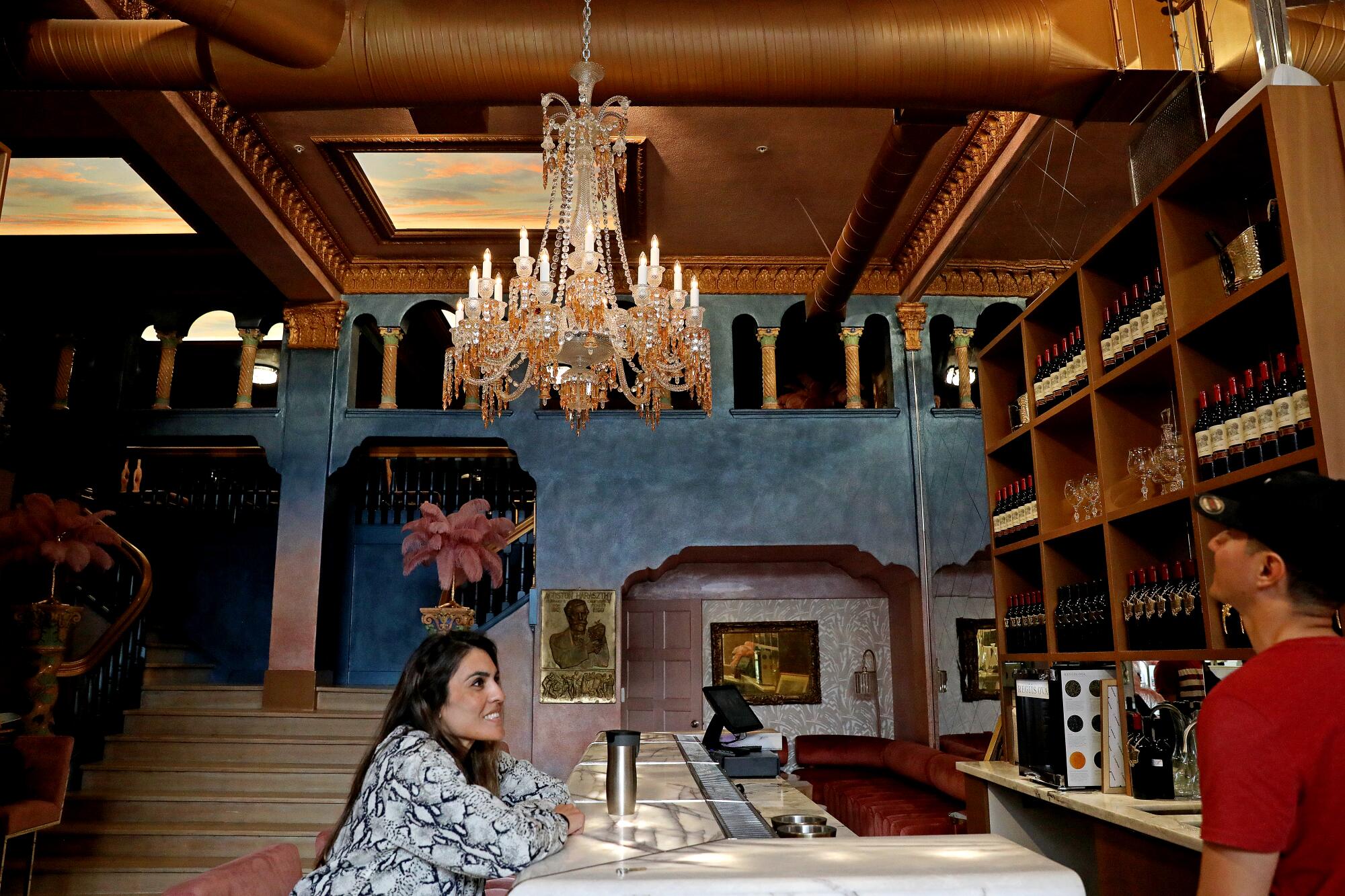
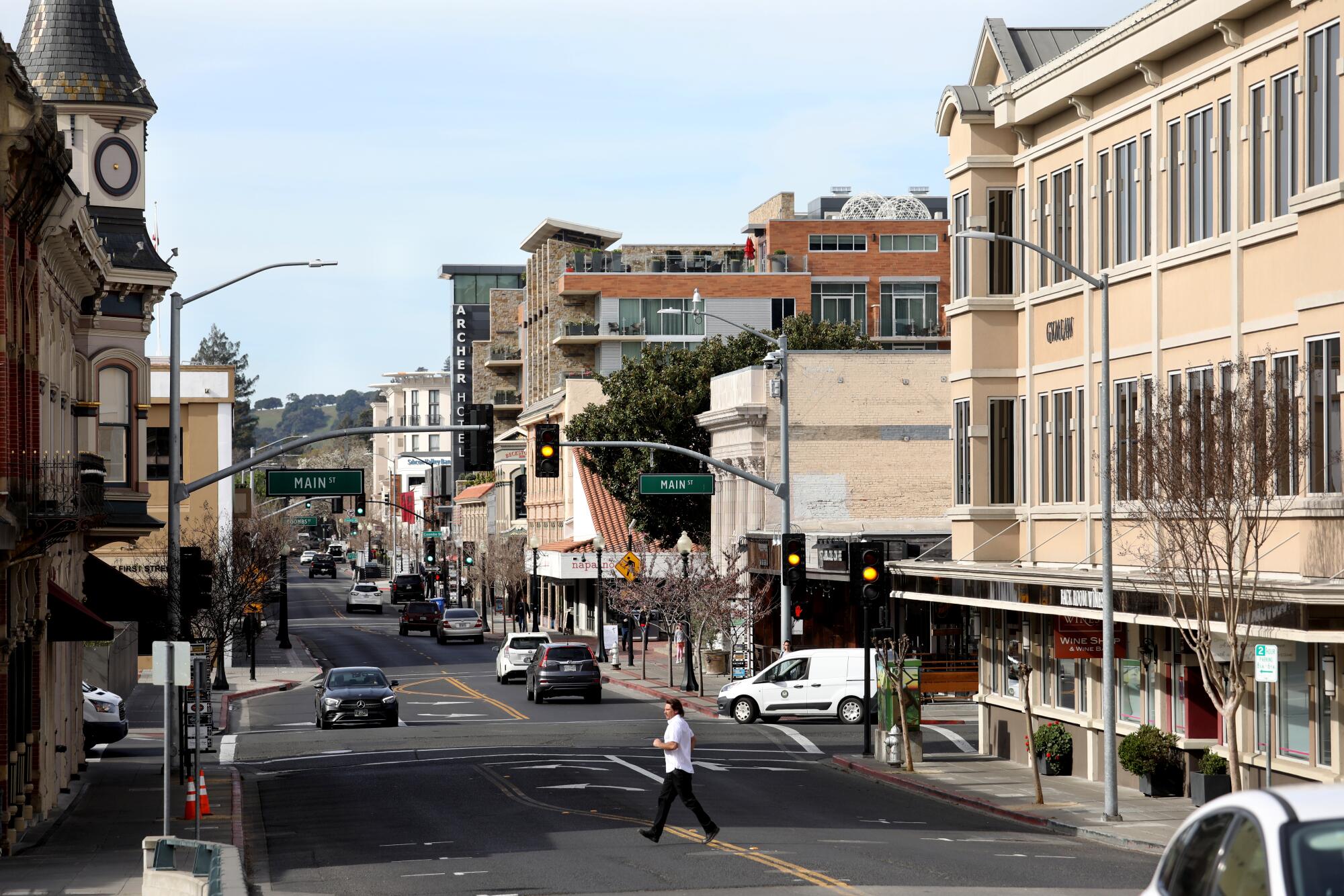
NAPA, Calif. — The Buena Vista tasting room is not just another downtown Napa wine bar.
It is a conspicuously indulgent place, where epicureans can fill their glasses with cabernet and sink into the carefully restored mezzanine’s dark velvet lounges for a tasting of fine caviar and artisan chocolates resembling museum pieces.
One vibe this nook of luxury does not give off is that of a community in distress. Its neighbor in the ornate 1920s Italianate edifice known as the Gordon Building is an Anthropologie store.
The redevelopment of the building, damaged in an earthquake, was bankrolled using a tax shelter created in 2017 for the wealthiest Americans on the promise it would bring opportunity to the most downtrodden places.
