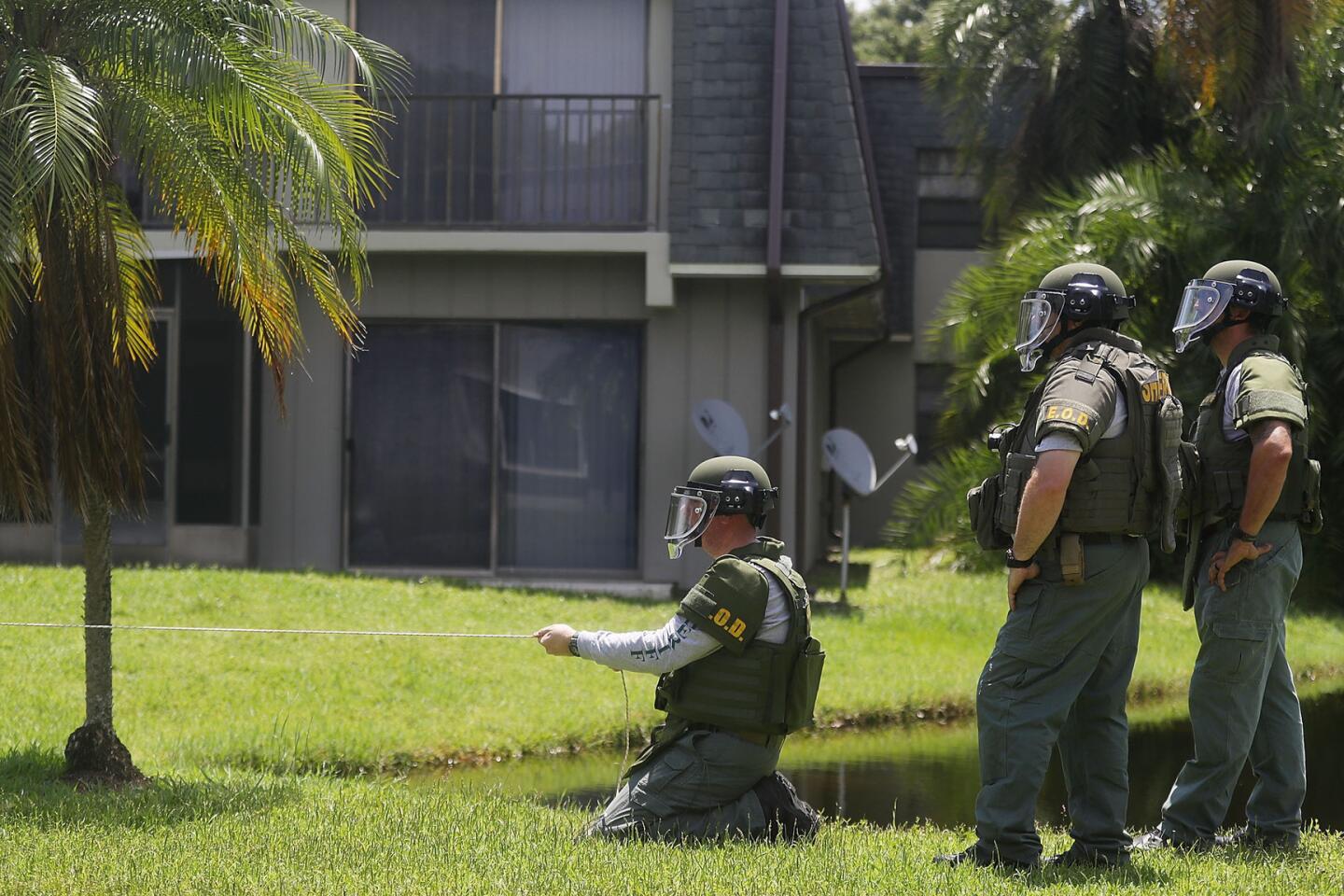
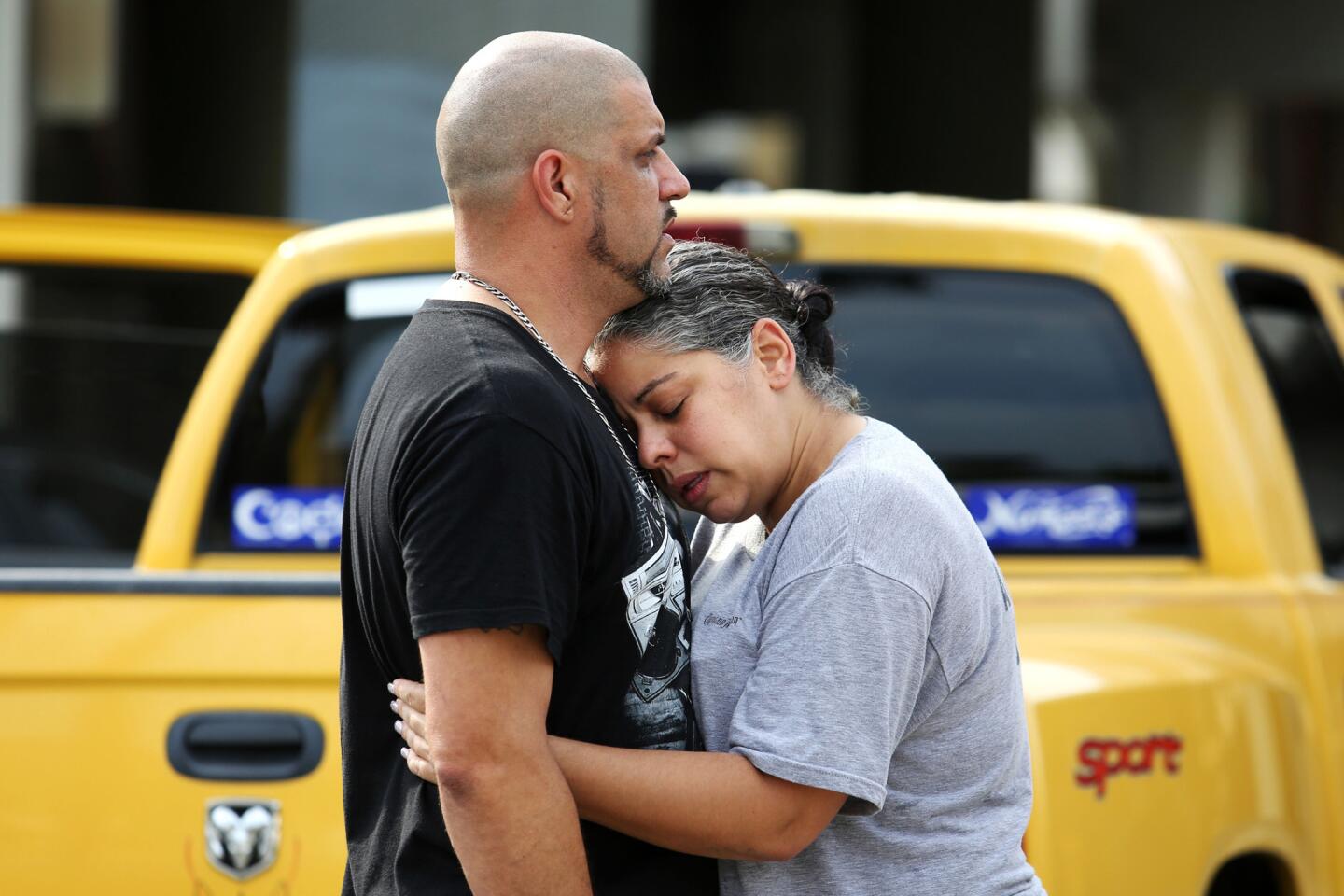
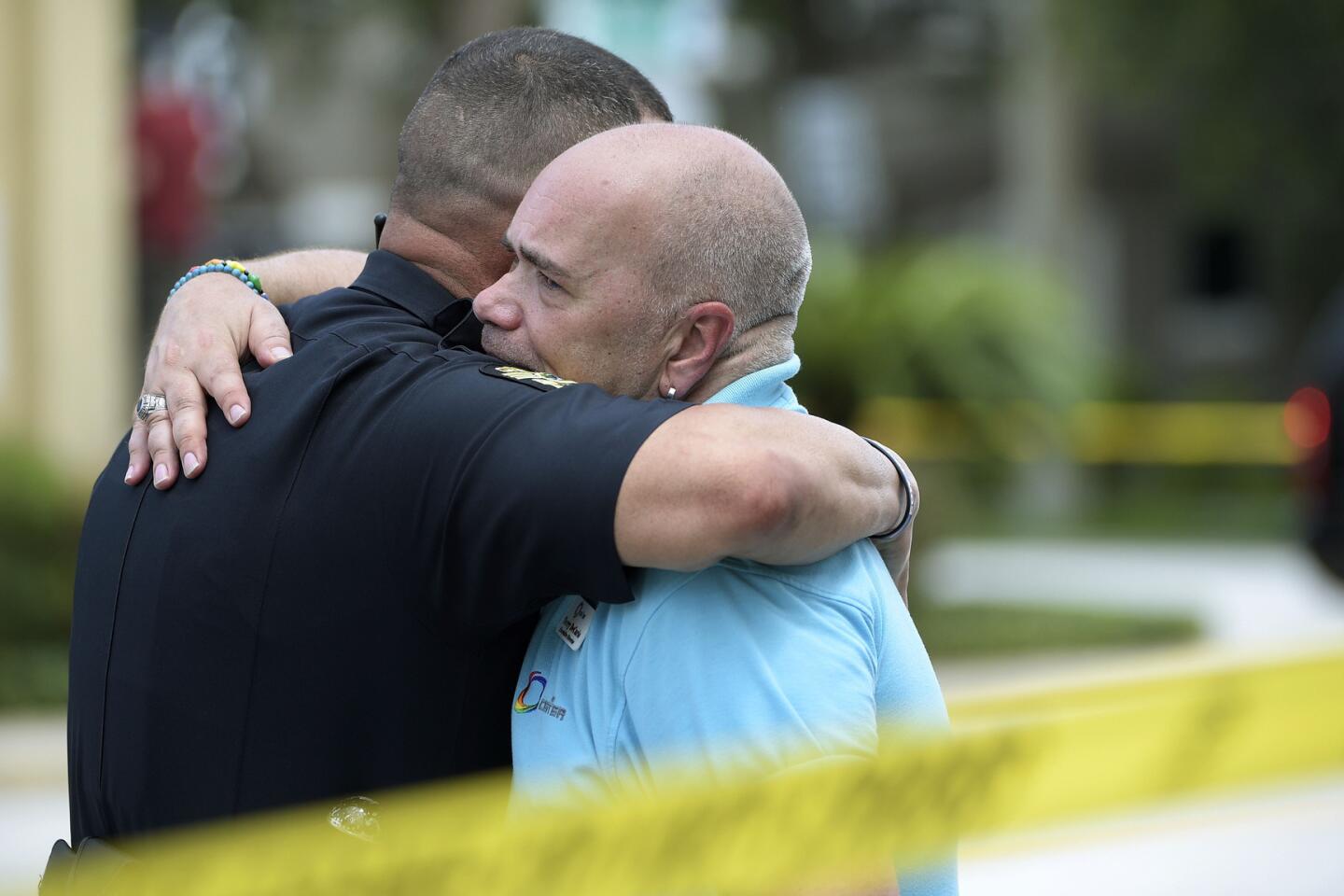
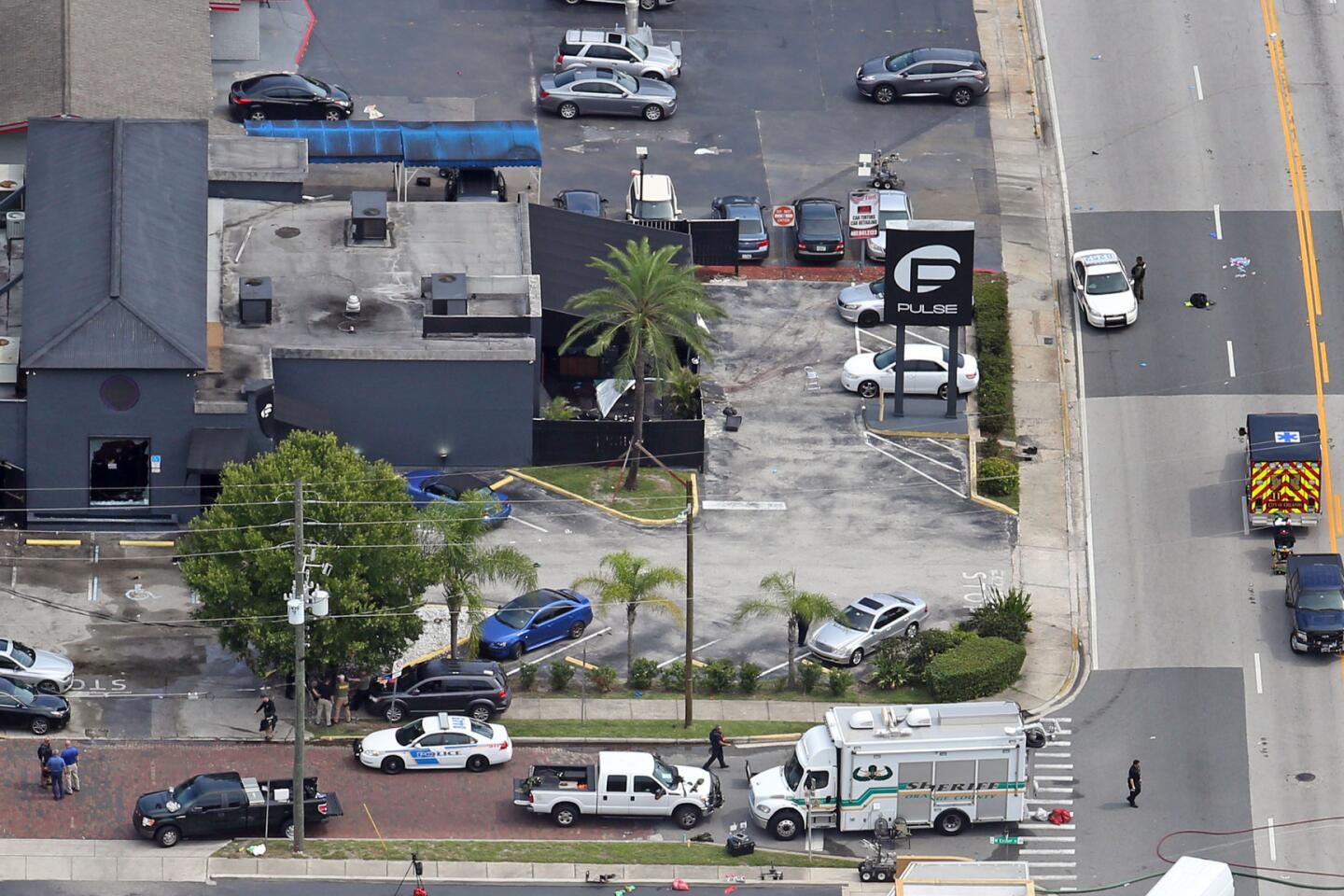
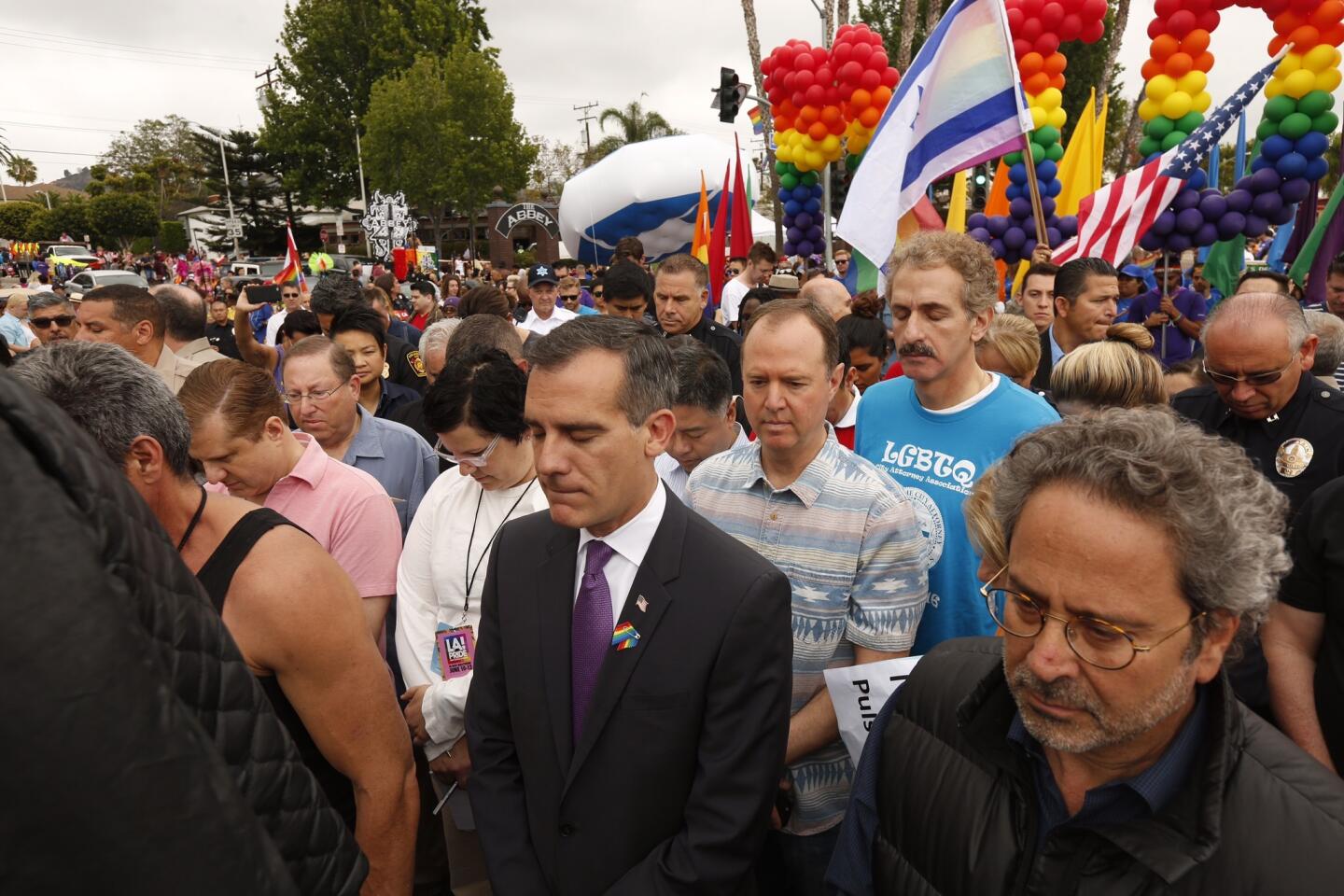
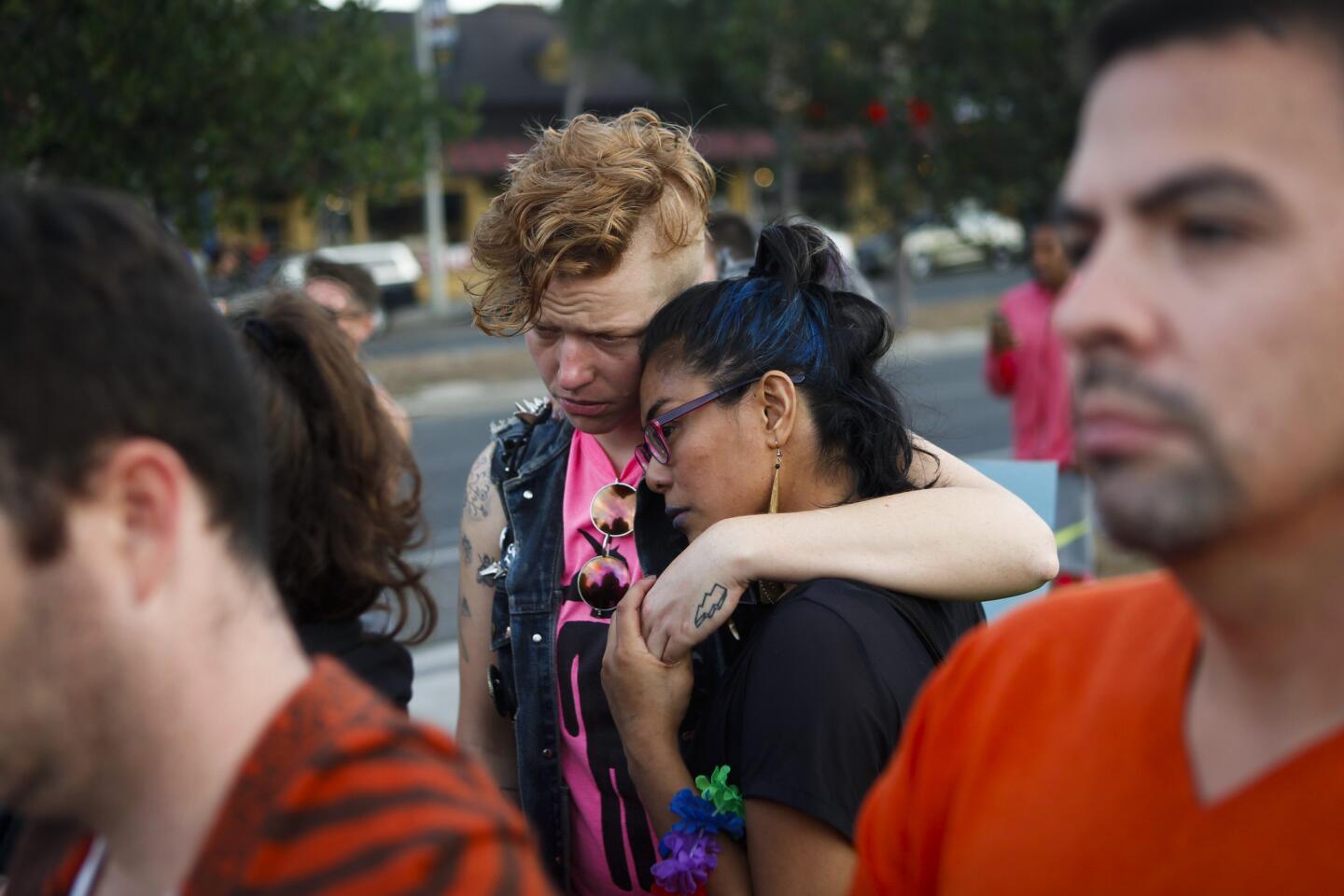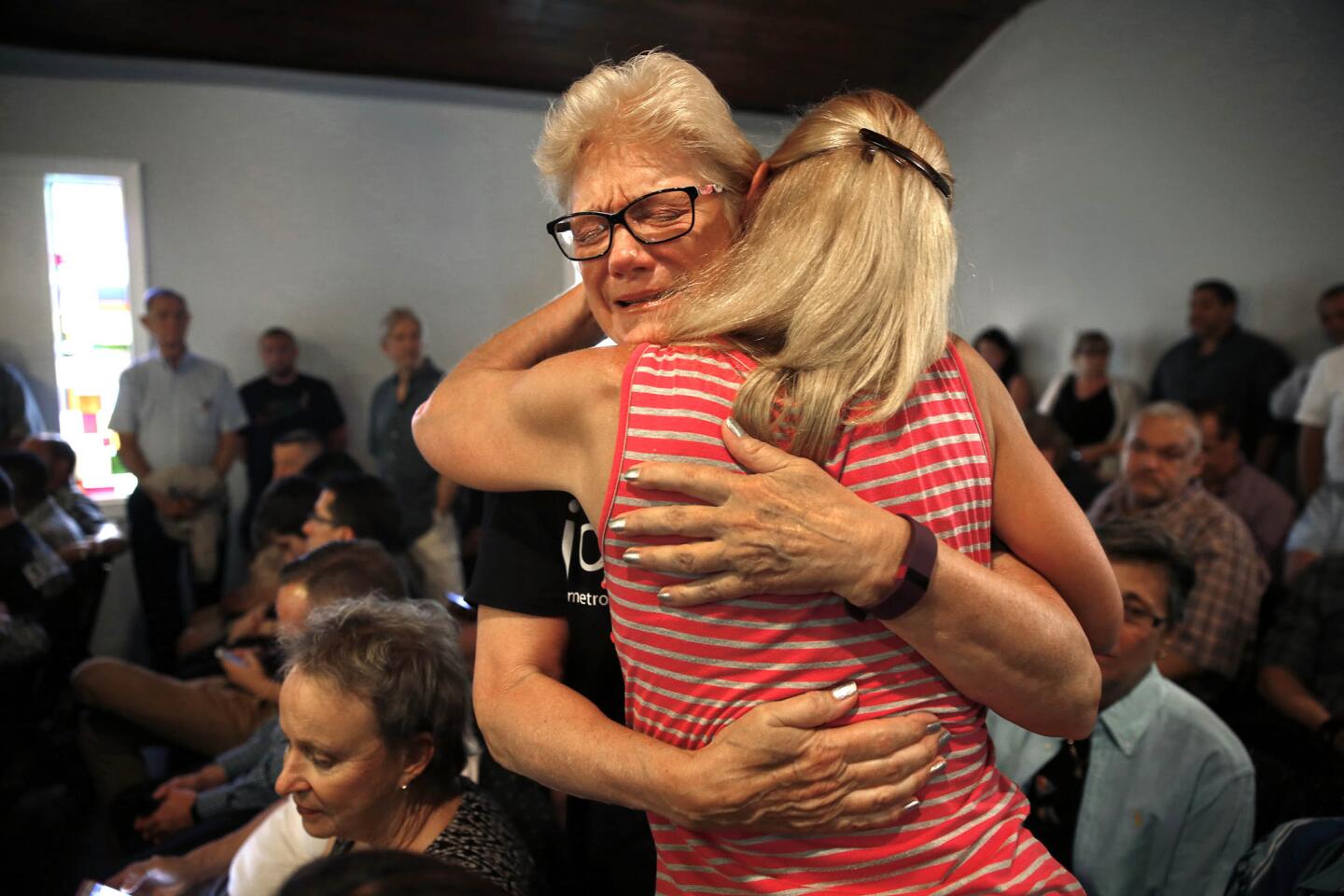Among the most chilling details to emerge in the Orlando massacre is that the killer paused during his three-hour rampage at the Pulse nightclub to search Facebook for news about it.
“Pulse Orlando” and “shooting,” Omar Mateen typed into his smartphone, investigators found.
His real-time search is a striking data point in what has become a pattern in mass shootings: Killers deeply attuned to their media coverage and in some cases engineering it.
The 2007 Virginia Tech shooter interrupted his killing spree to mail a videotape to NBC to claim credit and explain his motives. The 2014 Isla Vista killer posted a manifesto on YouTube. Others have discussed their plans in online forums.
Media outlets have long taken the position that they simply report the news. But experts who study mass violence say they are also part of the story, because the intense coverage that such tragedies receive can inspire new shooters.
The perpetrators of these attacks are often disillusioned young men, and they inhabit the same publicity-obsessed culture as everybody else. Killing offers the prospect of becoming a household name.
“This seems like a way to achieve some recognition and respect they lack in their daily lives,” said Dewey Cornell, a forensic clinical psychologist at the University of Virginia.
“We live in a world where people are really conscious of their social standing and audience,” he said.
Around the world, mass shooters have left suicide notes and manifestos describing how they were inspired by the 1999 killings at Columbine High School in Littleton, Colo., one of the first school massacres in the age of 24-hour cable news coverage.
Sherry Towers, a researcher at Arizona State University, has conducted one of the few studies looking at connections between shootings.
She spent most of her career studying how social behavior spreads diseases such as influenza and Ebola. But in 2014, after noticing three shootings within about 10 days on various college campuses, she began wondering whether mass violence was also contagious.
So she built a statistical model to analyze databases of hundreds of shootings.
NEWSLETTER: Get the day’s top headlines from Times Editor Davan Maharaj »
The study found that shootings that occurred in schools or ones in which at least four people died — the sorts of incidents that receive widespread media coverage — occurred in clusters. That suggested to researchers the kind of copycat effect that has been well documented for suicides.
After the shootings, the risk of more shootings rose significantly and remained elevated for an average of 13 days, according to the analysis published last year in the journal PLOS One. However, the research found no increased risk after shootings in which at least three people were hit but not necessarily killed, incidents that are so common they usually receive only local news coverage.
“When there was likely to be national or international media coverage, those were the ones where we found contagion,” Towers said.
1/81
Inaya Bava, 5, on June 16, 2016, draws on crosses set up to remember the victims of the Pulse nightclub shooting at the Orlando Regional Medical Center.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 2/81
Relatives of those killed and wounded in the Pulse nightclub attack arrive at Amway Center on June 16, 2016, for private meetings with President Obama.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 3/81
President Barack Obama and Vice President Joe Biden bring flowers to the makeshift memorial at the Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts.
(Joe Burbank / Orlando Sentinel) 4/81
Jiffy Lube employee Ralph Nieves puts up a sign of support for the Orlando community following the shooting at the Pulse nightclub.
(Spencer Platt / Getty Images) 5/81
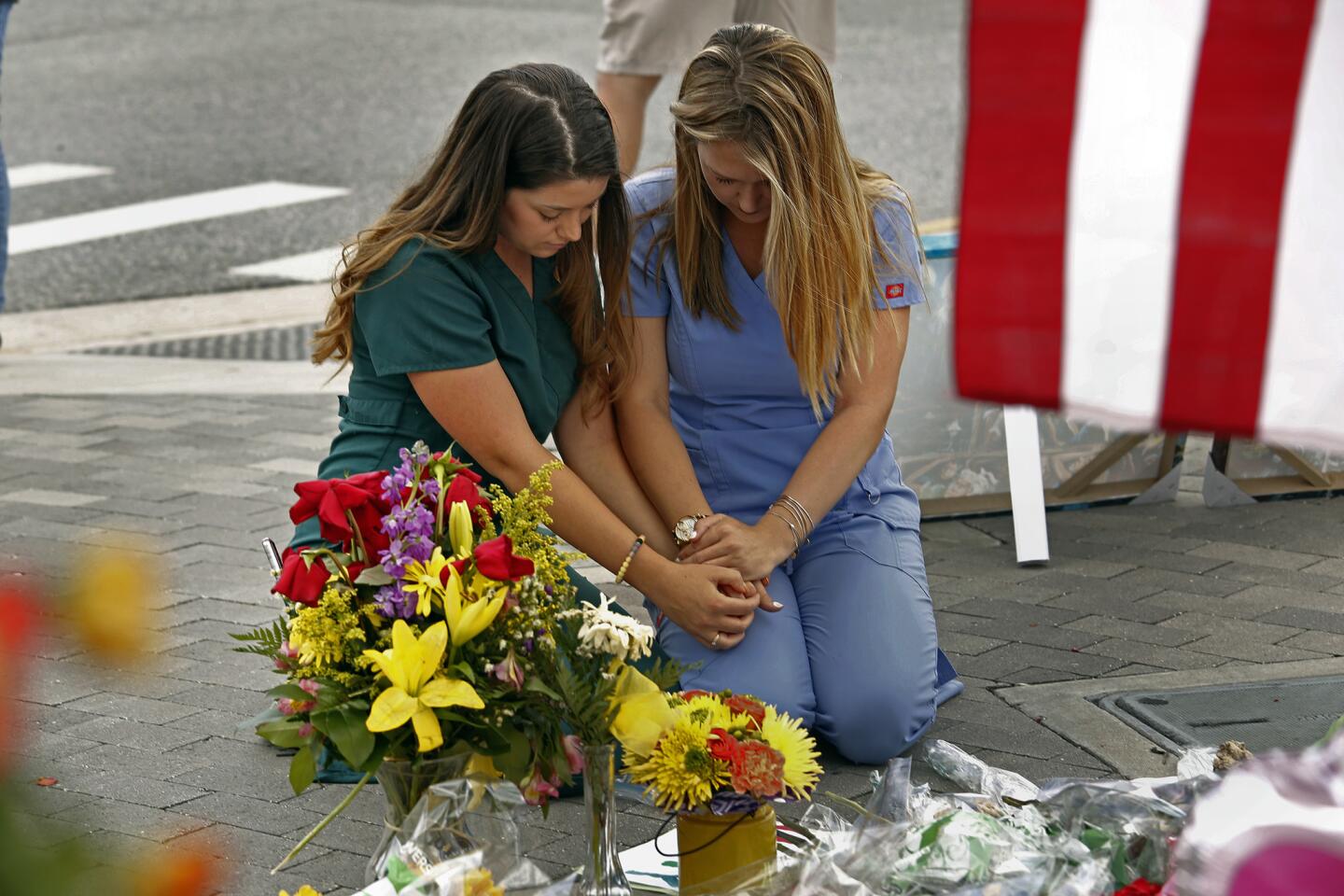
Sarah Roemer, left, and Brandi Van Dongen, nurses at Arnold Palmer Childrens Hospital in Orlando, pray at one of the memorials.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 6/81
The Parliament House is one of the largest nightclubs catering to the LGBT clients.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 7/81
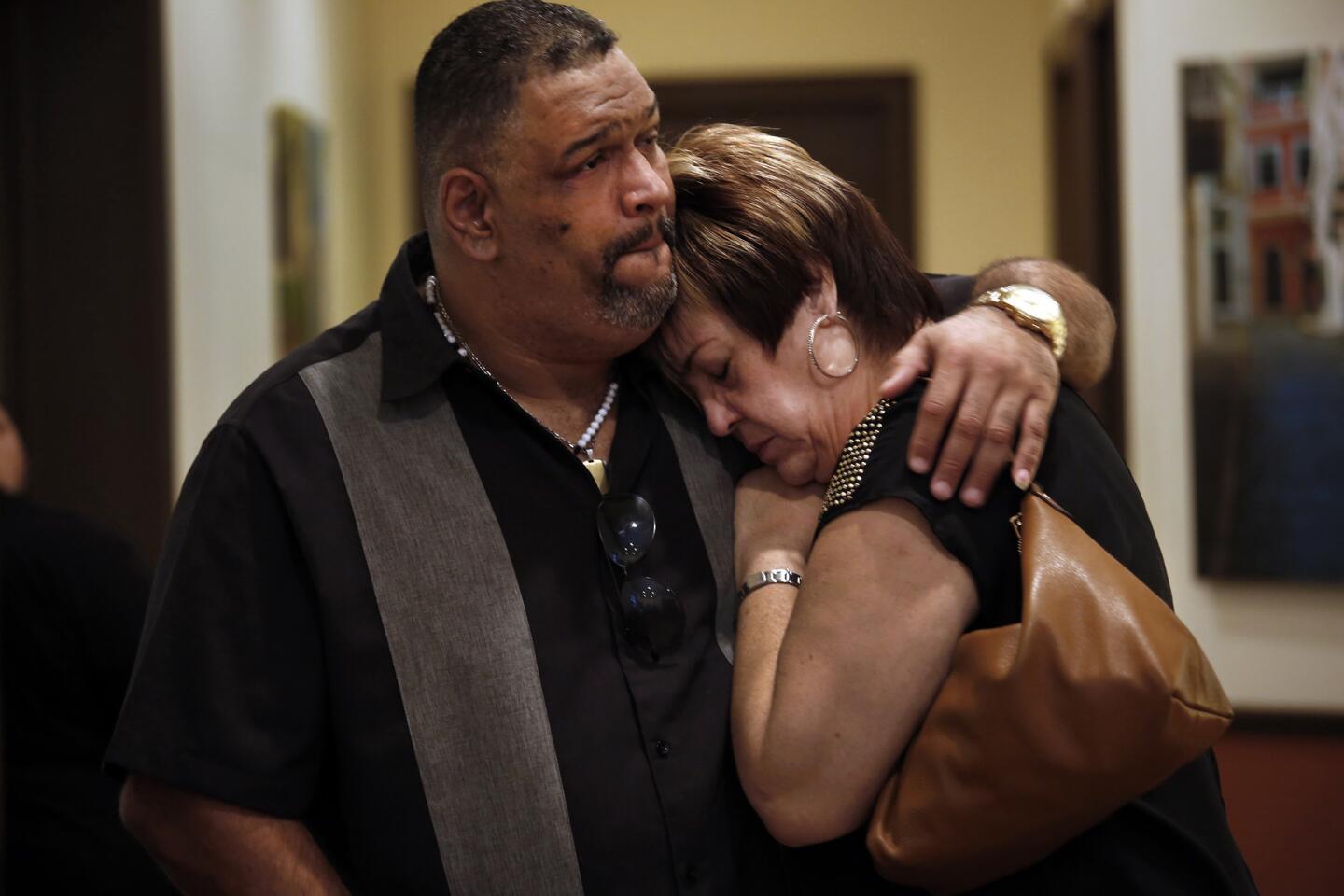
Rafael Rivera, left and Jeannette Gonzalez grieve at a wake for Eric Ortiz, one of the victims of the Pulse nightclub shooting.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 8/81
Members of the media and public wait to catch a glimpse of President Obama at Amway Center.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 9/81
A prayer service is held on June 15, 2016, for the victims of the Pulse Nightclub shooting at Delaney Street Baptist Church in Orlando, Fla.
(Drew Angerer / Getty Images) 10/81
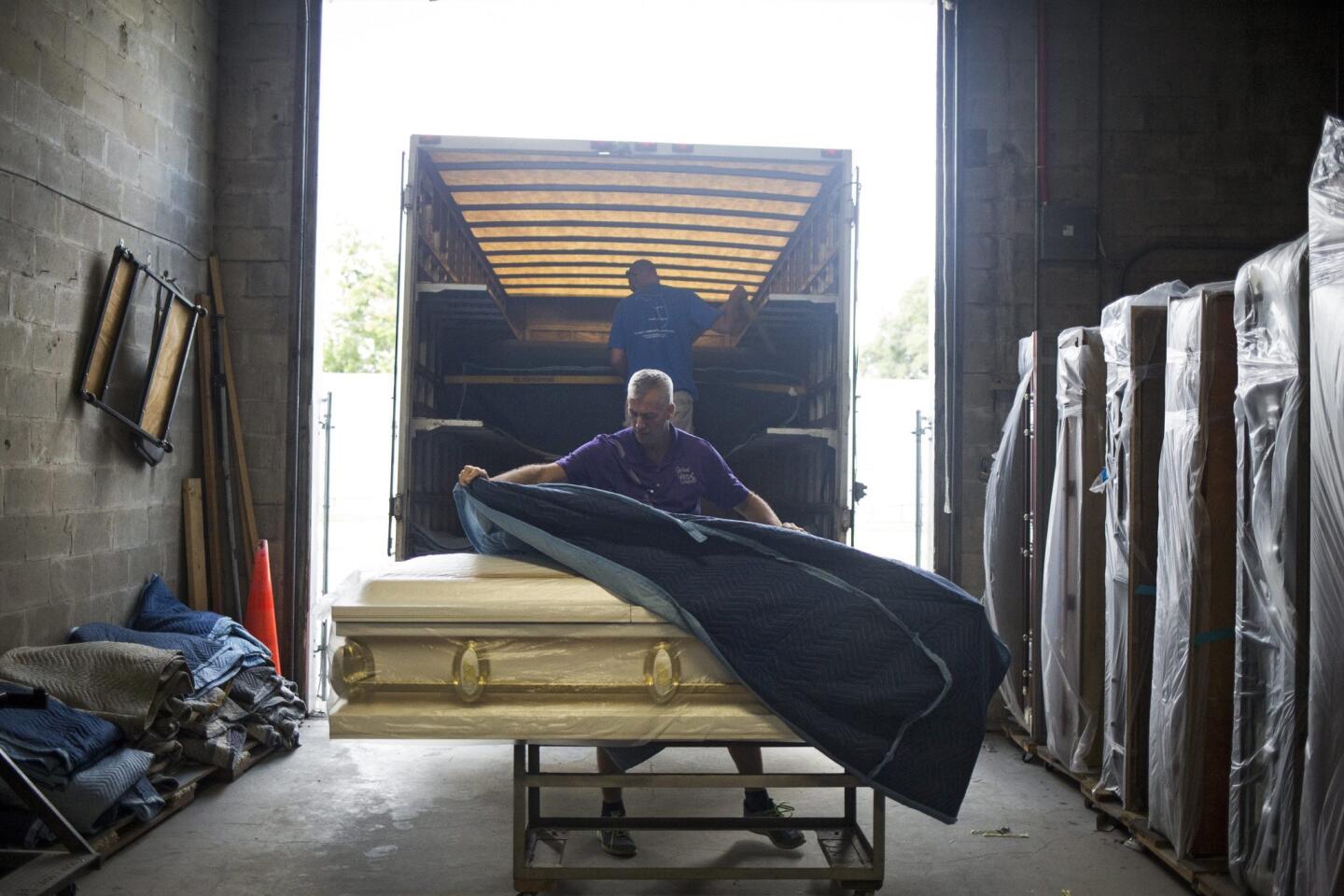
Kelly Greenwood prepares a casket on June 16, 2016, at the Cardinal Casket Company in Orlando, Fla.
(John Taggart / EPA) 11/81
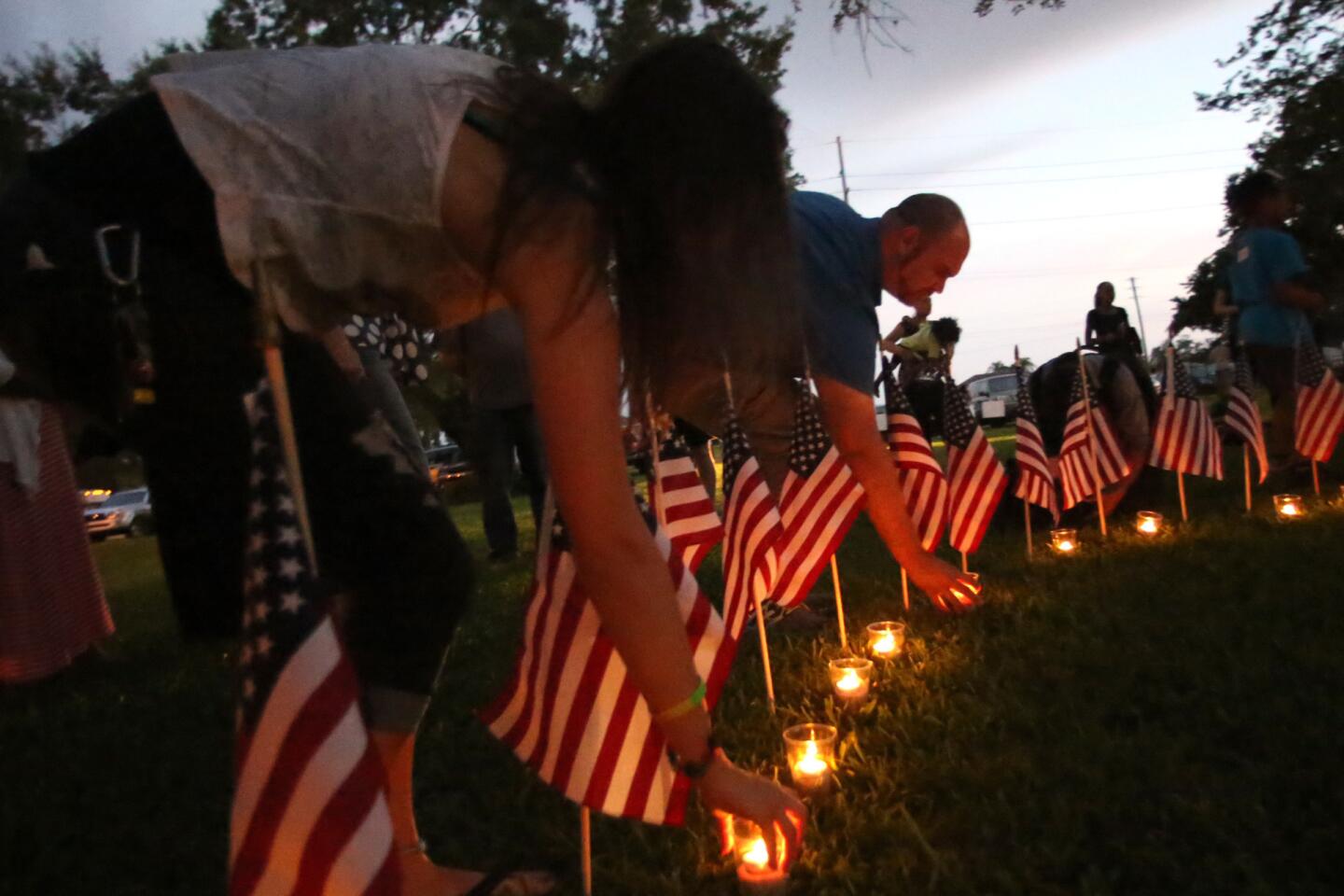
Candles are placed under American flags set in a circle outside a vigil at Christ Church Unity for the shooting victims.