Billions of dollars’ worth of tax breaks for the wealthy are being generated by the Opportunity Zone program, often in pursuit of luxury high-rises, high-end hotels and swank office space. It has subsidized hulking self-storage units nestled alongside freeways and upmarket apartments for employees of the hottest Bay Area tech firms.
One thing the tax break has fallen short on: creating opportunities in low-income communities.

Opportunity zones were supposed to encourage investment in low-income communities. But billionaires are building luxury hotels and high-rises, instead.
“This has been perverted into a huge gift for people who did not need it,” said Aaron Seybert, managing director of social investment at the Kresge Foundation, which has found it difficult to put the tax break to work toward its effort to bring opportunity to America’s struggling communities.
“They are spending my money and yours. They said they would do that because these low-income areas are falling behind and they want to help people who live there,” Seybert said.
“The places I work in every day have raised virtually nothing” through the program, he said.
Electric cars, climate credit schemes, diverse boardrooms and legal weed: How California exports its ideas and policies across the U.S.
The same grievance can be heard from mayors of struggling towns throughout the nation. Among those declaring the program a bust is the East Baltimore pastor who went to the White House in 2018 to help President Trump unveil it. His community has been passed over as investors chase the double-digit returns that accompany the tax shelter in upscale markets.
The story of how this all happened has deep California roots, sprouting from the vision of a Silicon Valley billionaire who inserted himself into the machinations of federal policymaking.
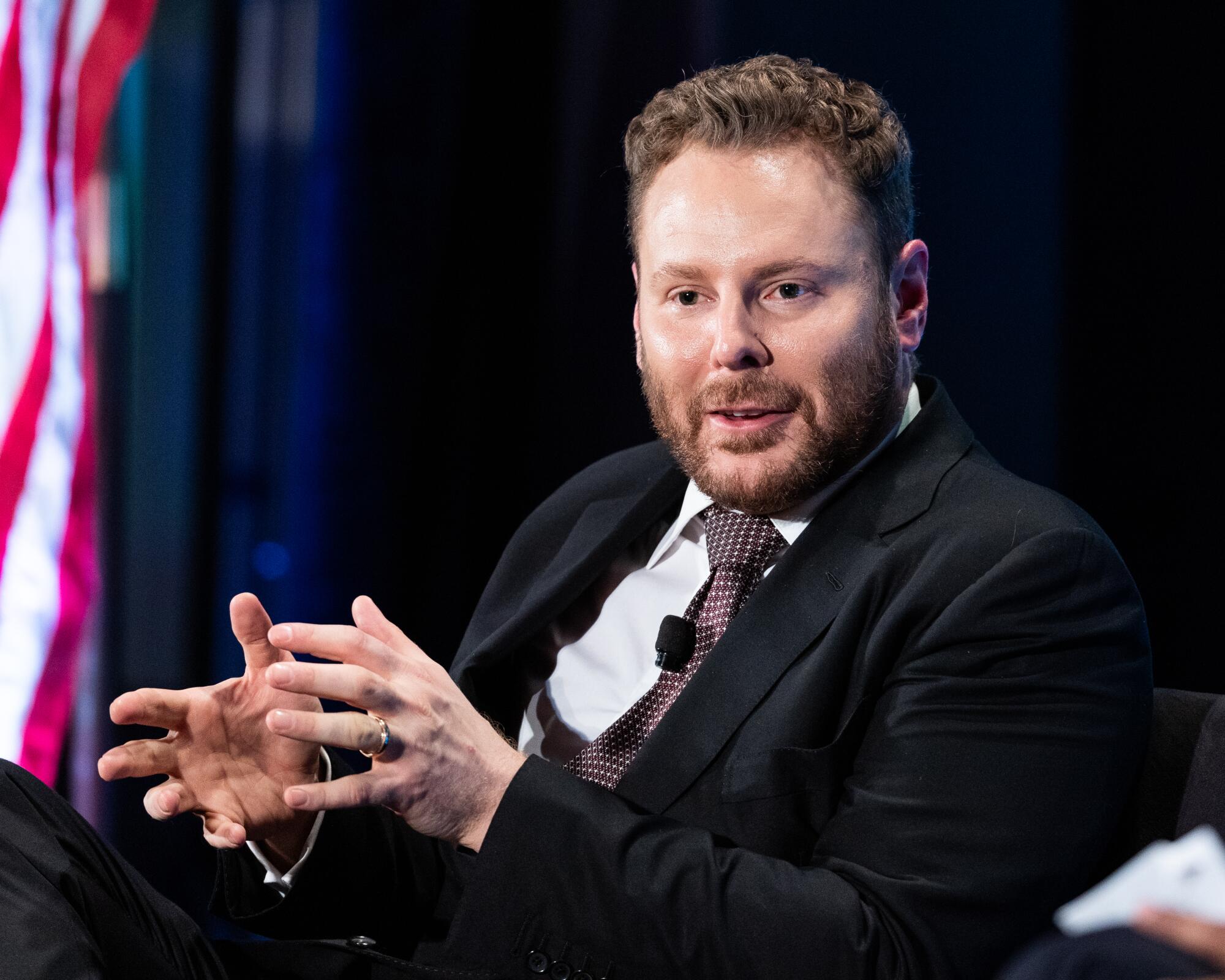

Sean Parker — founder of Napster, Facebook’s first president and the Silicon Valley bad boy depicted in the film “The Social Network” — seemed a stretch for this role.