(Charles King / Orlando Sentinel) 12/81
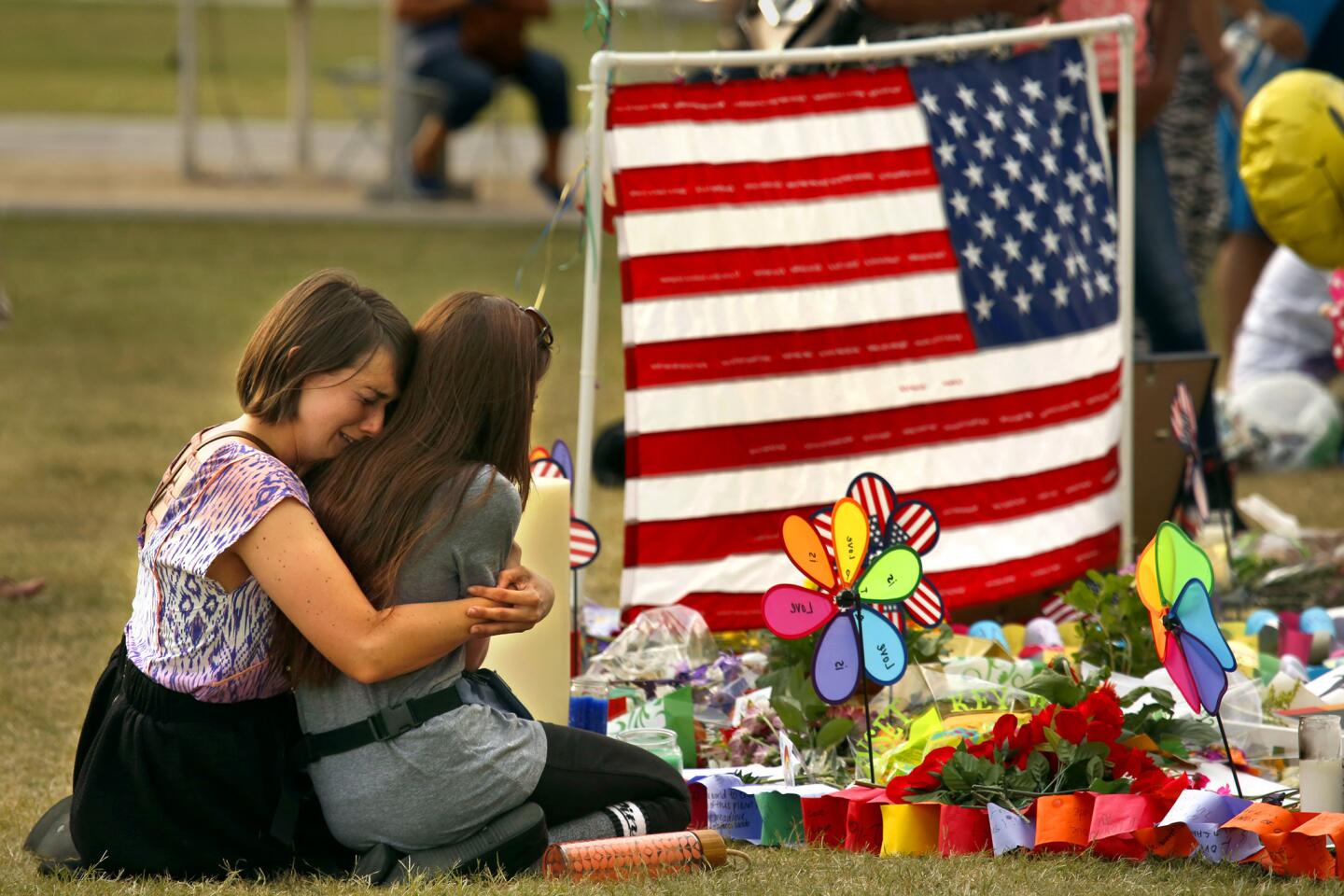
At the Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts, Taylor Green, 25, left, and Brittany Spencer, 25, grieve for those killed in the Pulse nightclub attack.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 13/81
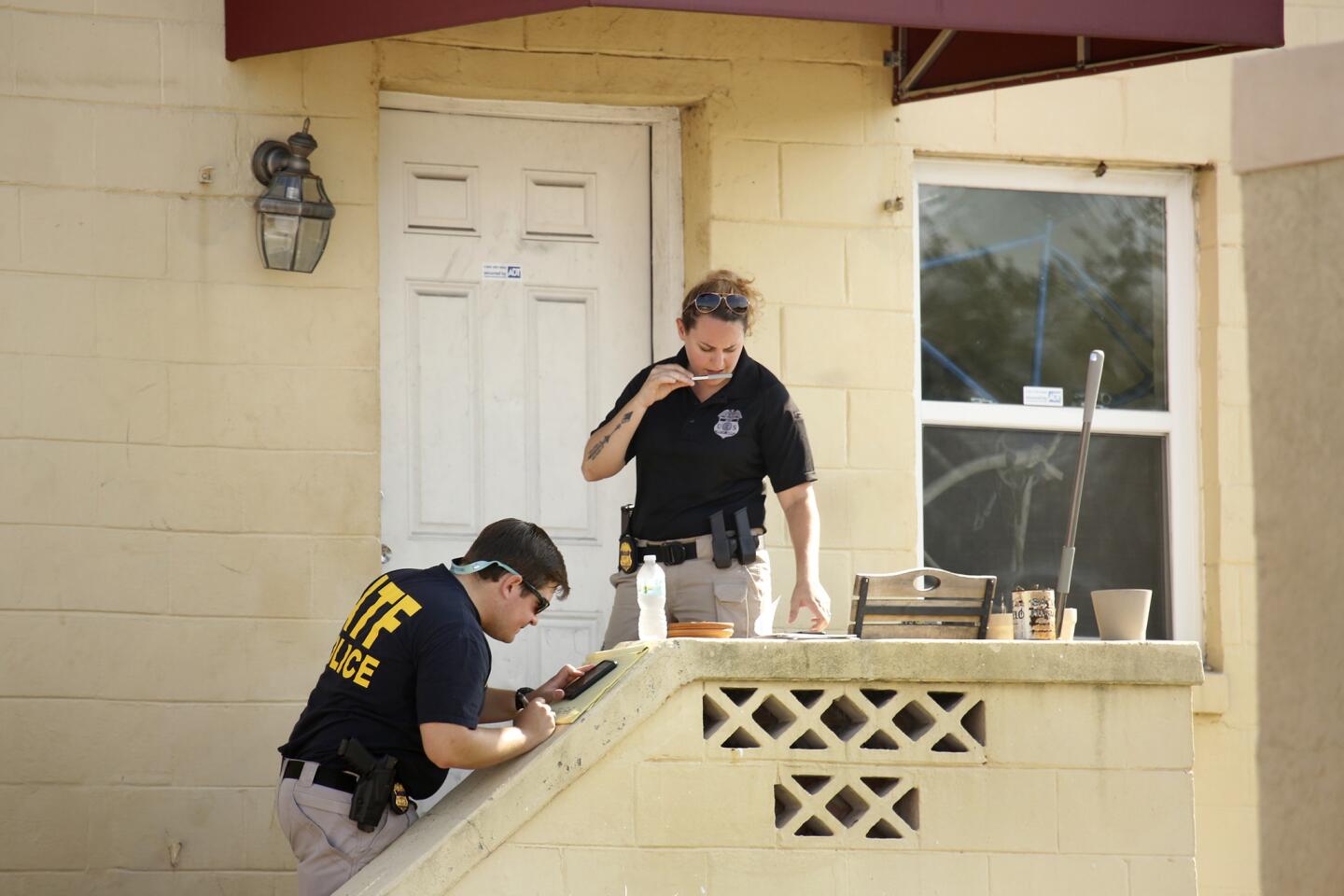
ATF investigators continue to work the scene of the Pulse nightclub shooting along Orange Ave.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 14/81
Friends and family attend the funeral of Angel Luis Candelario-Padro. It was the first funeral for the 49 victims of the Pulse nightclub shooting.
(Jacob Langston / Orlando Sentinel) 15/81
Doctors, nurses and first-responders at a prayer service in the emergency room at Florida Hospital in Orlando to honor the victims of the nightclub shooting.
(Joe Burbank / Orlando Sentinel) 16/81
FBI investigators continue to work at the Pulse nightclub on June 15.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 17/81
Mourners embrace outside the visitation for Pulse nightclub shooting victim Javier Jorge-Reyes.
(David Goldman / Associated Press) 18/81
Mourners gather at the Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts in Orlando for a vigil in honor of the nightclub attack victims.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 19/81
Mourners gather at the Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts in Orlando for a vigil in honor of the nightclub attack victims. (Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times)
20/81
Mourners gather at the Dr. Phillips Center for the Performing Arts in Orlando for a vigil in honor of the nightclub attack victims. (Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times)
21/81
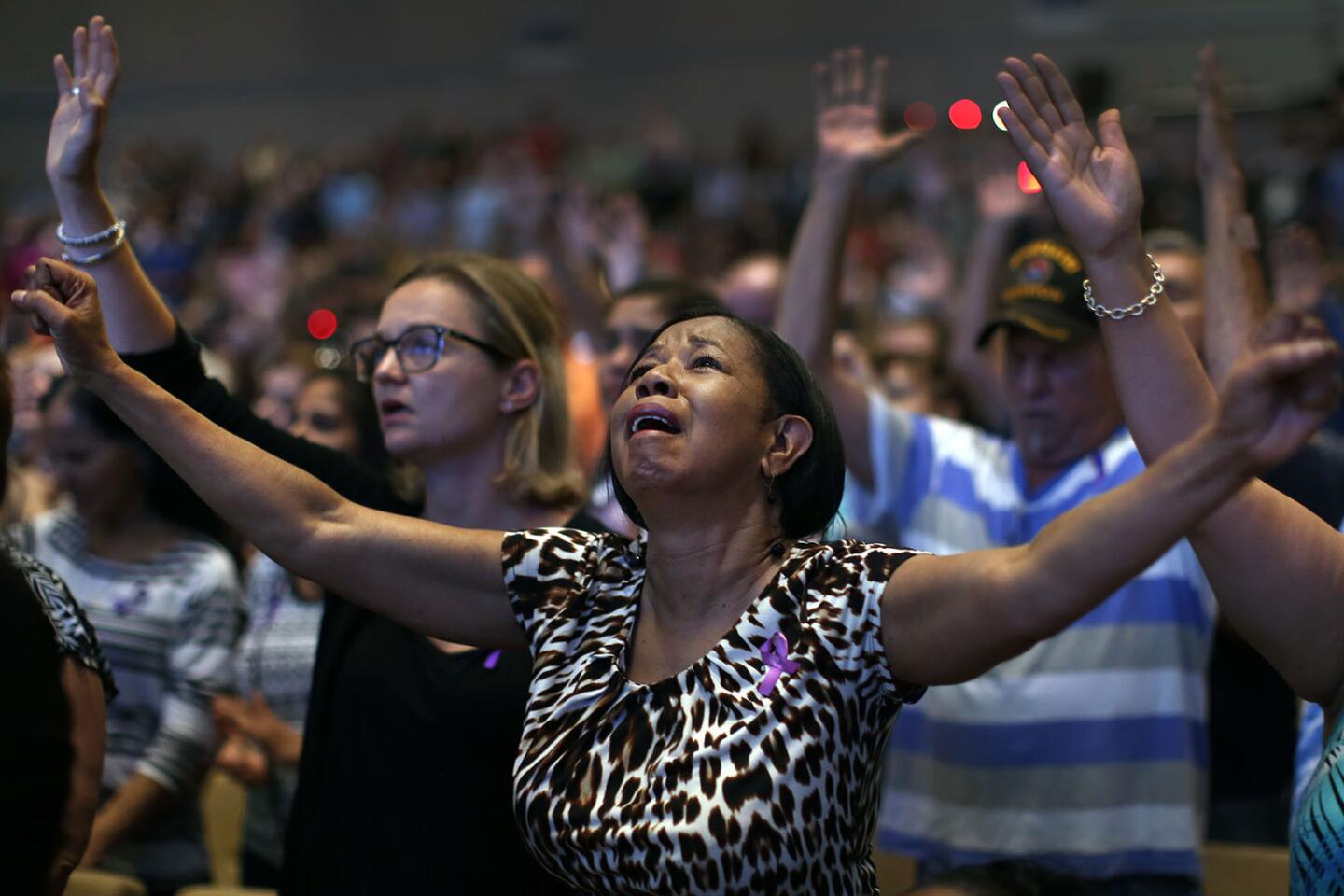
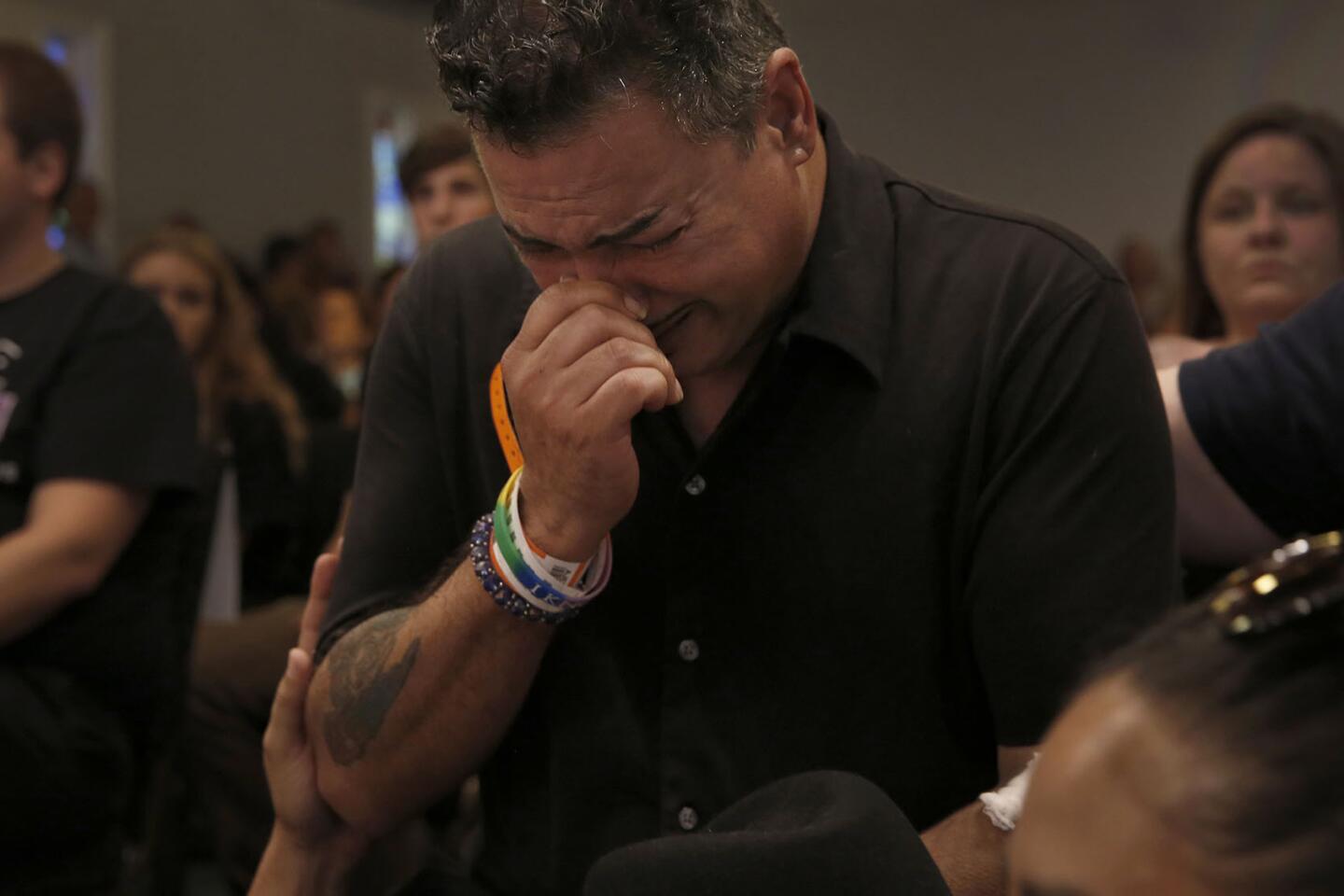
Michelle Moment sing praise during a service at the First Baptist Church of Orlando during a special prayer service for the attack on Pulse nightclub.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 22/81
“We were protected, we were saved it was just a miracle,” said Orlando Torres, 52. A promoter at Pulse, Torres was trapped in a bathroom stall with a friend. (Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times)
23/81
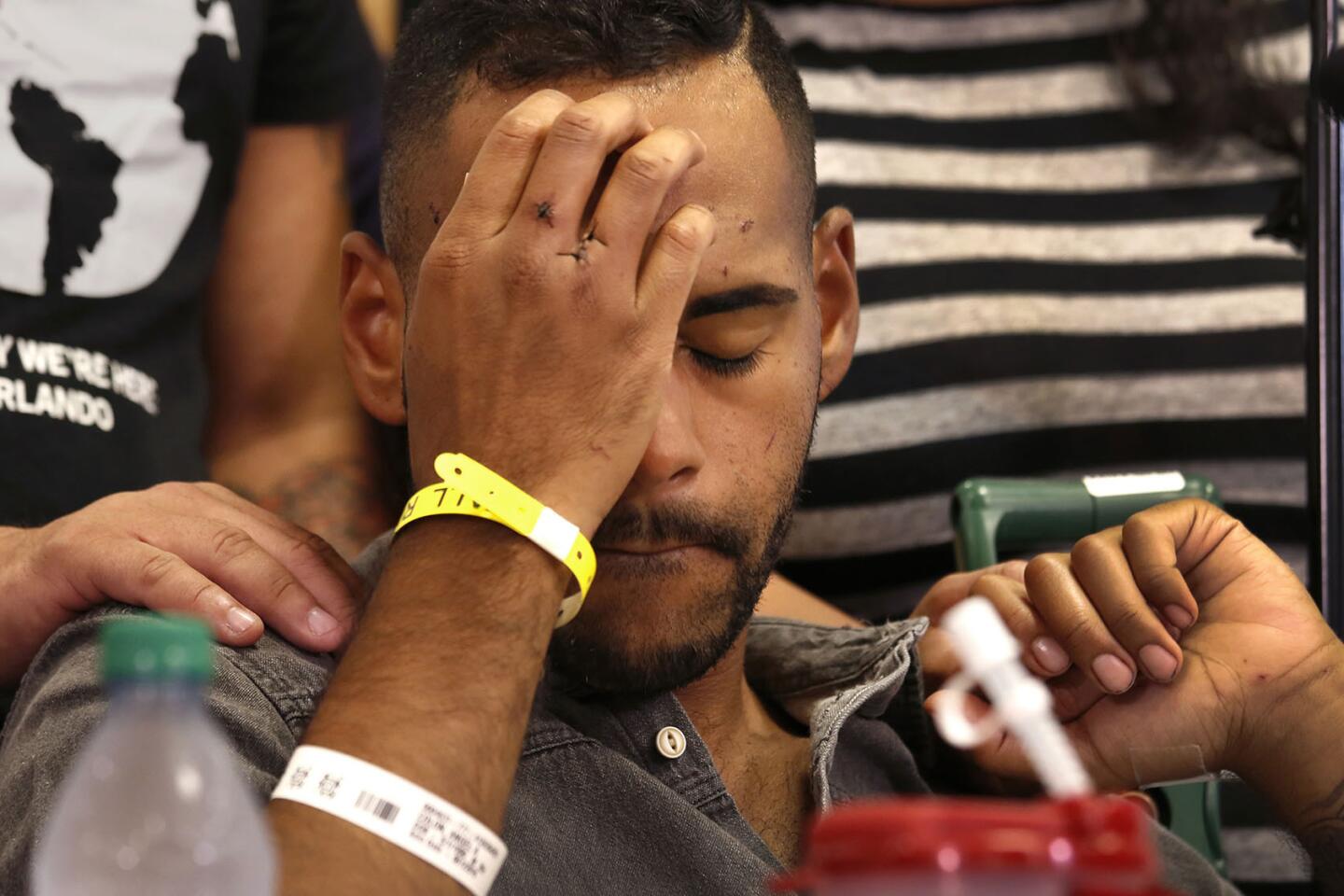
With stitches in his hand, gunshot victim Angel Colon tells his story to the media at a news conference at Orlando Regional Medical Center on Tuesday.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 24/81
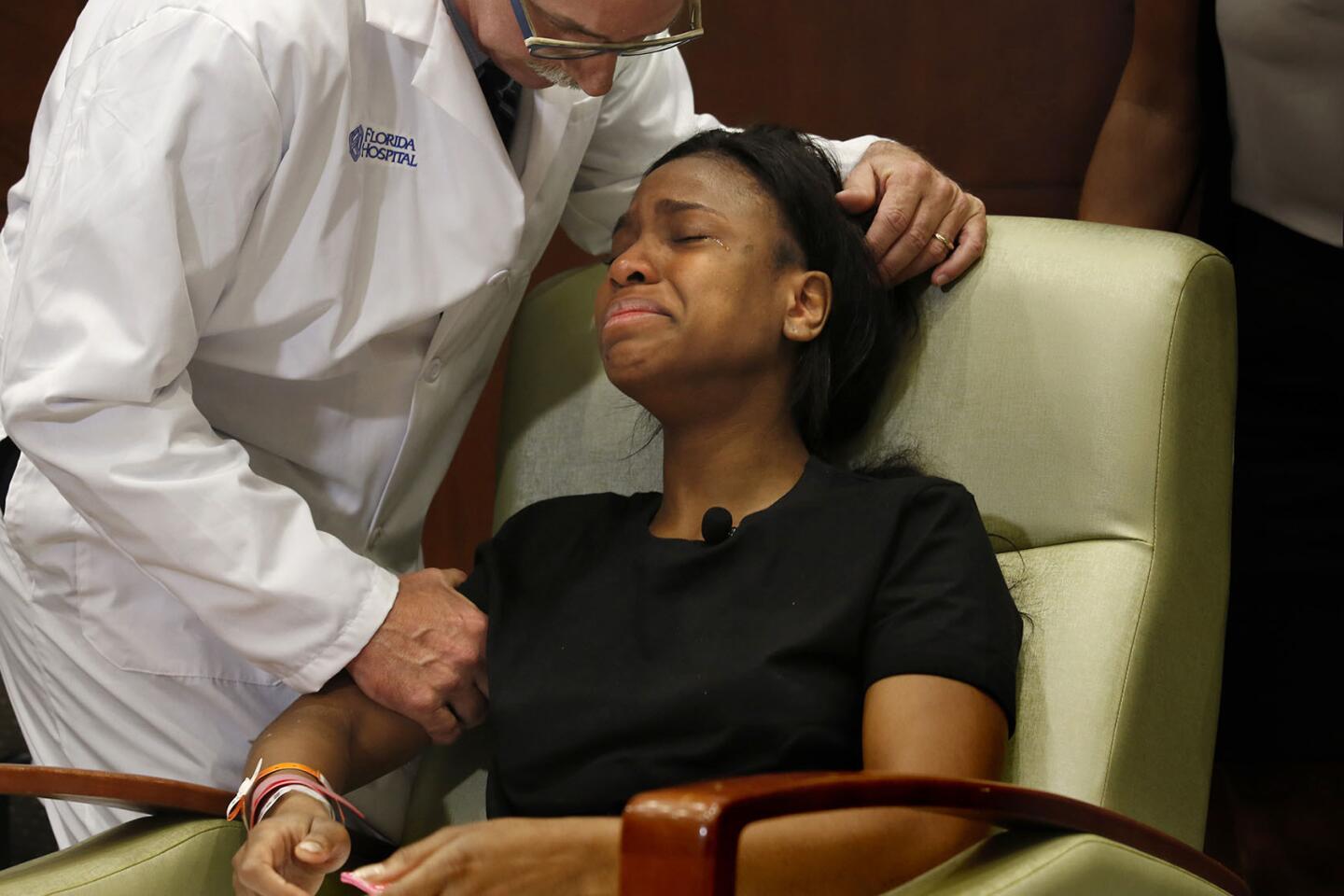
Patience Carter after describing the attack on the Pulse nightclub in Orlando. (Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times )
25/81
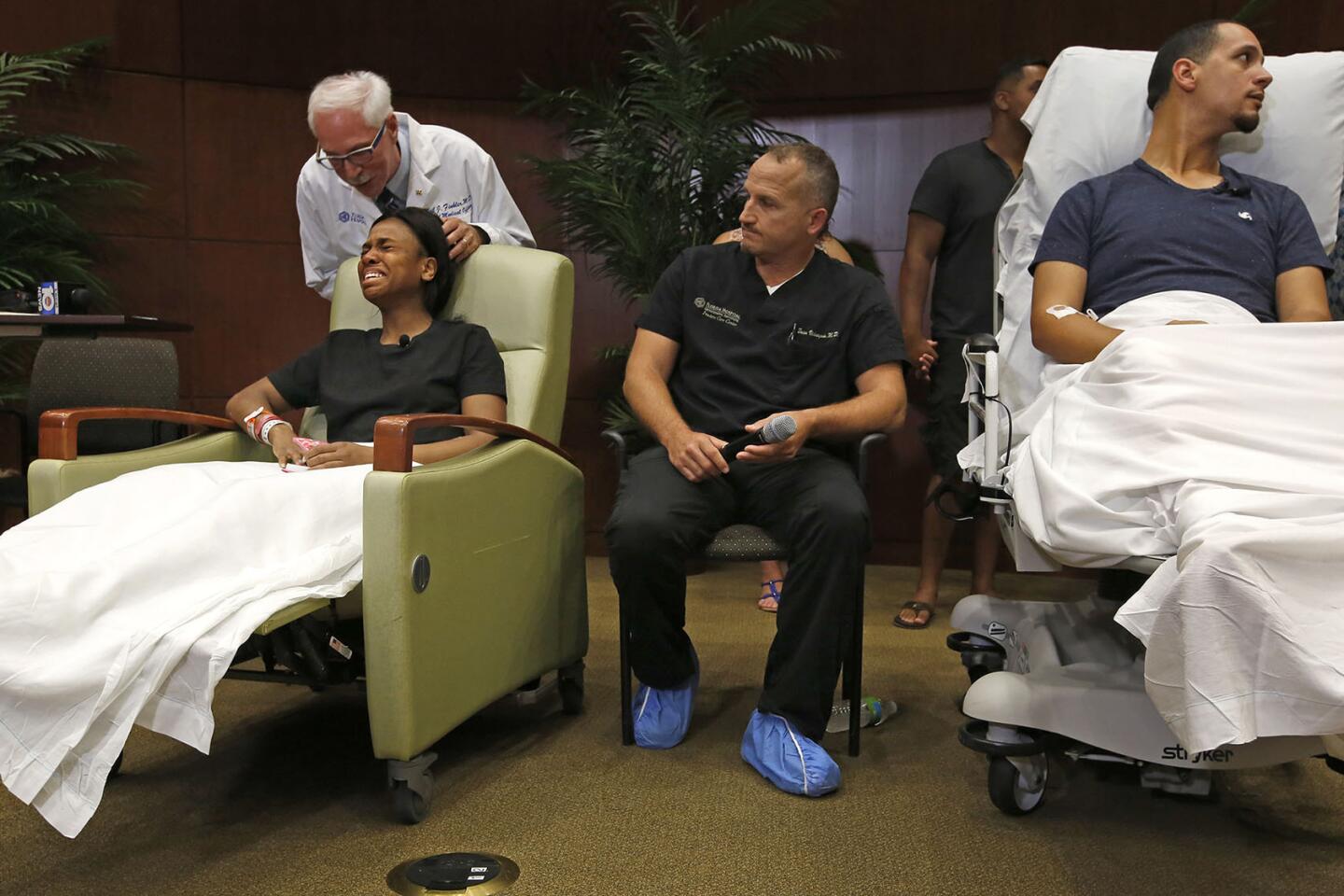
Gunshot victim Patience Carter, 20, left, is consoled by Dr. Neil Finkler at a news conference at Florida Hospital, joined by Dr. Brian Vickaryous, center, and fellow survivor Angel Santiago, 32, right, where they described the attack and its aftermath.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 26/81
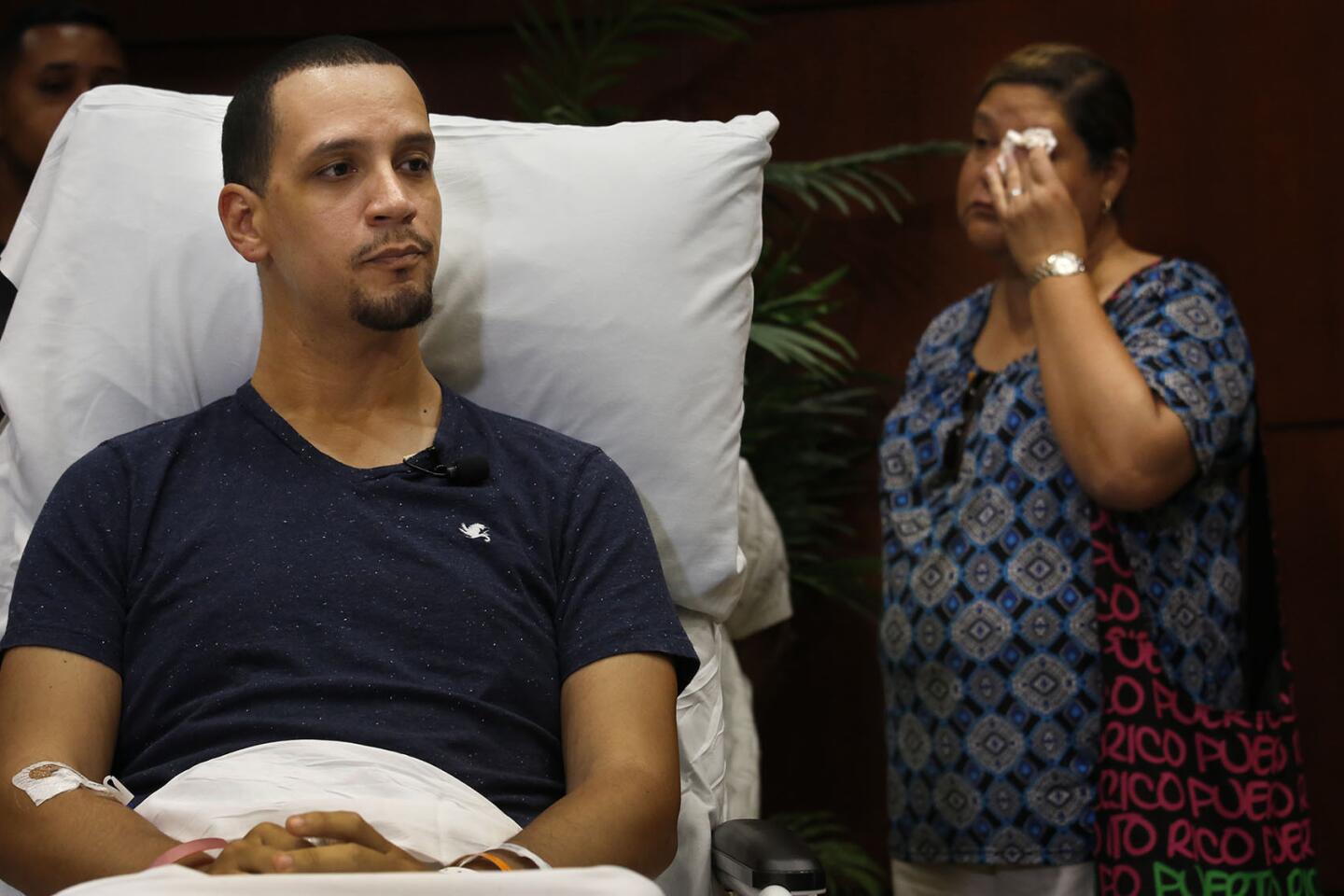
Angel Santiago on June 14, describes how events unfolded during the mass shooting at the Pulse nightclub in Orlando two days earlier.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 27/81