Parker began working the Washington circuit late in the Obama era, when it was still hospitable to super-rich tech innovators but few had the patience or humility to navigate it. Washington is not about moving quickly and breaking things. Long, slow insider games of horse-trading precede almost every big new federal policy.
Yet Parker’s plan had bipartisan appeal. It focused on the wealth of Americans loath to reinvest their stock market, real estate and other capital gains profits because of the hefty tax bills that come when that money is moved. The idea was to give them a break on those taxes if they steered the money to communities desperate for investment.

Subscribers get exclusive access to this story
We’re offering L.A. Times subscribers special access to our best journalism. Thank you for your support.
Explore more Subscriber Exclusive content.
“He really went to school on how Washington works,” said David Wessel, author of “Only the Rich Can Play: How Washington Works in the New Gilded Age,” which chronicles Parker’s quest and what became of the program he championed. “He hired a couple of Washington insiders, one a Democrat and one a Republican, and they created this think tank with the goal of getting Opportunity Zones into law…. They laid the foundation by making the case that we have a problem with geographic inequality in the United States, and it is not just incremental.”
Parker held private dinners with lawmakers of competing ideological loyalties, and he donated generously across the aisle.
“The idea initially sounded great,” said Rep. Ro Khanna, a Silicon Valley Democrat who had been approached by Parker to run the think tank, called the Economic Innovation Group. “I was quite enthusiastic about it.” Khanna passed on the job offer, as he was gearing up for a congressional run at the time, but once elected, he would join the push behind the tax break.


It allows investors to park their capital gains in Opportunity Zone projects. When they do, they can put off paying taxes on those gains for years, and cut that tax bill by as much as 15% when it does come due. The bigger draw: If they keep their money in the Opportunity Zone project for a decade, they don’t pay any taxes at all on the potentially large profits they make off that investment. The cumulative cost of the incentive is $1.6 billion in foregone tax revenue per year, which the Urban Institute says makes it one of the largest federal programs for steering investment into distressed places.
It seemed a price worth paying for even some progressive Democrats like Khanna if the end result was a flourishing of opportunity in the nation’s economic deserts.
But the California dreaming was disrupted by Washington deal-making. There was no hearing or any public vetting of the measure by lawmakers before it got quietly tucked into the Trump tax cut package of 2017. The final regulations were astoundingly permissive, full of provisions that allowed census districts in some of the nation’s wealthiest places to qualify as Opportunity Zones.
“It has not been used in ways that actually ended up creating jobs,” Khanna said. “It has been gamed.”
California had a plan for the government to do your taxes for you. Tax software firms led by Intuit worked to kill it. Why it’s getting another look in Washington.
The money often has flowed to projects promising big financial returns that analysts — including those on then-President Trump’s Council of Economic Advisors — conclude would have happened without the tax break.
While Parker and his think tank remain bullish that with some tweaks Opportunity Zones will be the “Marshall Plan for the heartland” they promised, many erstwhile backers are angry about what the program has become.