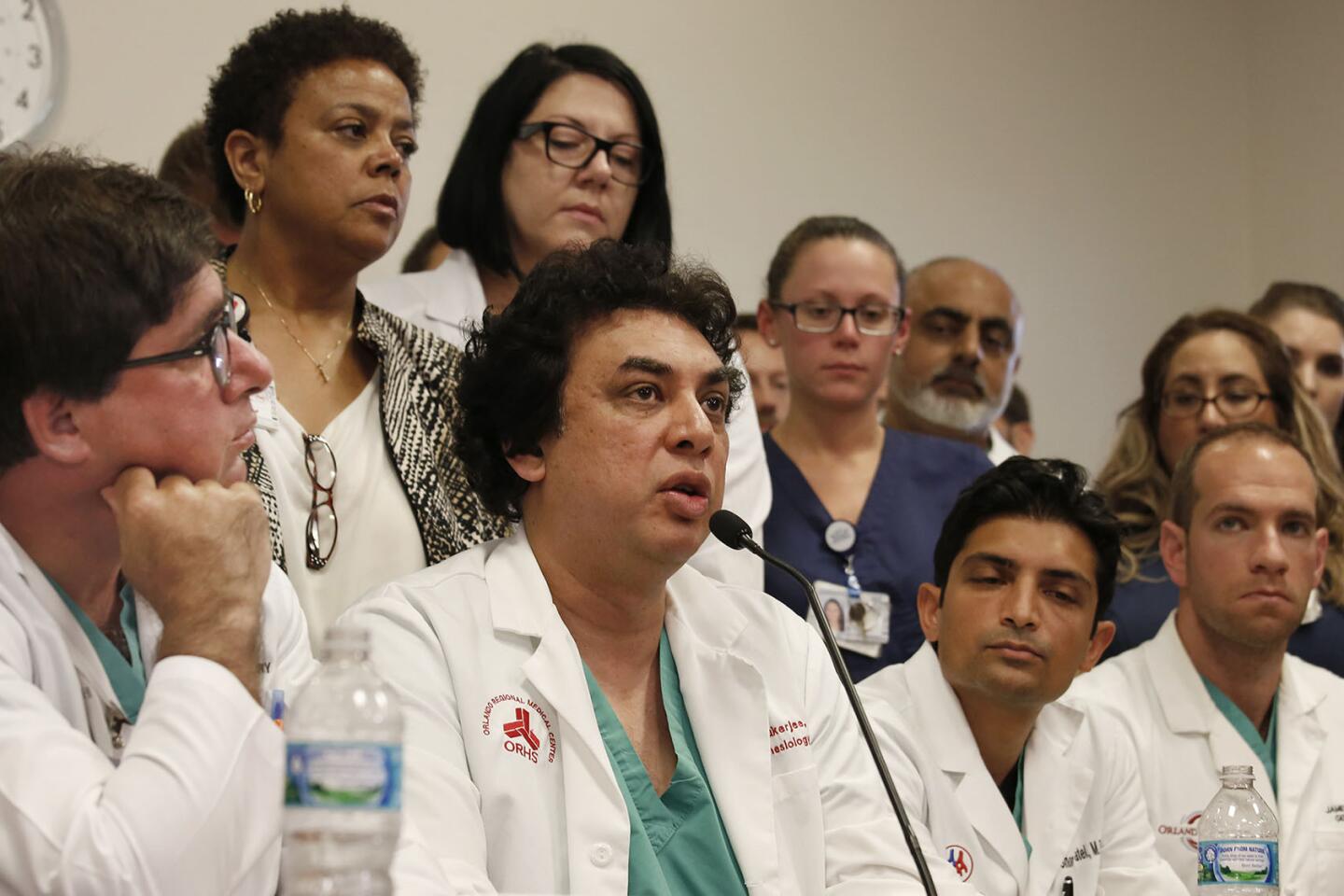
Doctors and other staff at Orlando Regional Medical Center involved in the response to the nightclub shooting answer questions at a news conference on June 14, 2016.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 28/81
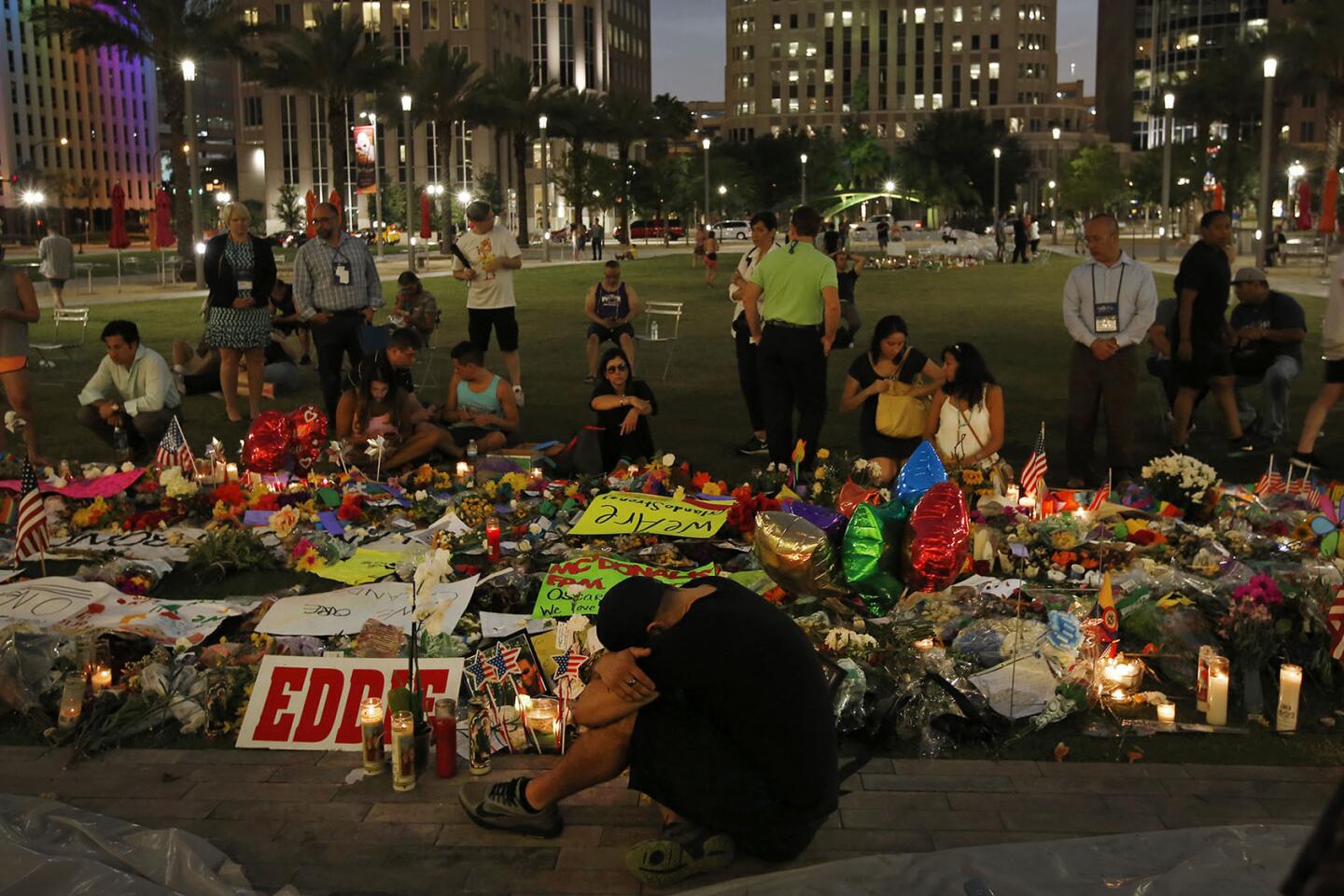
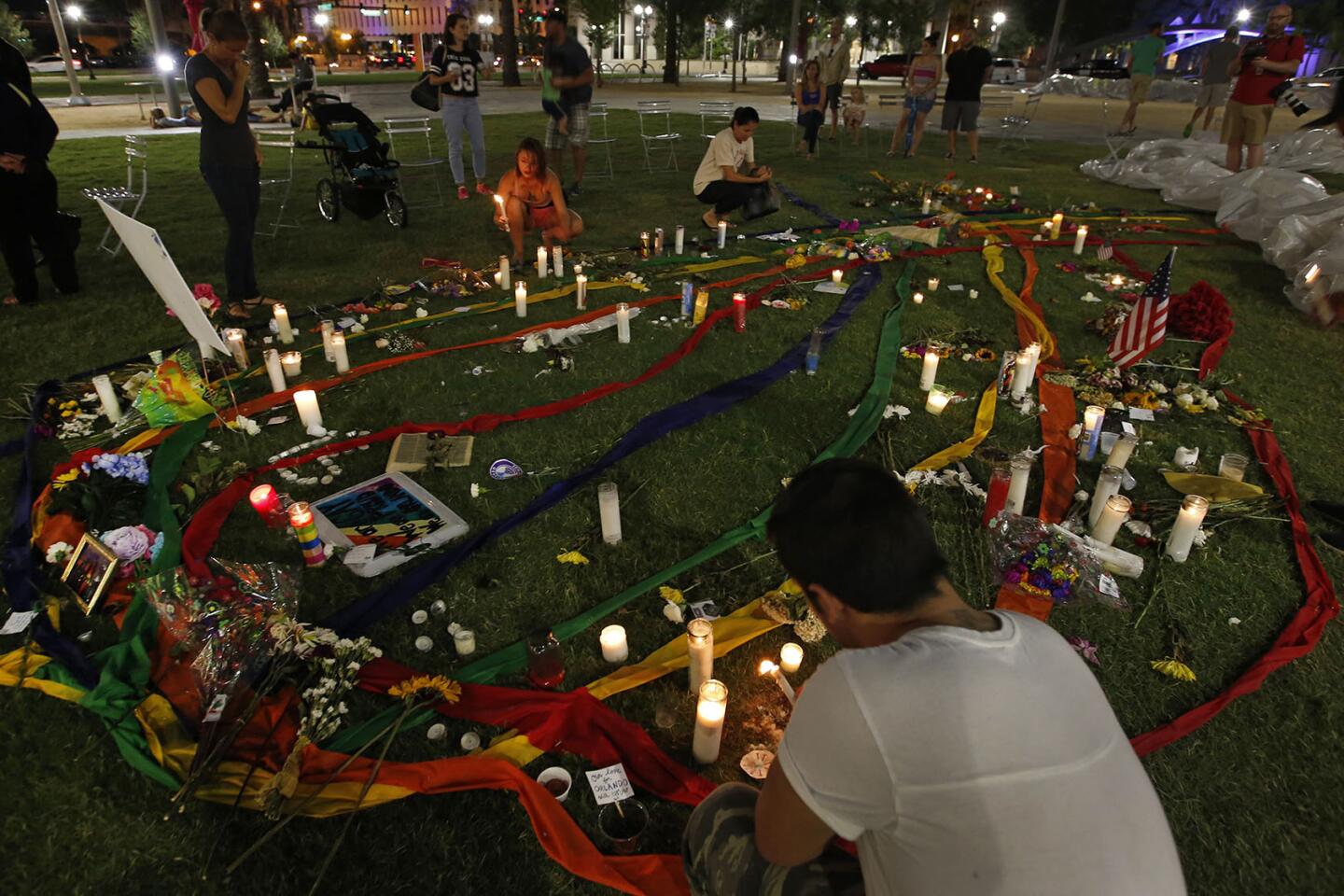
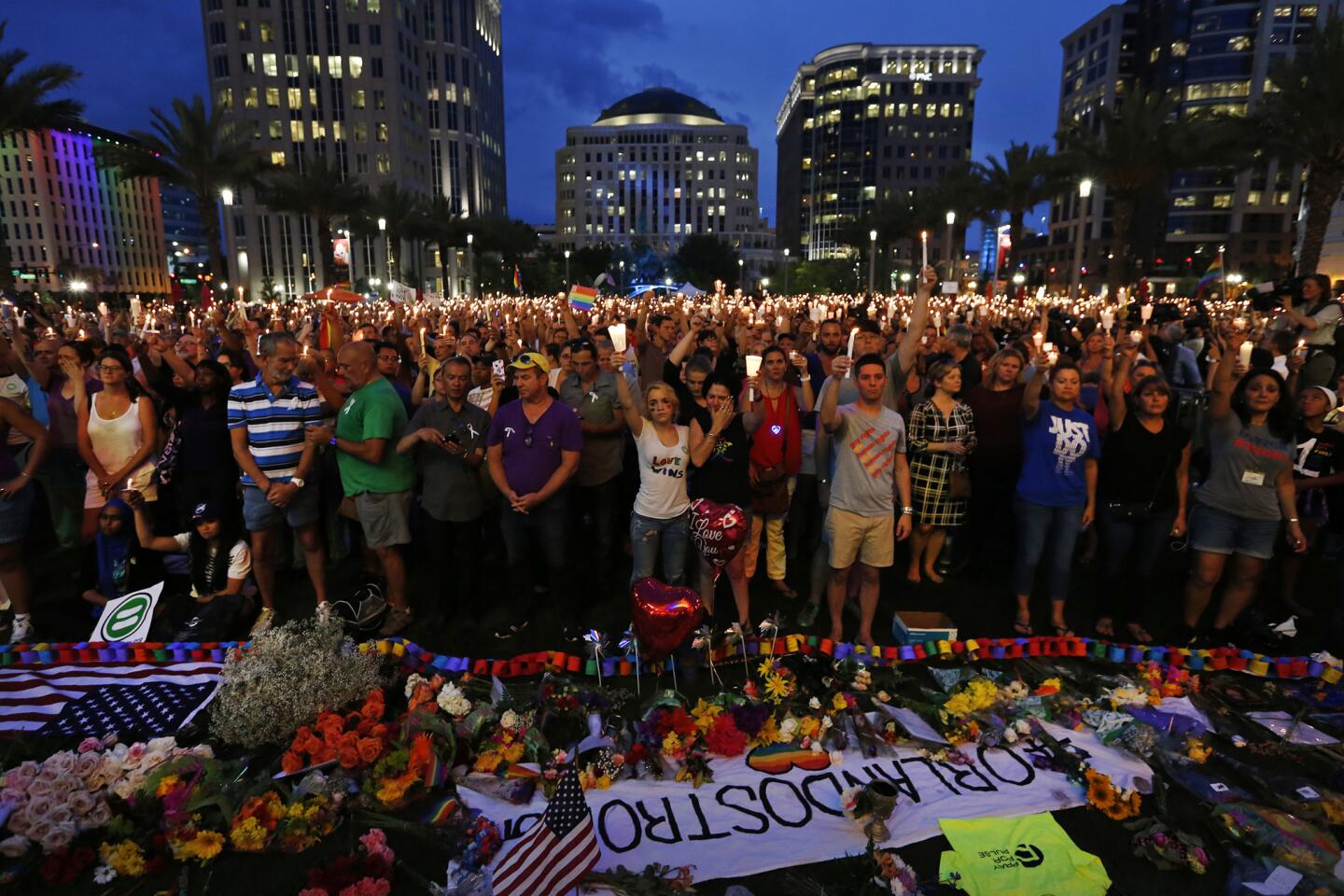
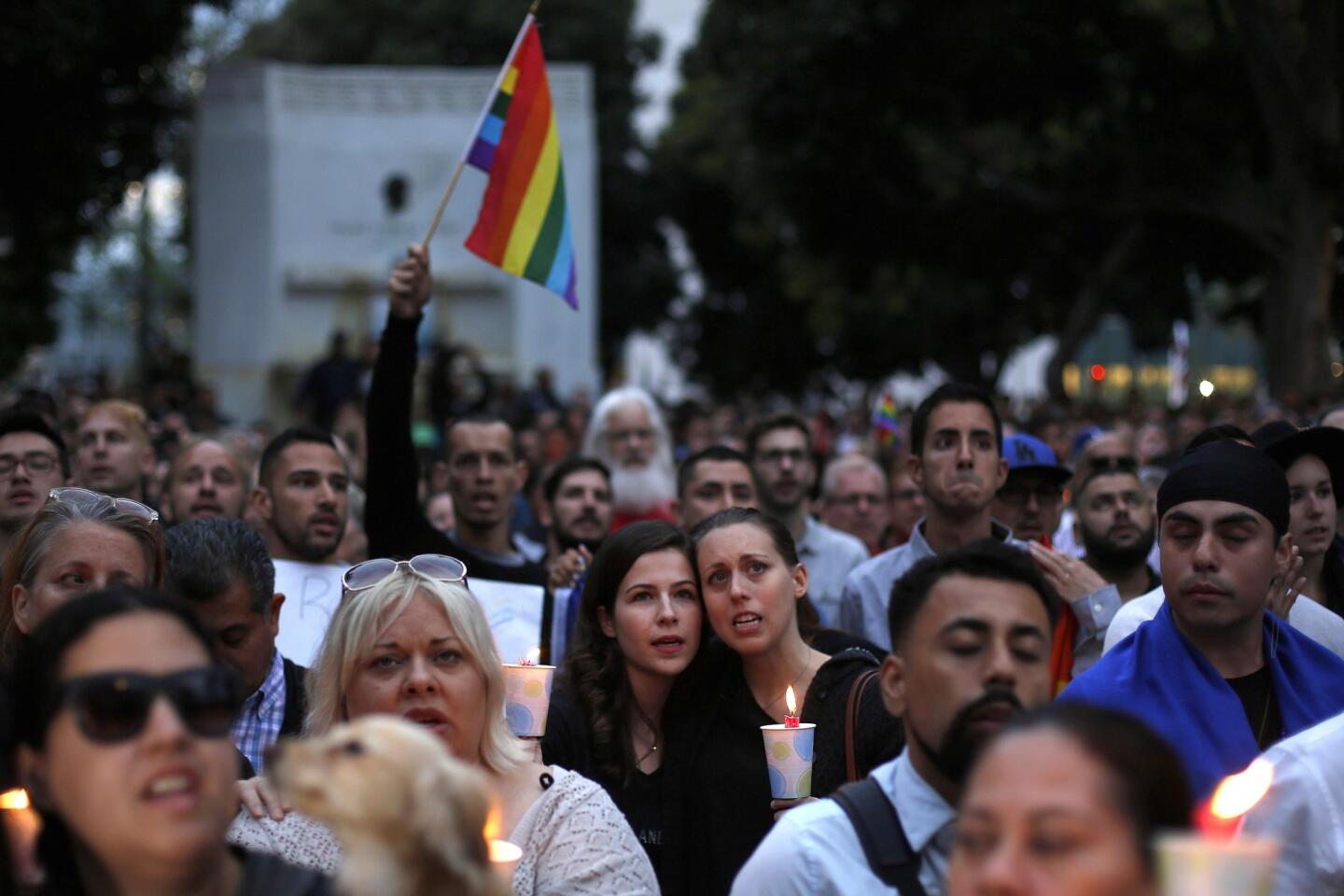
Thousands gather for a memorial at the Plaza at the Dr. Phillips Performing Arts Center in downtown Orlando on June 13, 2016, to honor those killed and wounded in the Pulse nightclub attack.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 29/81
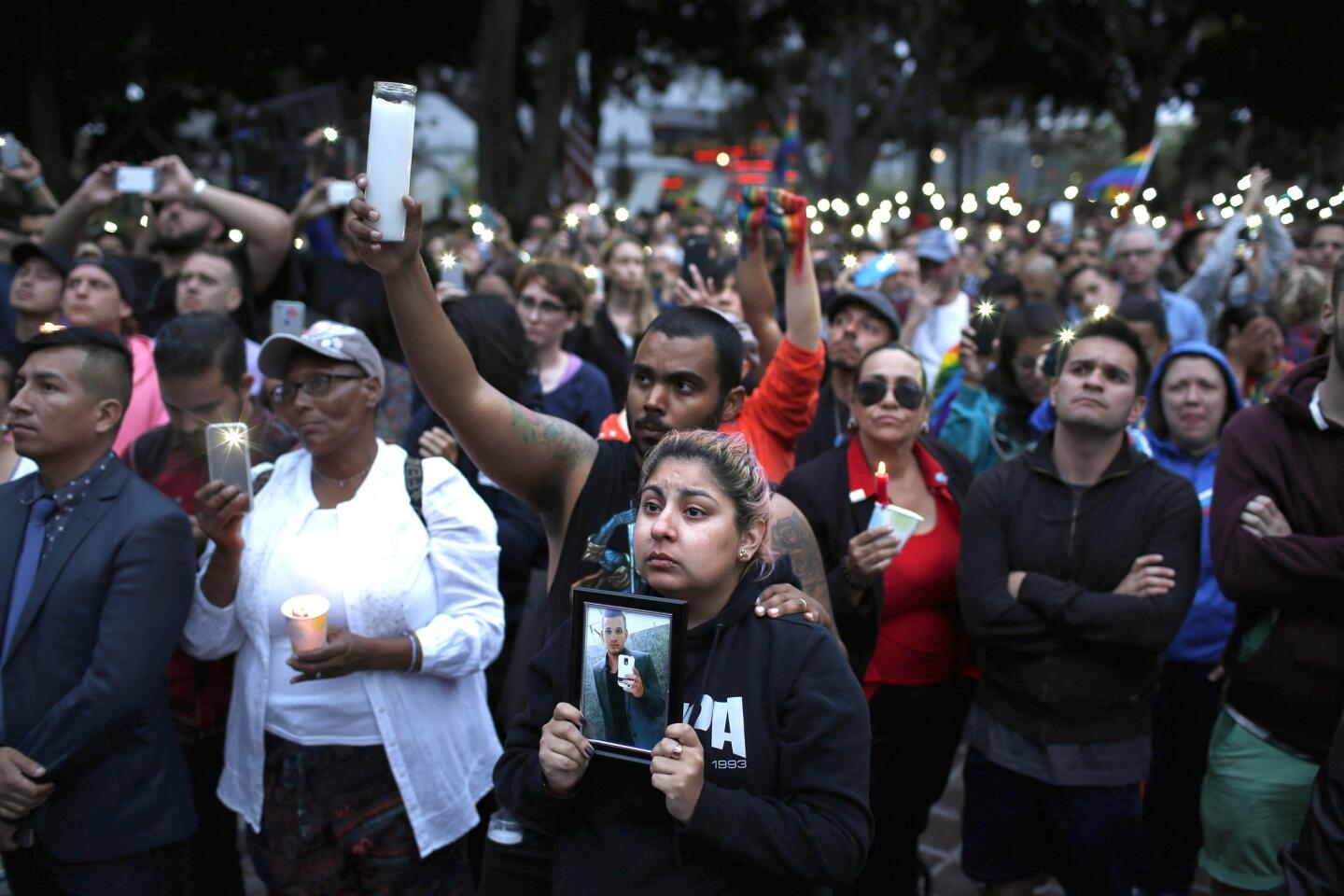
Alison Cossio, center, holds a photo of her friend Christopher Sanfeliz, who one of the victims of the Orlando shooting, during a June 13, 2016, candlelight vigil and rally, hosted by the Los Angeles LGBT Center, at Los Angeles City Hall.
(Katie Falkenberg / Los Angeles Times) 30/81
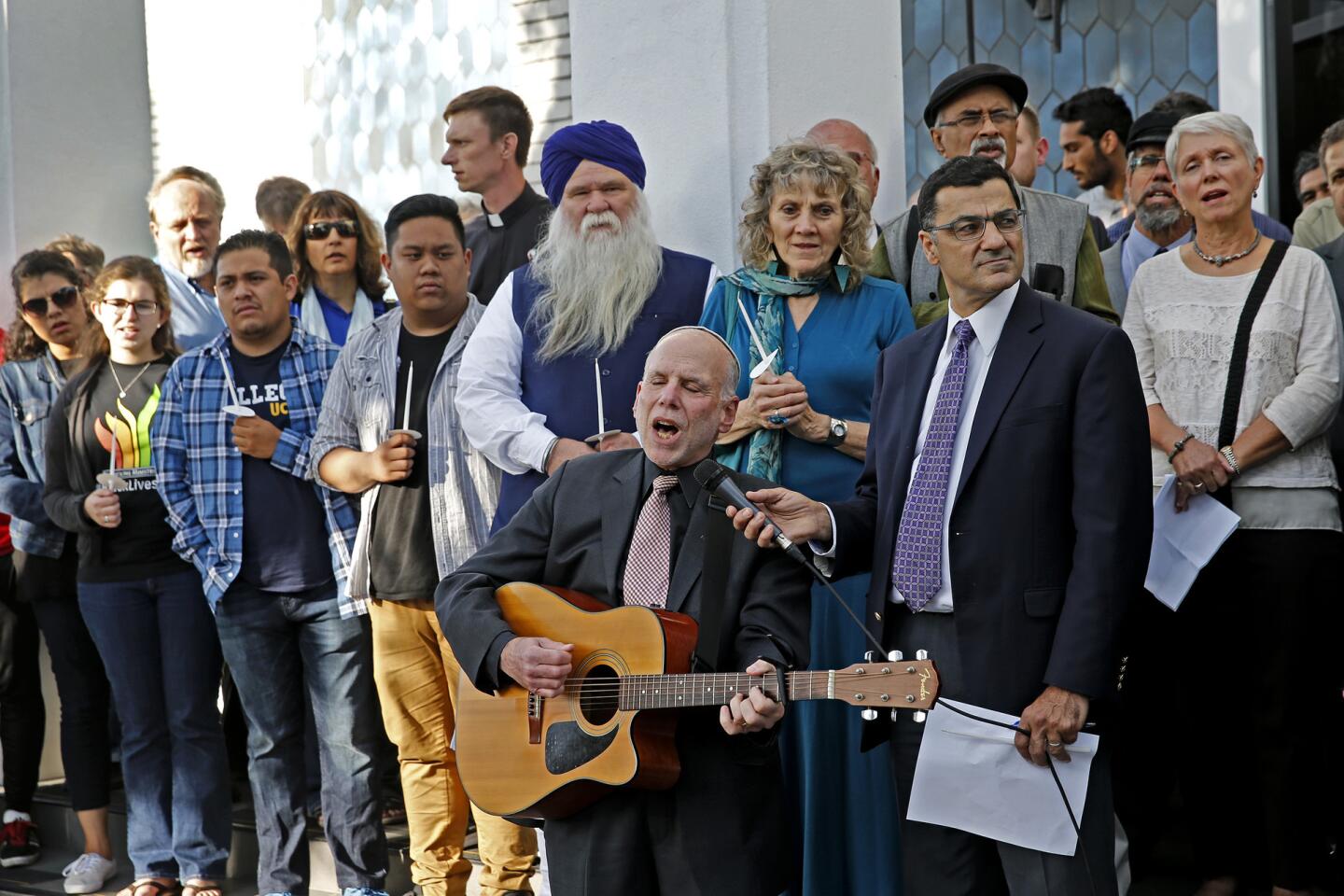
Rabbi Neil Comess-Daniels plays guitar and sings during the Islamic Center of Southern California and ICUJP Interfaith Vigil Against Violence and Hatred Monday,night in remembrance of the 50 people killed in Orlando.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times) 31/81
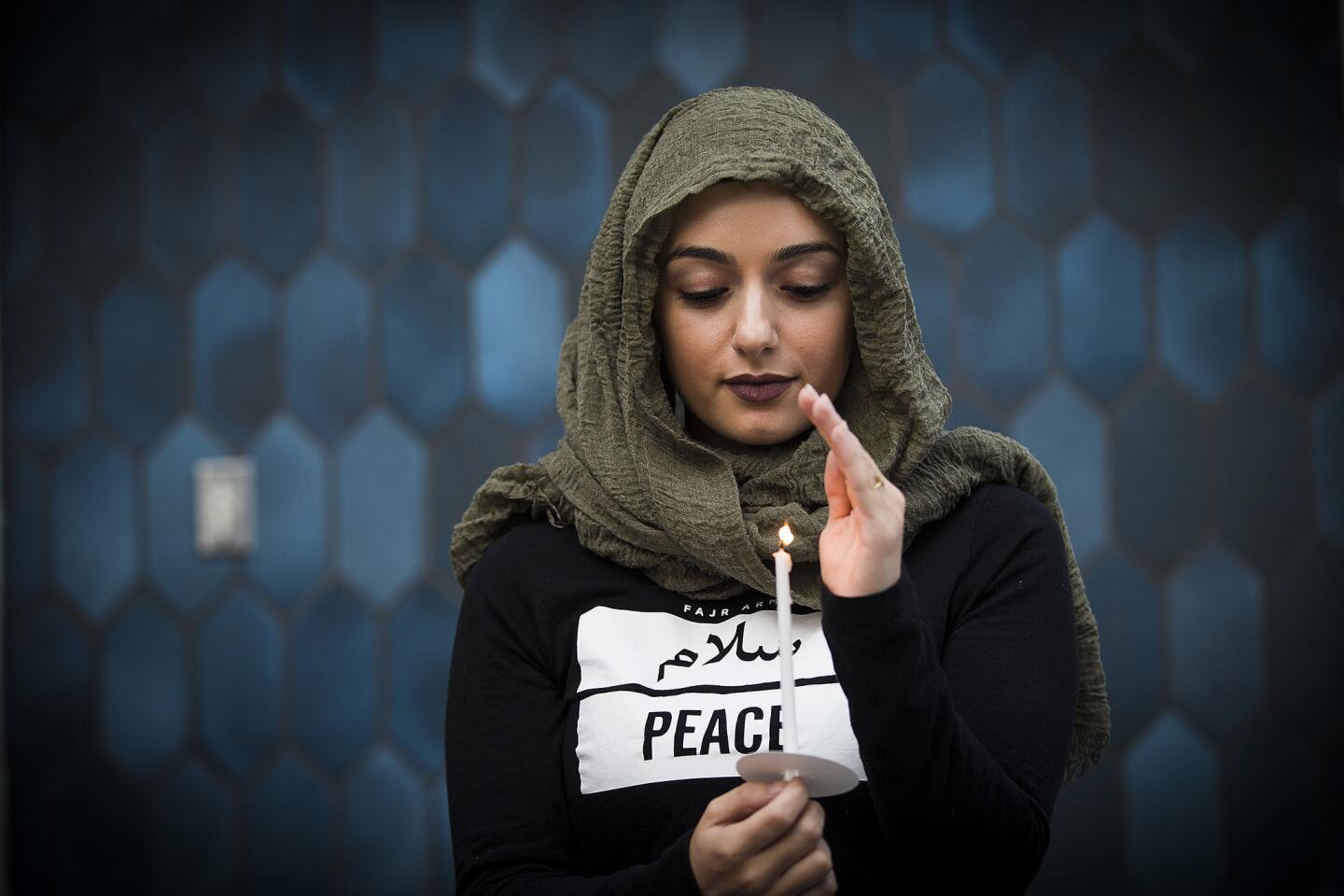
Marwa Balkar holds a candle at the Islamic Center of Southern California and ICUJP Interfaith Vigil Against Violence and Hatred on June 13, 2016, in remembrance of the 49 people killed in Orlando, Fla.
(Allen J. Schaben / Los Angeles Times) 32/81
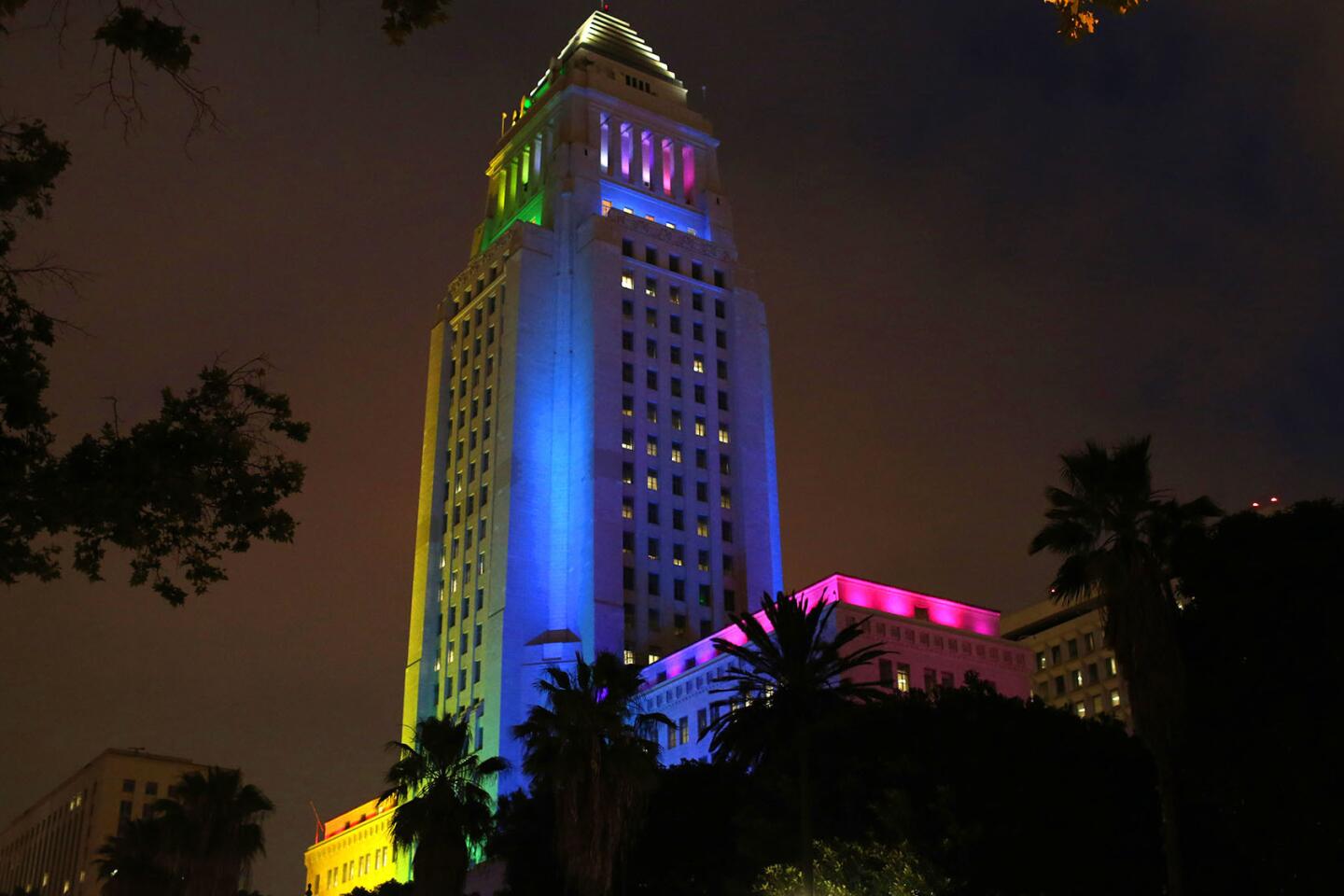
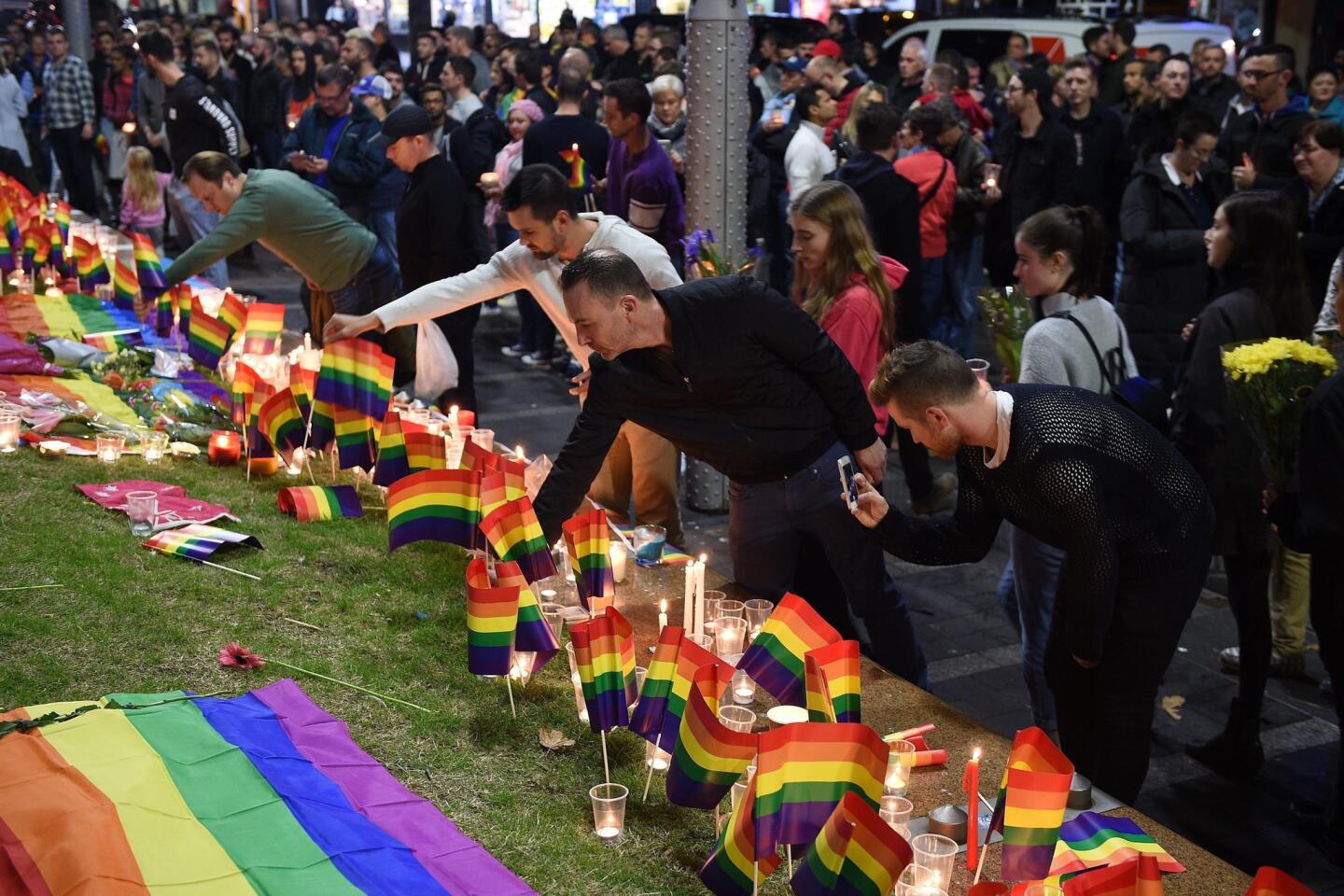
Los Angeles City Hall is lit up in colors of the rainbow during a candlelight vigil and rally, hosted by the Los Angeles LGBT Center.
(Katie Falkenberg / Los Angeles Times) 33/81
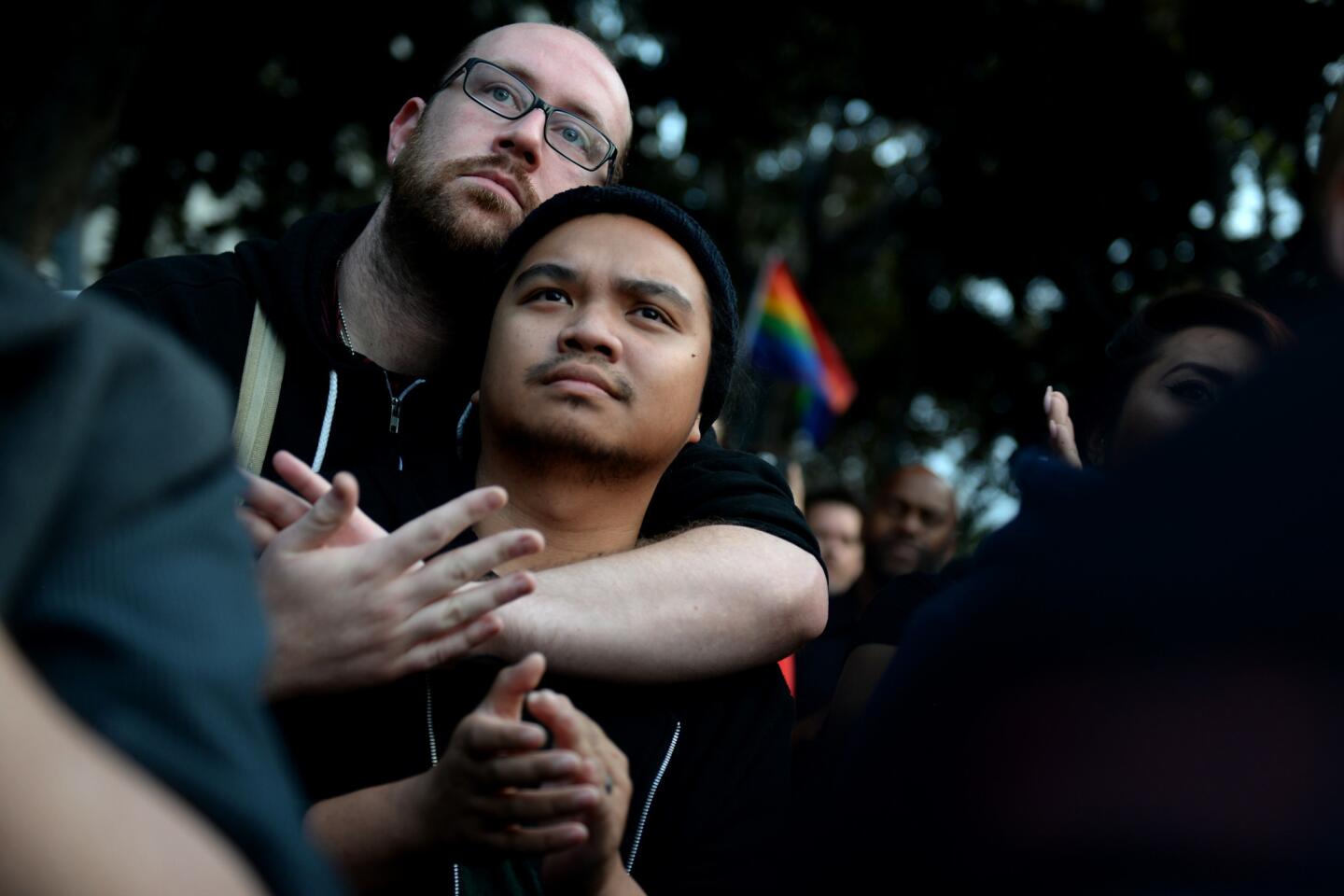
Scott Phillips and Em Enagan mourn for the 49 lives lost in the Orlando shooting during a vigil at Los Angeles City Hall.
(Callaghan O’Hare / Los Angeles Times) 34/81
A song is sung during a candlelight vigil and rally, hosted by the Los Angeles LGBT Center, at Los Angeles City Hall, for the victims of Sunday’s shooting massacre at a gay nightclub in Orlando.
(Katie Falkenberg / Los Angeles Times) 35/81
Thousands gather for a memorial rally at the Plaza at the Dr. Phillips Performing Arts Center in downtown Orlando on Monday to honor those killed and wounded in the Pulse nightclub attack.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 36/81
Madeline Lago, 15, and her mother Carmen Lago were among the thousands who gathered for a memorial at the Plaza at the Dr. Phillips Performing Arts Center in downtown Orlando on Monday to honor those killed and wounded in the Pulse nightclub attack. They bowed their heads as the bell was tolled.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 37/81
Thousands gather for a memorial at the Plaza at the Dr. Phillips Performing Arts Center in downtown Orlando on Monday to honor those killed and wounded in the Pulse nightclub attack.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 38/81
Friends and relatives bring flowers and remembrances to the plaza at the Dr. Phillips Performing Arts Center in downtown Orlando on Monday.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 39/81
Danielle Irigoyen brings flowers to the victims of the Pulse nightclub shooting. “I’m very close to many of the people who go to Pulse. Pulse was a safe place for us all,” she sail.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 40/81
Investigators gather at the Pulse nightclub on Monday morning.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 41/81
Investigators set up at the Pulse nightclub.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 42/81
Family gather for victims at Beardall Senior Center in Orlandoon Monday.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 43/81
Friends of Shane Tomlinson, who was killed in the Pulse nightclub shooting, gather in prayer and remembrances in downtown Orlando on Monday. (Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times)
44/81
Friends of Shane Tomlinson, including Richie Compton, left, and Erik Winger, right, gather in prayer and remembrances in downtown Orlando on Monday. Shane Tomlinson was killed killed in the Pulse nightclub shooting.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 45/81
Family and friends arrive at the Senior Center in Orlando as they await news on their loved ones on Monday. (Carolyn Cole/Los Angeles Times)
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 46/81
Volunteers gather in prayer on Monday at the Senior Center in Orlando where they are there to help grieving family and friends of those killed and injured in the shooting at Pulse nightclub.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 47/81
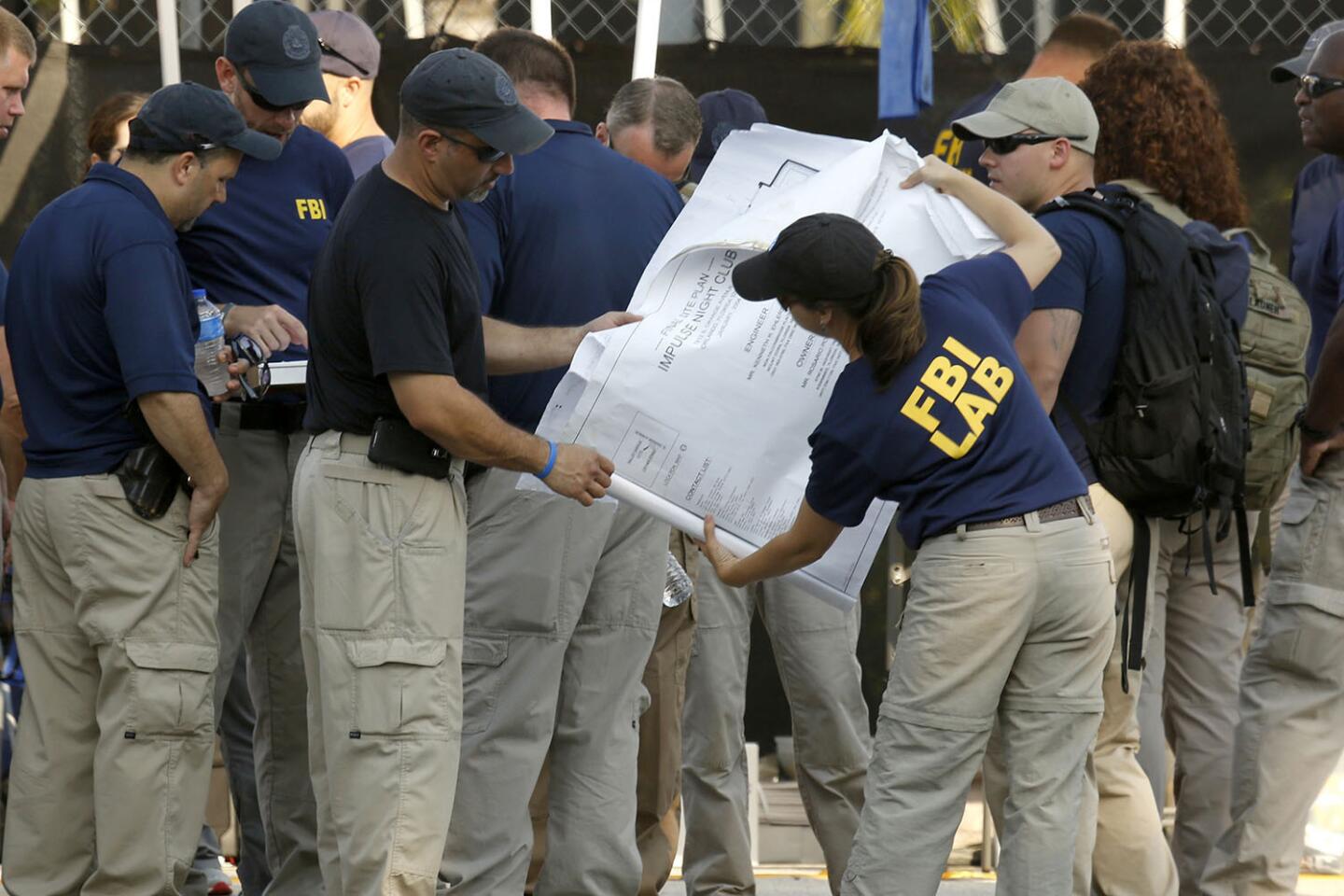
FBI investigators in Orlando, Fla., look at the floor plans of Pulse nightclub as they gather on Monday morning to continue the investigation.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 48/81
People gather at Taylor Square in Sydney, Australia, to show solidarity with victims of the Orlando nightclub shooting.
(Dan Himbrechts / EPA) 49/81
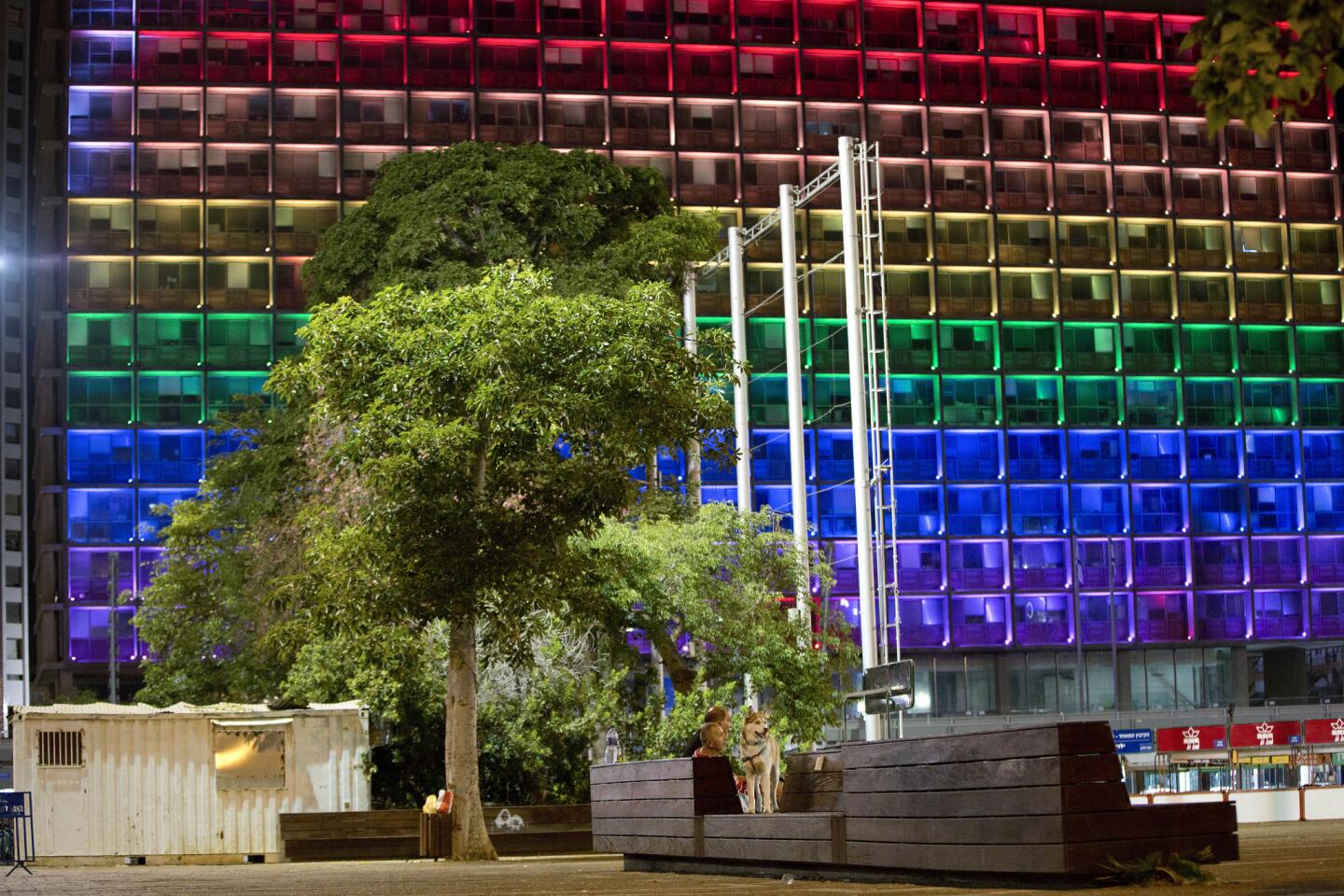
City Hall in Tel Aviv, Israel, is lit up in solidarity with Orlando’s shooting victims.
(Oded Balilty / Associated Press) 50/81
New Zealand residents gather at Frank Kitts Park in Wellingtond to mourn victims of the Pulse nightclub shooting in Orlando, Fla.
(Hagen Hopkins / Getty Images) 51/81
A man lights a candle in Paris on June 12 to remember those slain and wounded in the Orlando nightclub shooting. (Rapahel Satter / Associated Press)
52/81
New Zealand residents gather in Frank Kitts Park to mourn victims of the Orlando nightclub shooting.
(Hagen Hopkins / Getty Images) 53/81
Residents gather at Joy Metropolitan Community Church near the Pulse nightclub in Orlando to mourn the mass shooting victims of the early morning attack on June 12, 2016.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 54/81
Johnpaul Vazquez, right, and his boyfriend Yazan Sale sit by Lake Eola, in downtown Orlando, thinking of those killed and injured.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 55/81
Judy Rettig, center, and Dave Hack, left, hug after a prayer service held at the Joy Meropolitan Community Church in Orlando.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 56/81
Zafar Basith prays at a vigil for the Orlando shooting victims at the Baitul Hameed Mosque in Chino.
(Francine Orr / Los Angeles Times) 57/81
Raymond Braun, right, right, gets a hug after a vigil held in West Hollywood for the victims of the shooting at the nightclub in Orlando.
(Katie Falkenberg / Los Angeles Times) 58/81
Monte Dobbs and Jhoanna Galvez of Long Beach, comfort each other during a vigil service at the corner of La Cienega Blvd. and Santa Monica Blvd.
(Harrison Hill / Los Angeles Times) 59/81
Orlando, second from right, was at the nightclub and trapped for three hours in a bathroom. Orlando and family attend a vigil and church service held at Joy Meropolitan Community Church very close to Pulse nightclub.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 60/81
People hug in solaceafter a vigil and church service held at Joy Meropolitan Community Church very close to Pulse nightclub.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 61/81
Susan Stephens, right, gets a hug from Karen Castelloes before a vigil and prayer service is held at Joy Meropolitan Community Church very close to Pulse nightclub.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 62/81
Investigators view the site of the early morning mass shooting on June 12, 2016, at Pulse nightclub in Orlando.
(Carolyn Cole / Los Angeles Times) 63/81
People hold signs in support of the Orlando shooting victims on Sunday.
(Jacob Langston / Orlando Sentinel) 64/81
Kelvin Cobaris, a local clergyman, consoles Orlando city commissioner Patty Sheehan (right) and Terry DeCarlo, an Orlando gay-rights advocate, as they arrive on the scene near where at least 50 people were reportedly shot and killed in Orlando, Fla., Sunday, June 12, 2016.
(Joe Burbank / Orlando Sentinel) 65/81
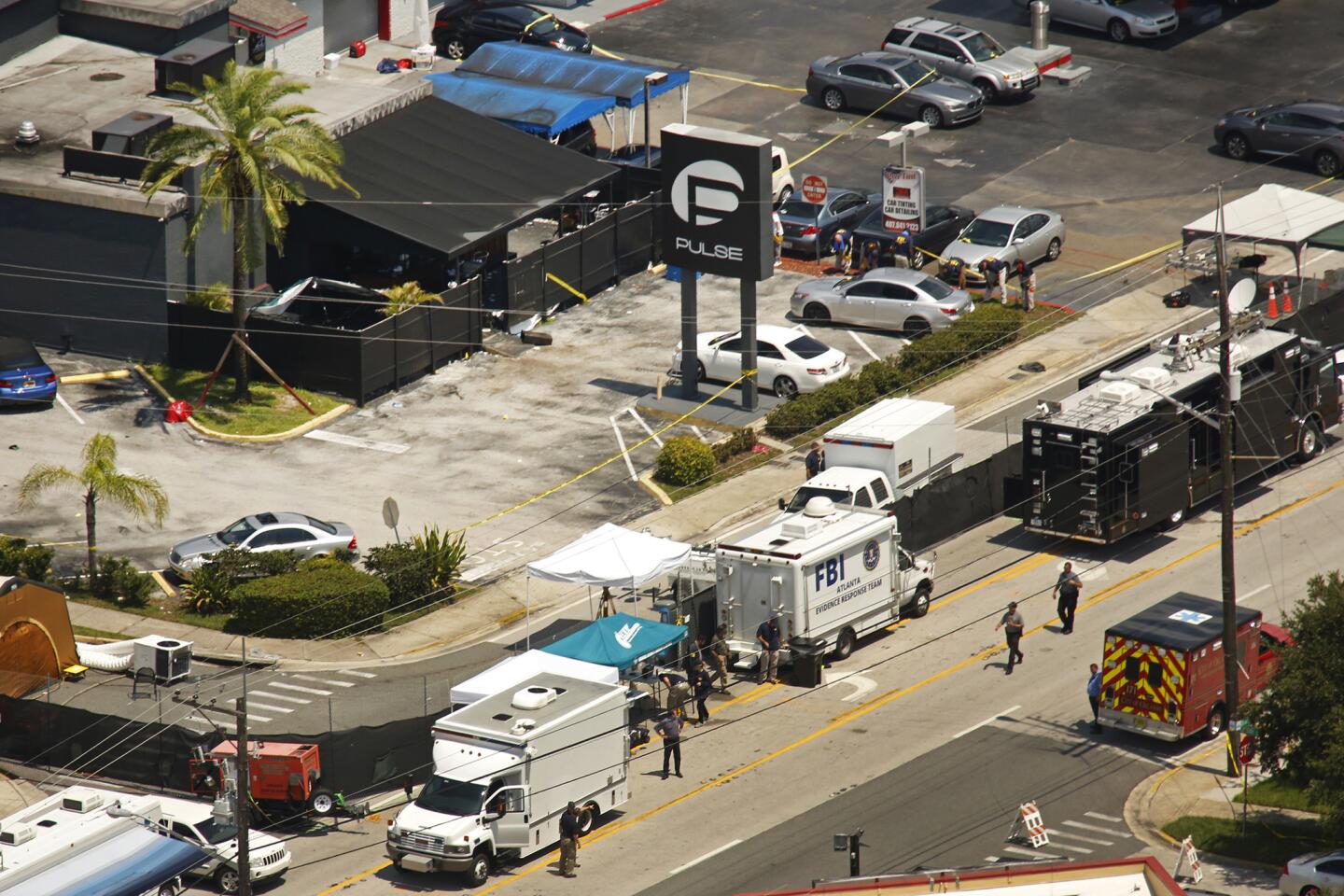
Aerial view of the shooting scene at Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla.
(Red Huber / Orlando Sentinel) 66/81
A bomb disposal unit checks for explosives around the apartment building where shooting suspect Omar Mateen is believed to have lived on June 12, 2016 in Fort Pierce, Florida.
(Joe Raedle / Getty Images) 67/81
Ray Rivera, a DJ at Pulse nightclub, is consoled by a friend outside of the Orlando Police Department after 50 people were killed at the club on Sunday.
(Joe Burbank / Orlando Sentinel) 68/81
Orlando police officers outside of Pulse nightclub after a fatal shooting and hostage situation on Sunday.
(Gerardo Mora / Getty Images) 69/81
Terry DeCarlo, executive director of the LGBT Center of Central Florida, right, is comforted by an Orlando Police officer after a shooting involving multiple fatalities at a nightclub in Orlando, Fla. on Sunday.
(Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press) 70/81
An aerial view of the shooting scene at Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla. (Red Huber / Orlando Sentinel)
71/81
Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti, center, and others have a moment of silence on June 12, 2016, in West Hollywood for the victims of the shooting in Orlando, Fla., that happened early that morning.
(Genaro Molina / Los Angeles Times) 72/81
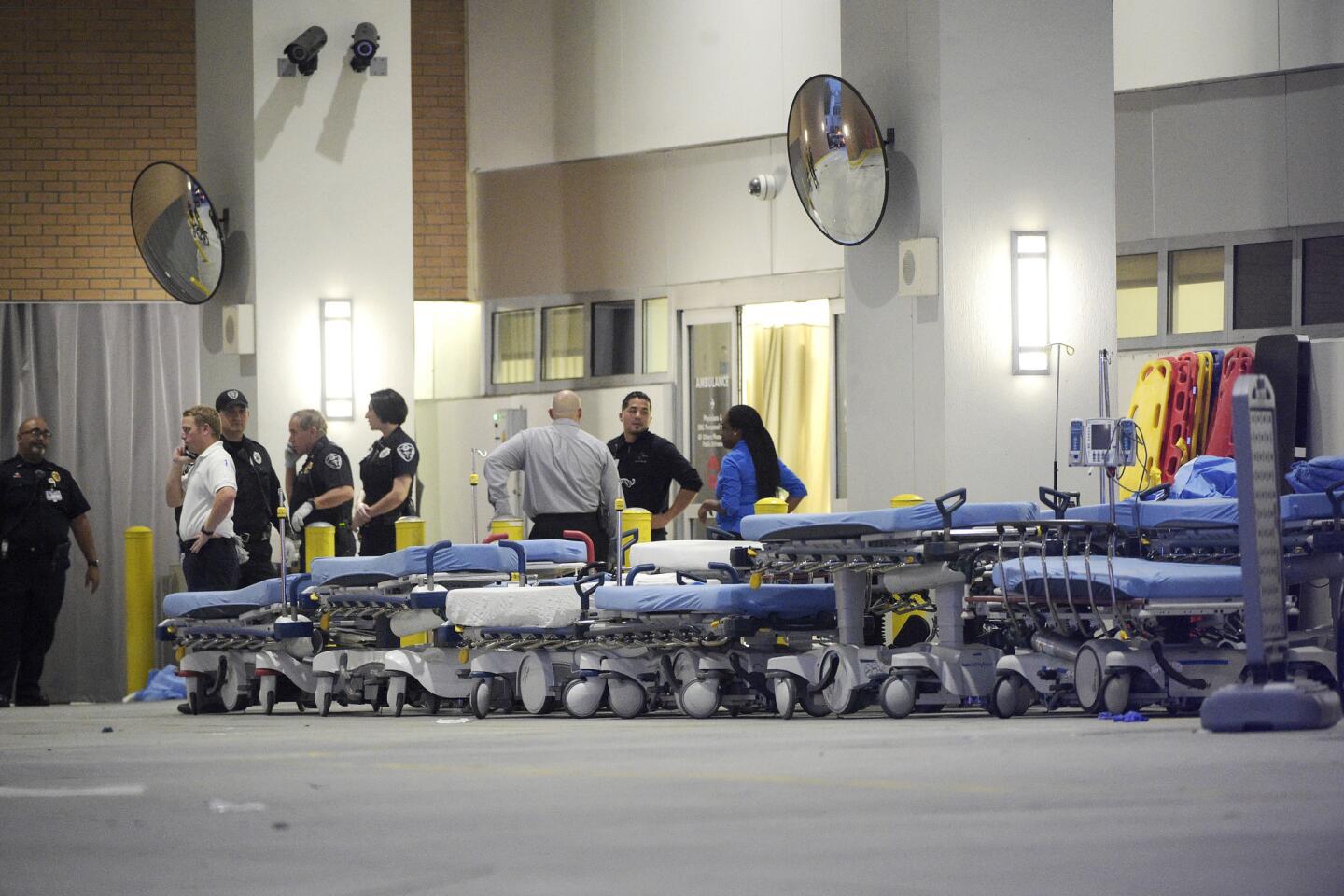
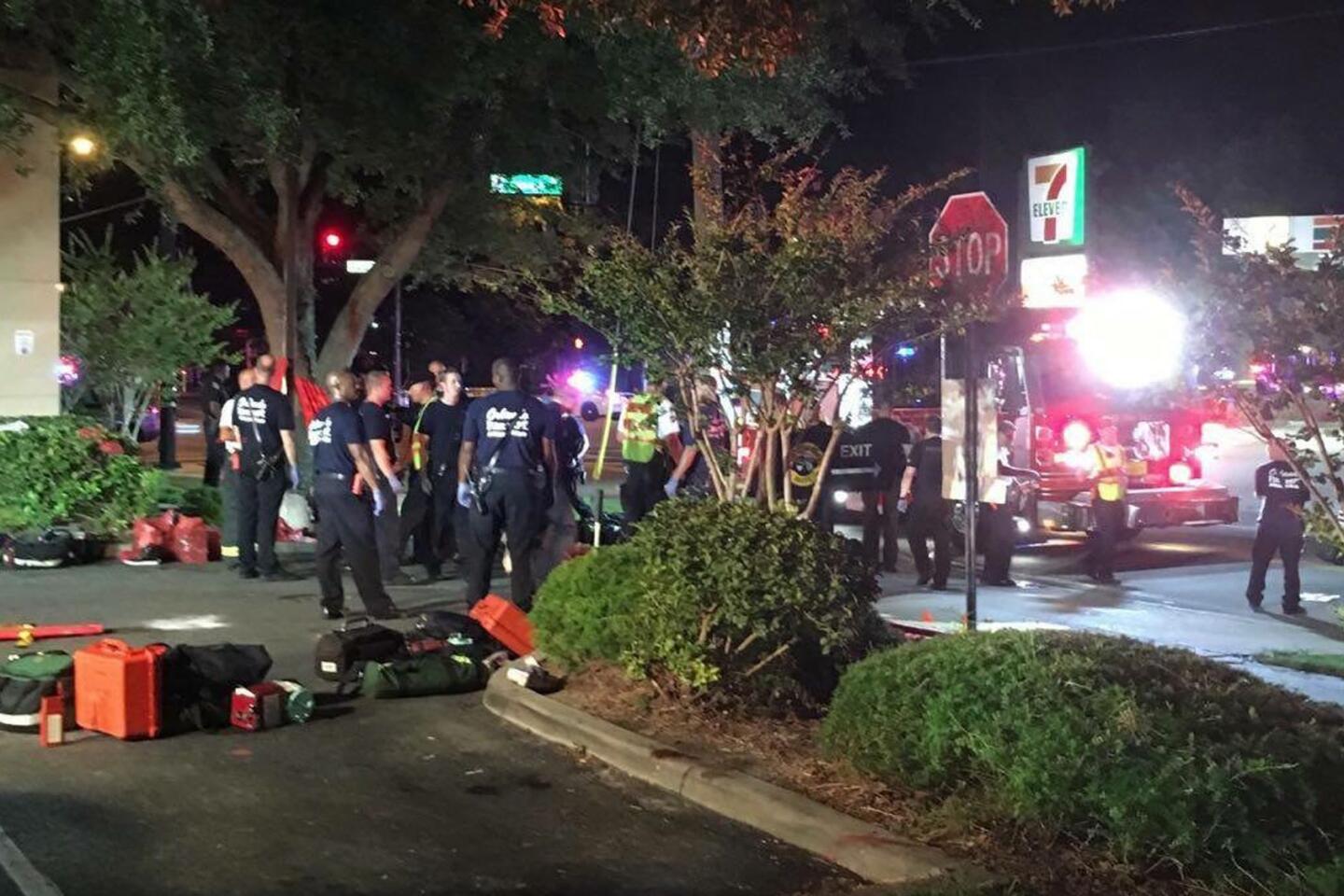
Emergency personnel at Orlando Regional Medical Center wait with stretchers for the arrival of victims from the fatal nightclub shooting.
(Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press) 73/81
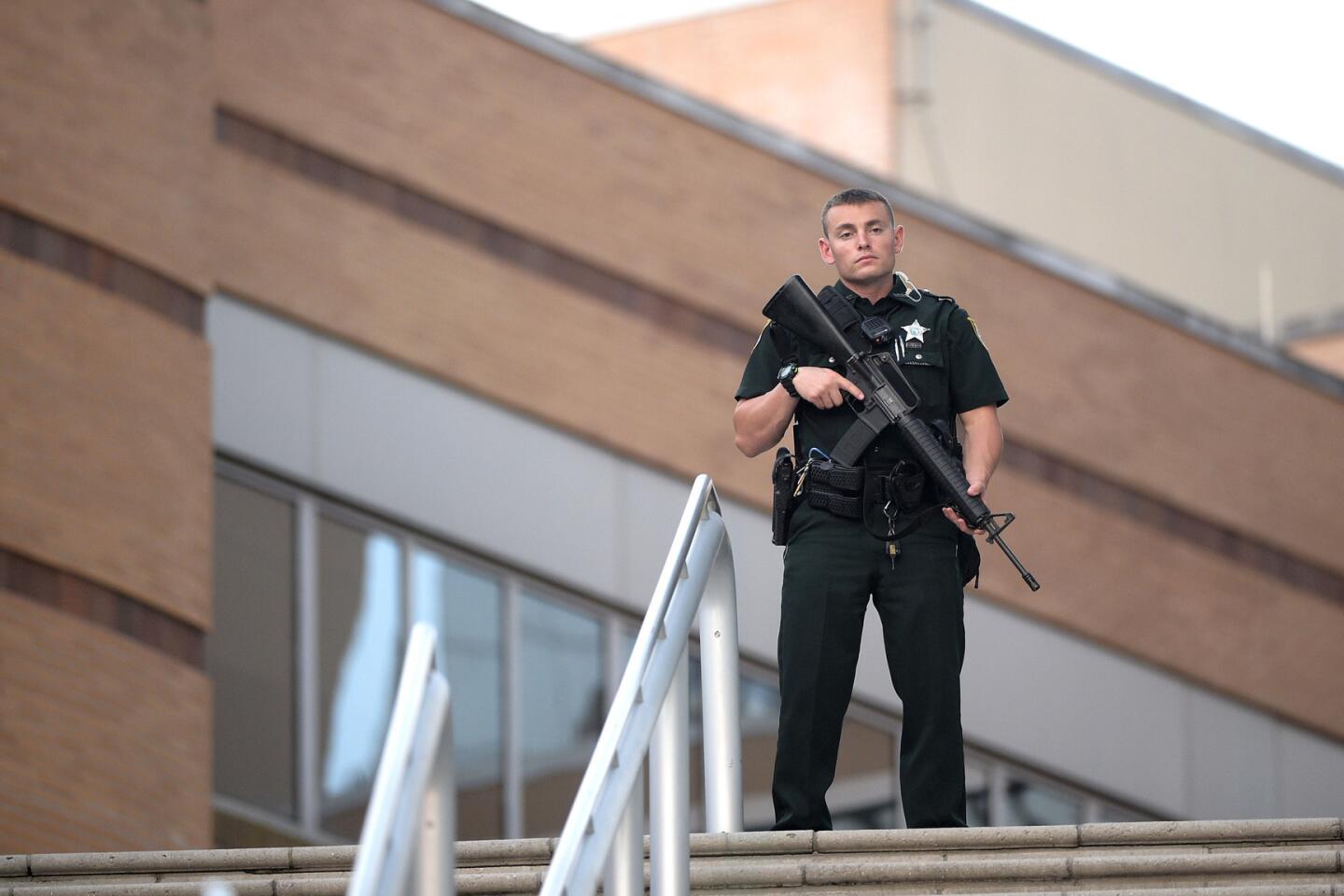
A police officer stands guard outside the Orlando Regional Medical Center after a fatal shooting at nearby Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla., on Sunday.
(Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press) 74/81
Law enforcement agencies and local city representatives speak at a news conference after 50 people were killed at the Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla.
(Jacob Langston / Orlando Sentinel) 75/81
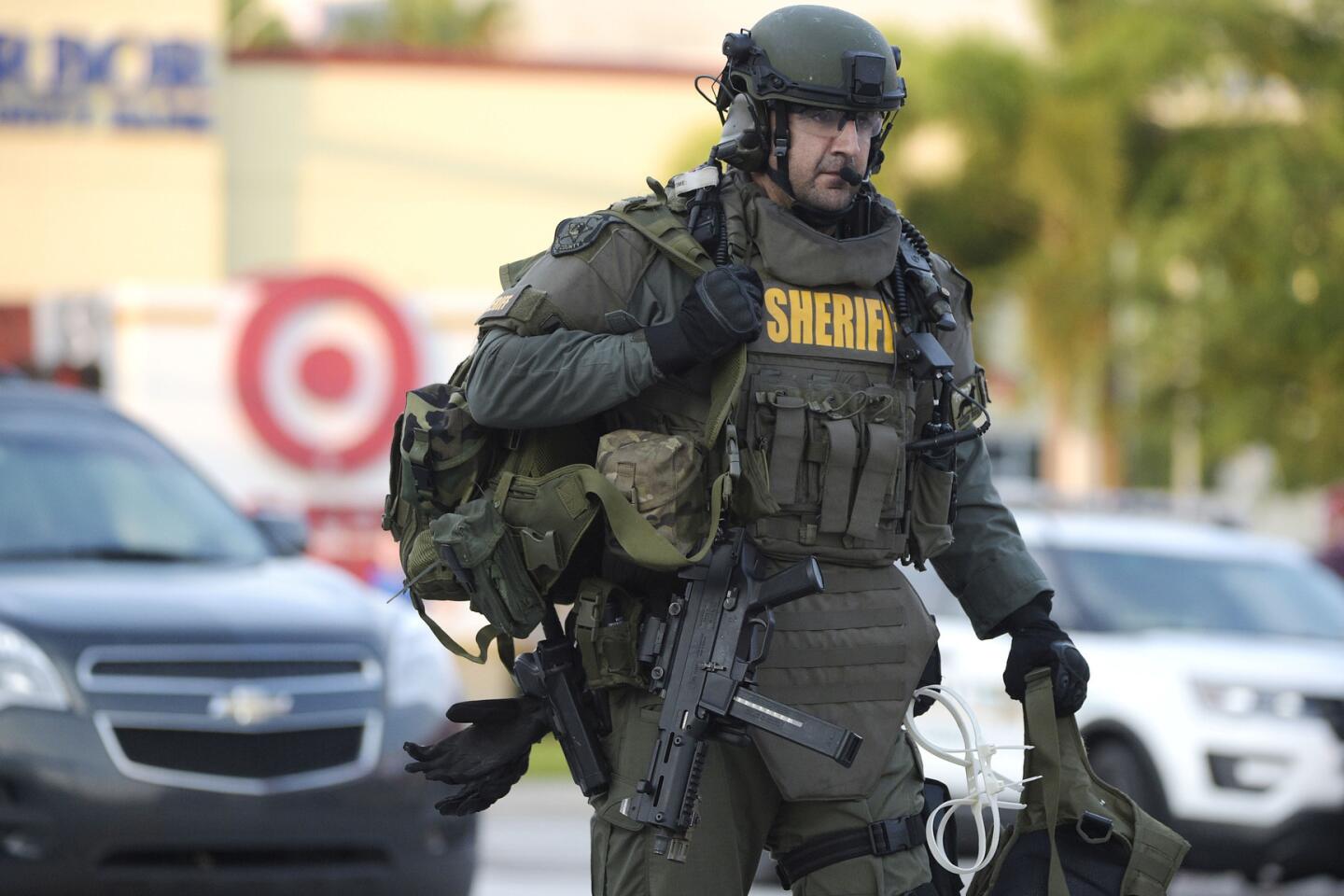
An Orange County (Fla.) Sheriff’s Department SWAT member arrives at Pulse nightclub.
(Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press) 76/81
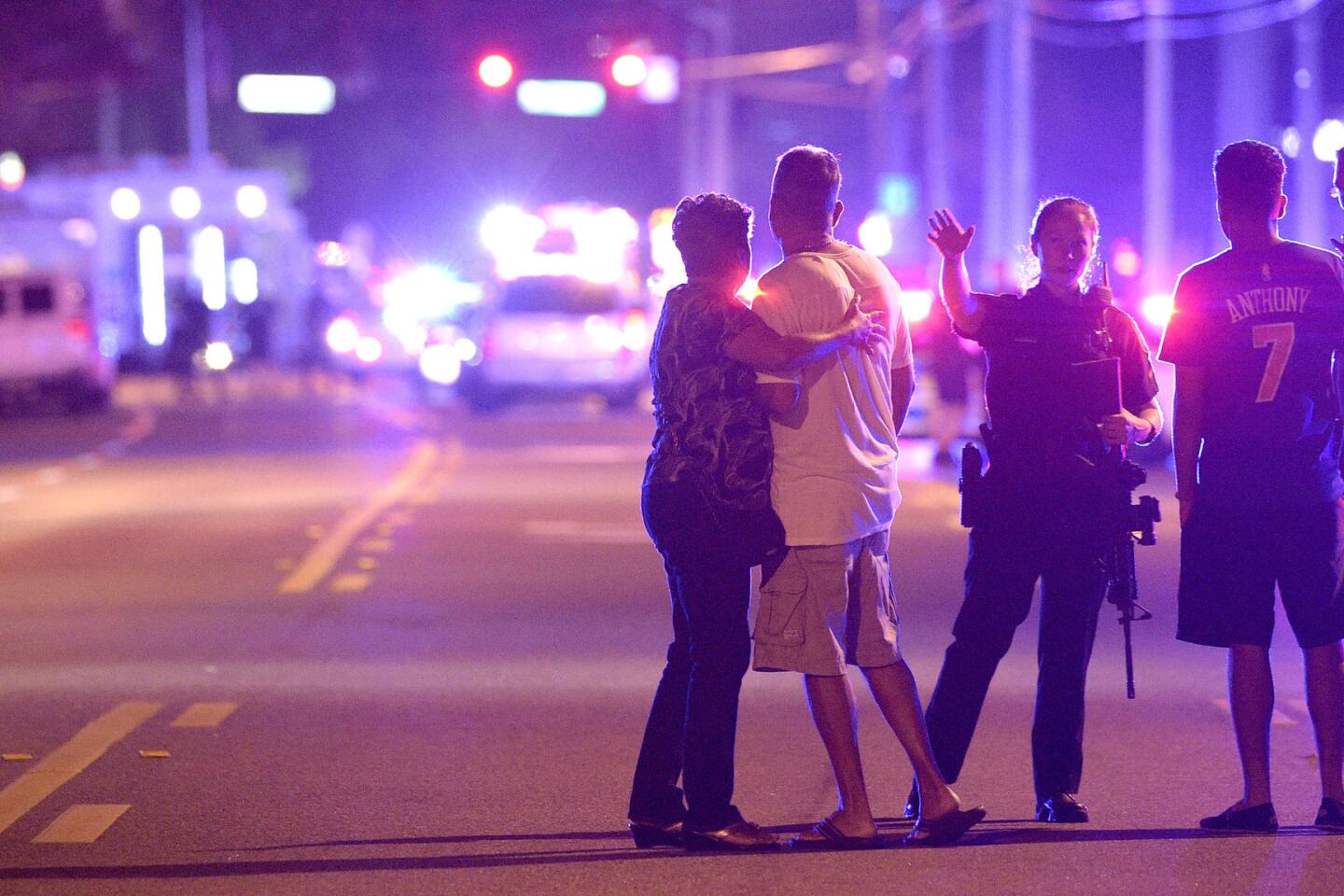
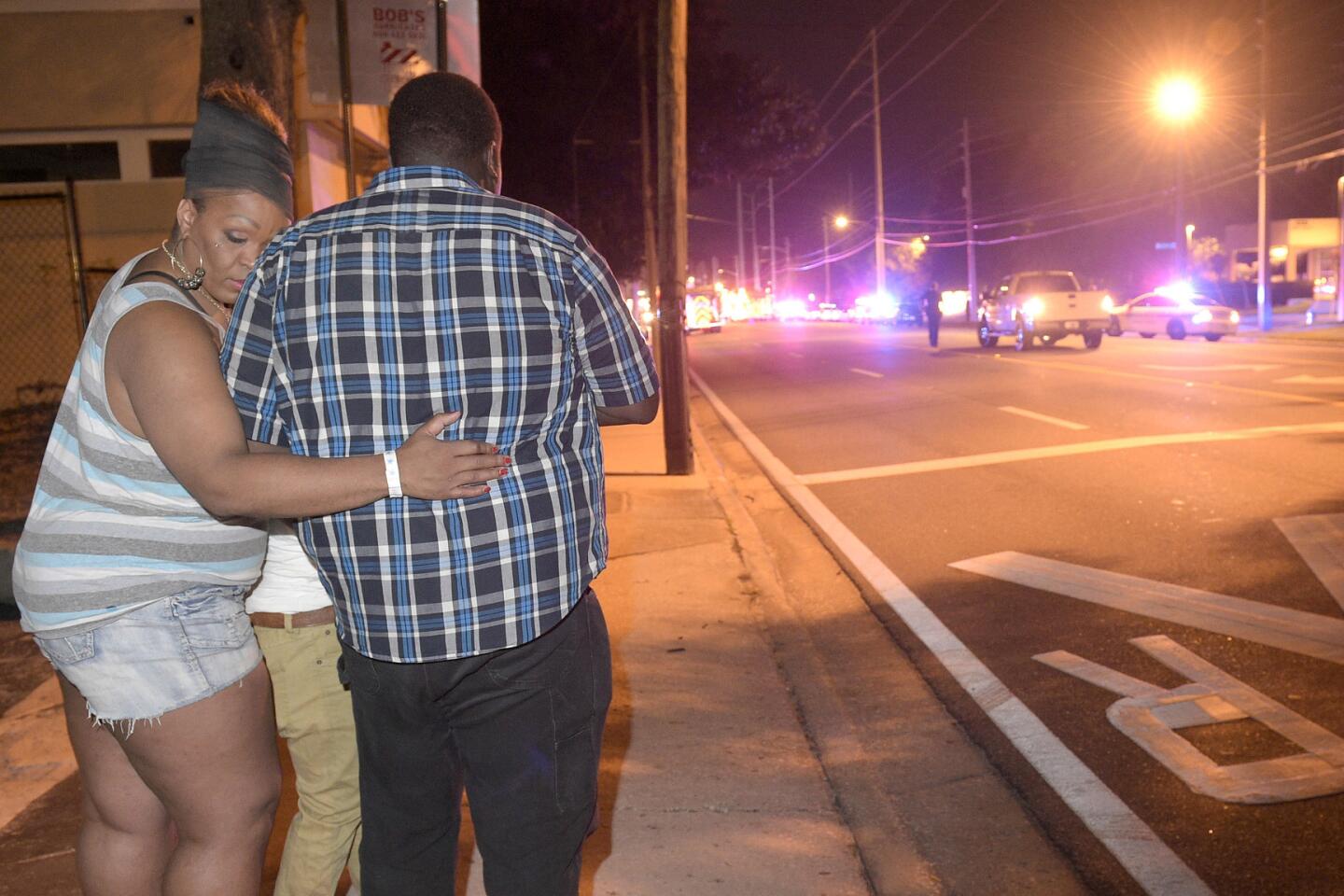
Orlando police direct family members away from the Pulse nightclub, where 50 people were killed.
(Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press) 77/81
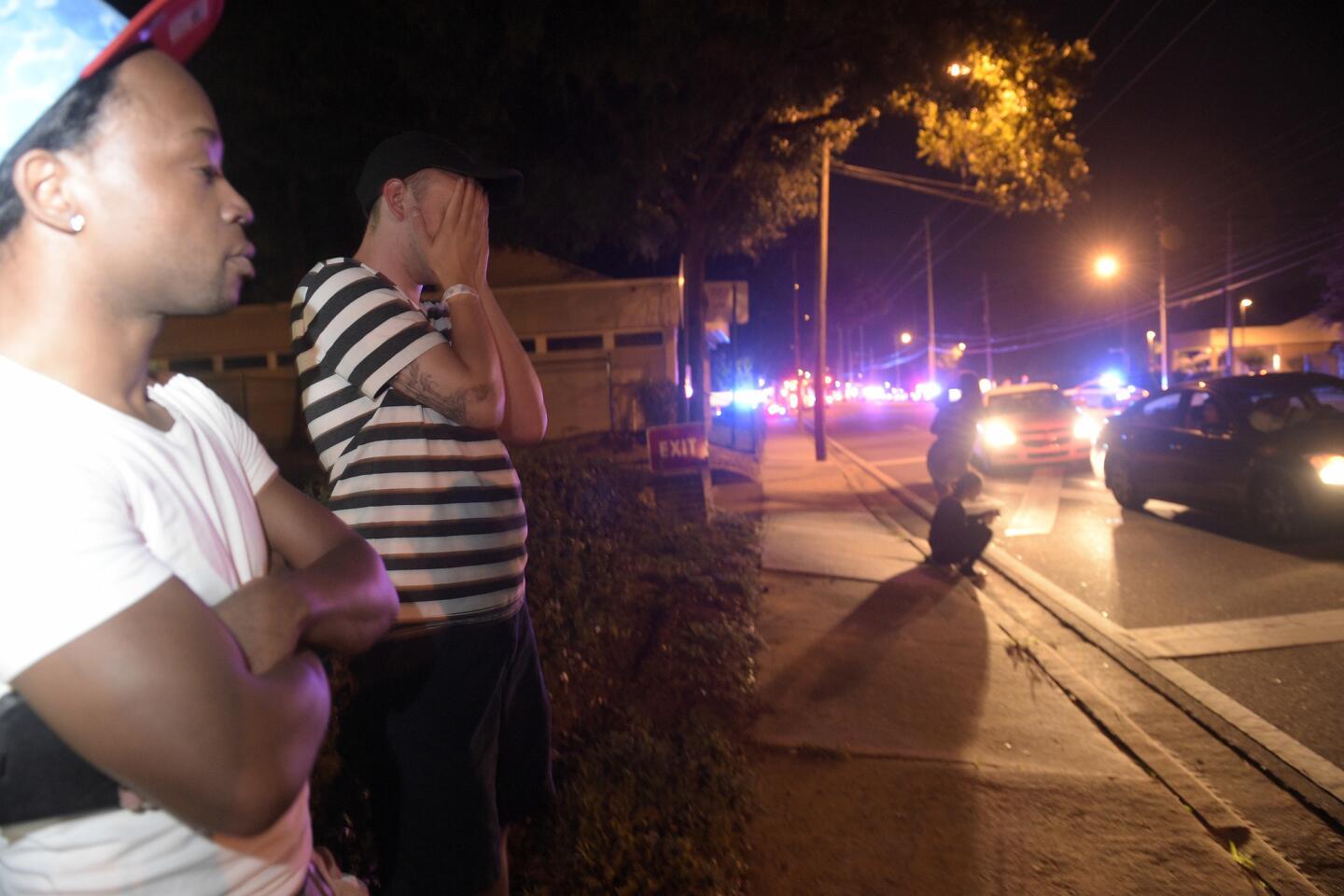
Jermaine Towns, left, and Brandon Shuford wait down the street from the Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla. (Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press)
78/81
Bystanders wait down the street after a mass shooting at the Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla.
(Phelan M. Ebenhack / Associated Press) 79/81
The scene outside Pulse nightclub in Orlando, Fla., after the shooting early Sunday.
(Univision Florida Central / EPA) 80/81
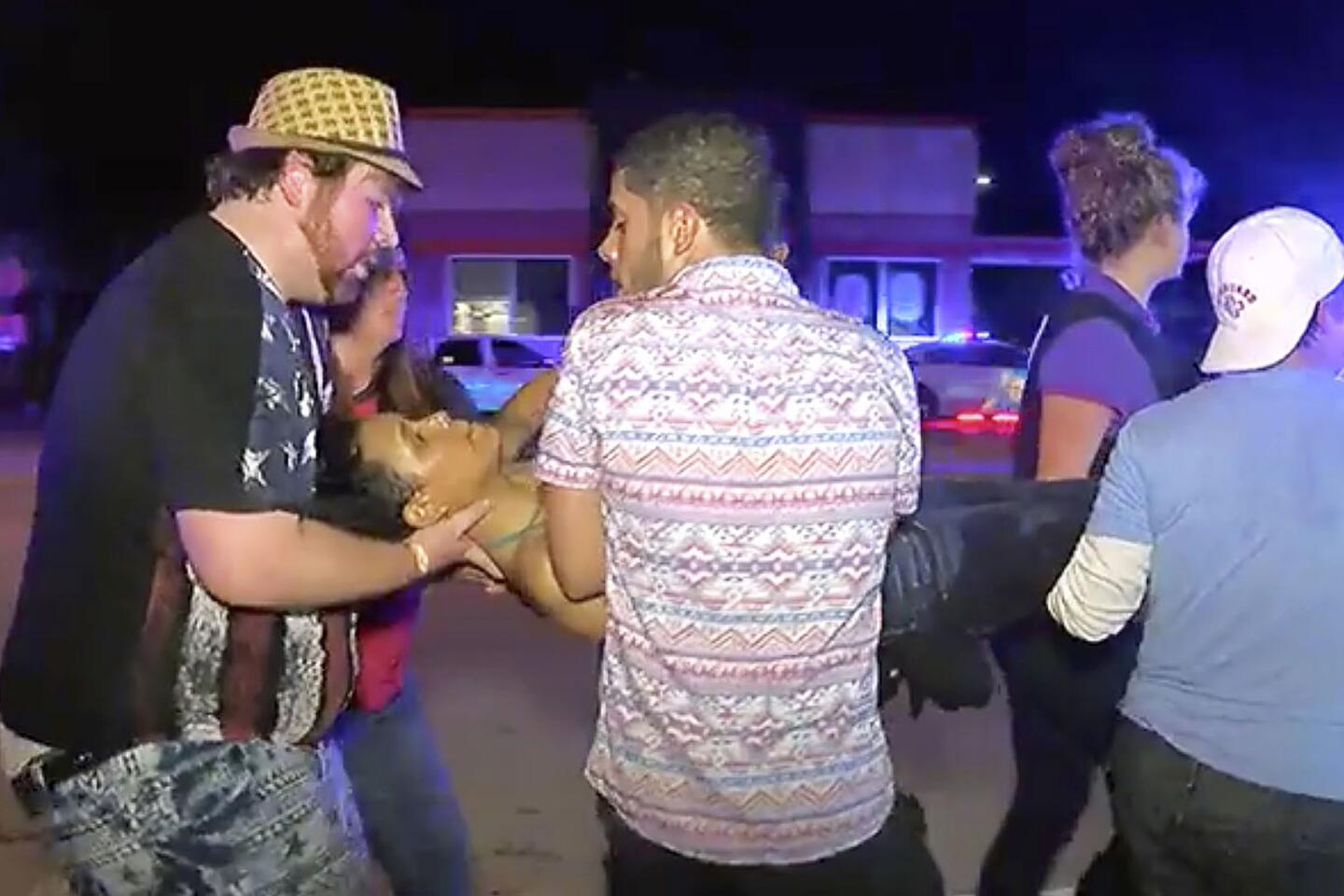
An injured person is escorted out of the Pulse nightclub after a shooting rampage Sunday morning in Orlando, Fla.
(Steven Fernandez / Associated Press) 81/81
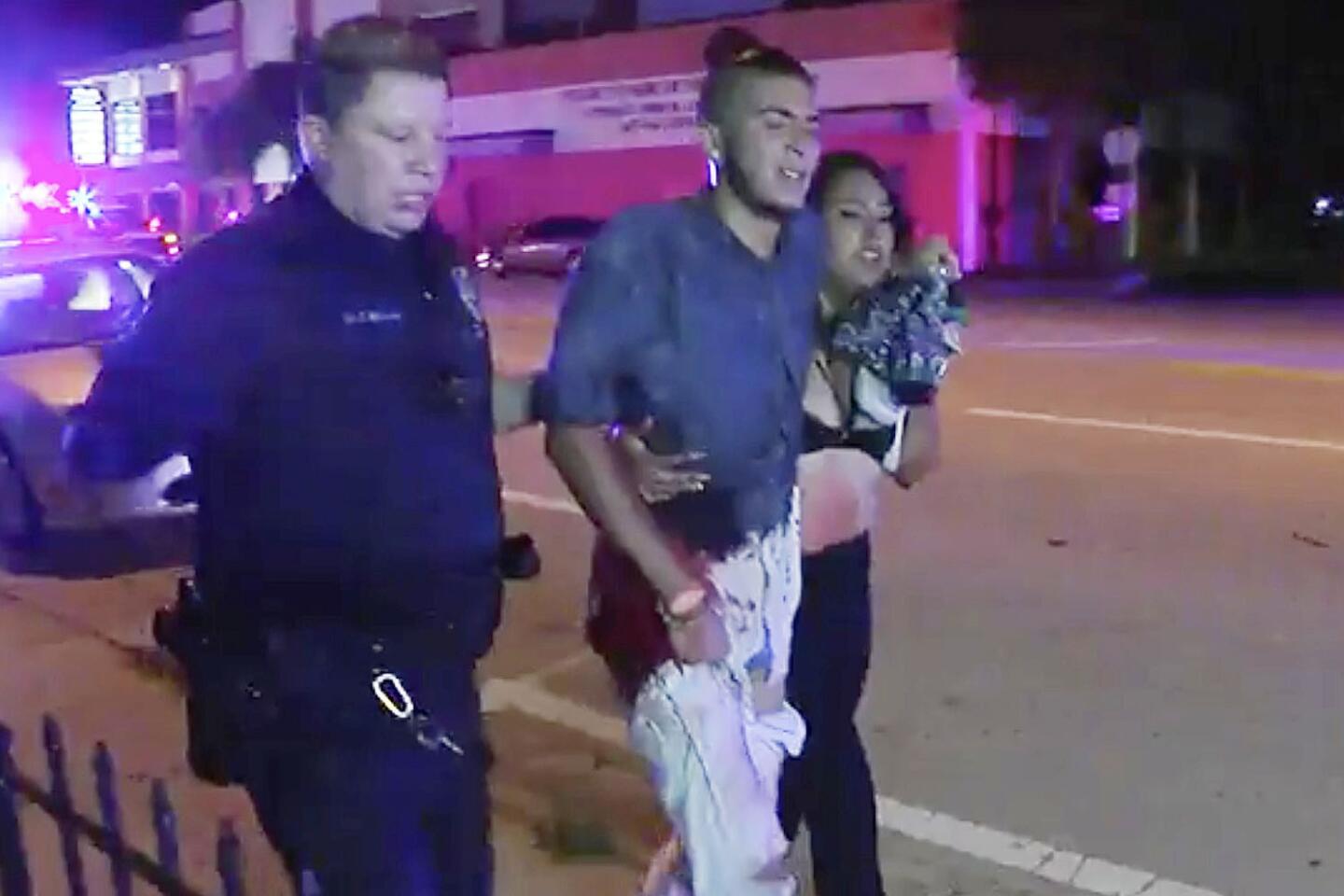
An injured man is escorted out of the Pulse nightclub after a shooting rampage Sunday morning in Orlando, Fla. A gunman with an assault-type rifle and a handgun opened fire inside a gay nightclub, killing at least 50 people before dying in a gunfight with SWAT officers, police said.
(Steven Fernandez / Associated Press) Still, she said the phenomenon has its limits, noting that mass shootings remain rare in Canada even though most people there live close to the U.S. border and are exposed to the same news coverage.
The difference, she suggested, could be that Canadians have more regulated access to firearms.
Much more research is needed to dissect the various factors that may be at work, she said.
With few formal studies on the role of the media, experts can only offer observations.
Jack Levin, a criminologist at Northeastern University in Boston who has tracked mass killings, said that beginning with Columbine there was a rash of school shootings that generated widespread media coverage.
The killings stopped abruptly after the terror attacks of Sept. 11, 2001, and did not resume for several months, he said. With the media focused on a story far bigger than any shooting, he said, “We robbed the copycat phenomenon of its inspiration.”
He also pointed to a trend of escalating death tolls in individual mass shootings, blaming the pattern on publicity-seeking.
“All these killers want the publicity,” he said. “They want to go down in infamy. Achieving the highest body count is one way to do that.”
“The media have not only a right but a responsibility to report the news,” Levin said. “The problem is the way the news gets reported. The emphasis is usually not on the victims but on the killer. … We make celebrities out of monsters.”
After the 2012 shooting at a movie theater in Aurora, Colo., some relatives of victims urged the media not to mention the shooter’s name. Colorado Gov. John Hickenlooper would only refer to James E. Holmes as Suspect A.
Some news figures have also complied with that wish.
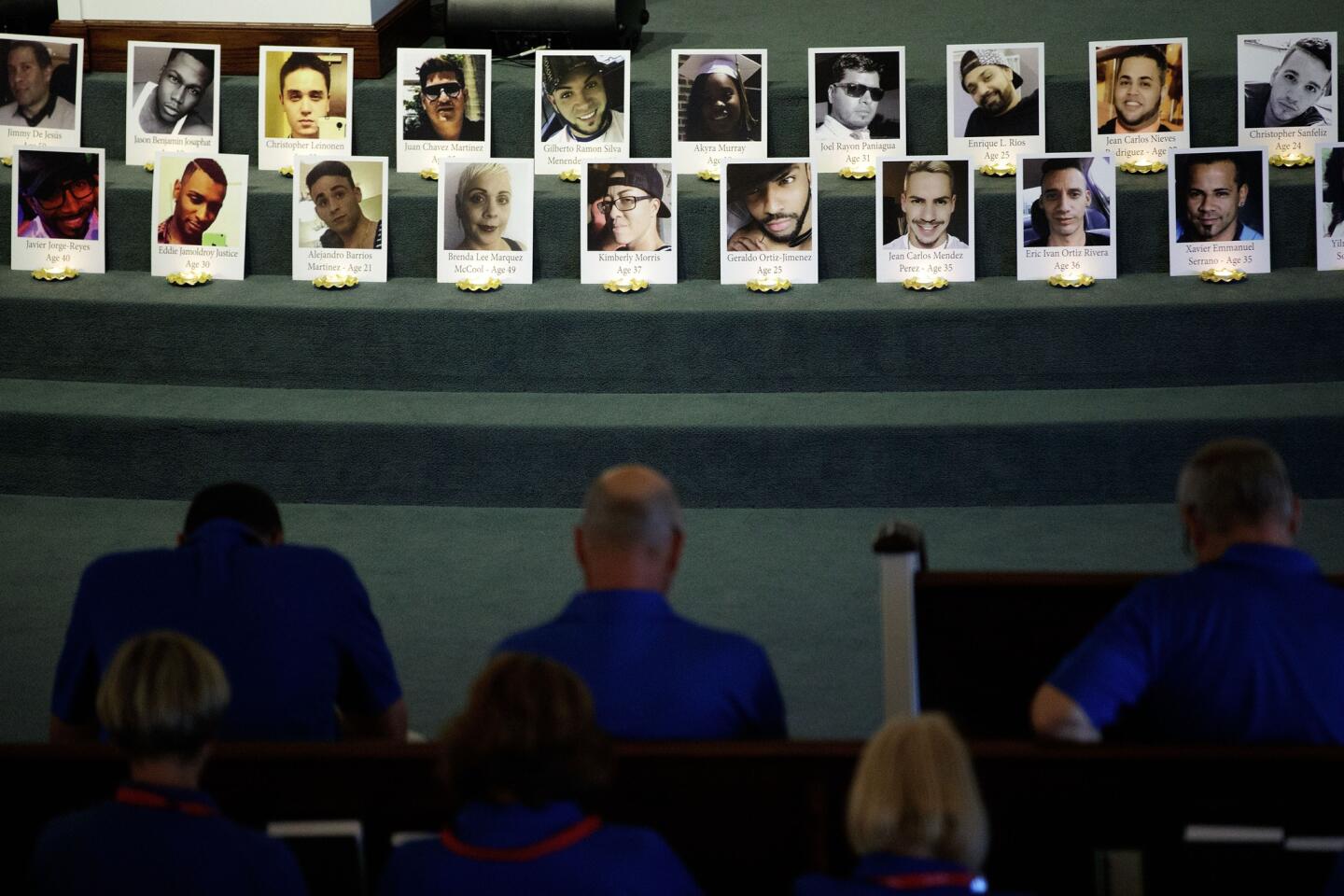
In a segment in which CNN’s Anderson Cooper read the names of the 49 people killed in Orlando, he said that out of respect for the dead the network would not air the name or photograph of their killer. Some officials have also refused to refer to Mateen by name at news conferences.
It is impossible to know if such gestures matter to potential killers — or if a blackout on naming shooters would slow the violence.
In any case, the rise of social media has given them — as it has everybody else — a platform to rapidly spread whatever messages they choose without the help of traditional media outlets.
Moments before he opened fire at the Pulse nightclub, Mateen went to his Facebook page and posted his political views and various threats and demands.
alan.zarembo@latimes.com
Times staff writer Molly Hennessy-Fiske contributed to this report.
ALSO
The worst mass shooting? A look back at massacres in U.S. history
Here’s who the major networks are sending to Orlando for mass-shooting coverage
The AR-15-style rifle: a popular seller tainted by mass murder