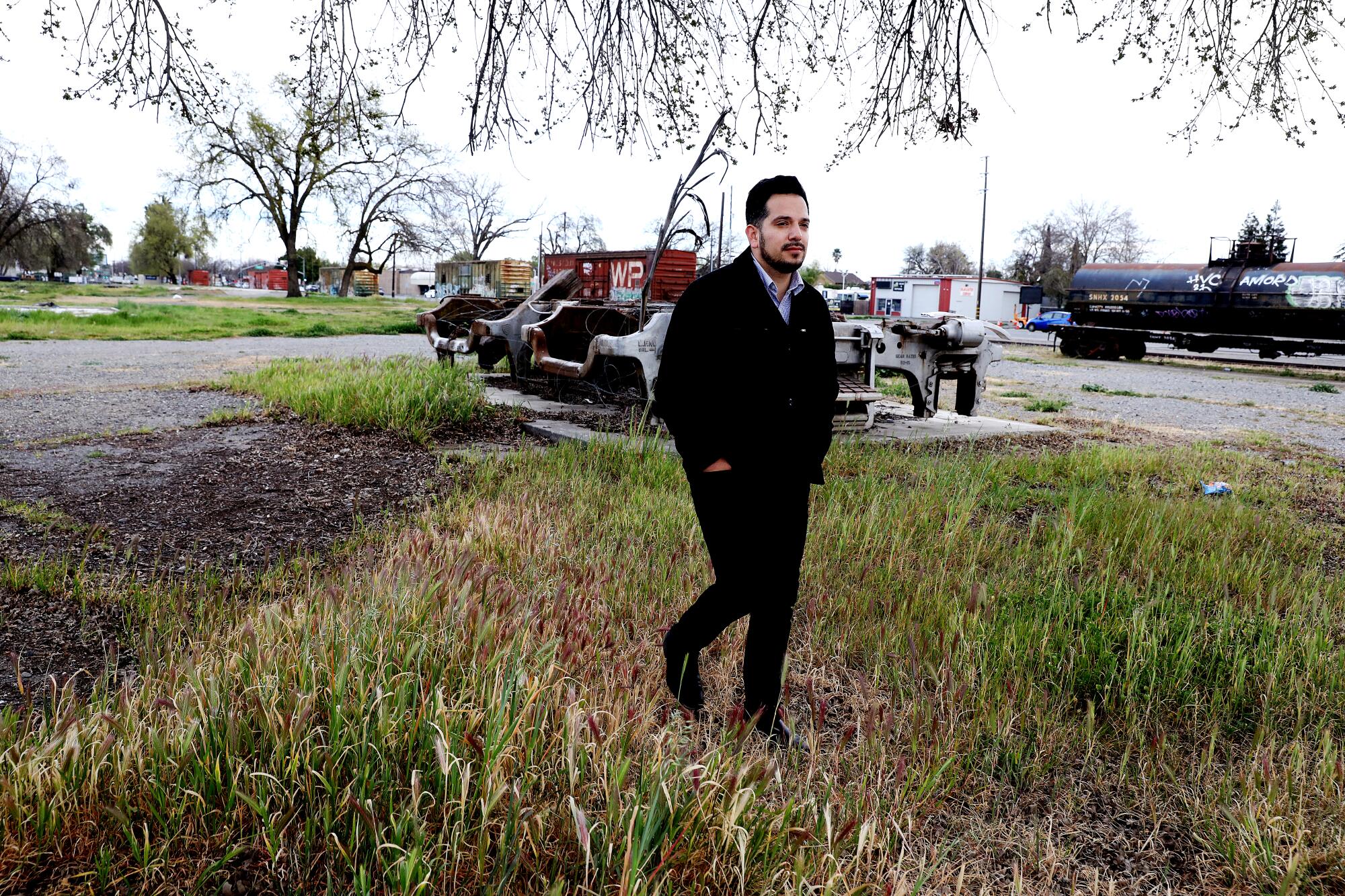

“Woodland needs housing, it needs infill development,” said Enrique Fernandez, the former mayor of the heavily Latino city west of Sacramento, which persuaded the state to designate two of its census tracts as Opportunity Zones. The tax break has drawn none of it.
“I am really skeptical about the true intentions of this law and how it was implemented,” Fernandez said.
The city of Woodland’s Opportunity Zone district is only an hour’s drive from Napa’s Gordon Building but is in a different universe economically, riddled with vacant lots and litter. It could be a ripe canvas for development as the nearby main street comes alive with new small businesses bolstered by home buyers and renters moving to the town in search of a cheaper alternative to Sacramento, but the tax break is doing nothing to speed that transition.
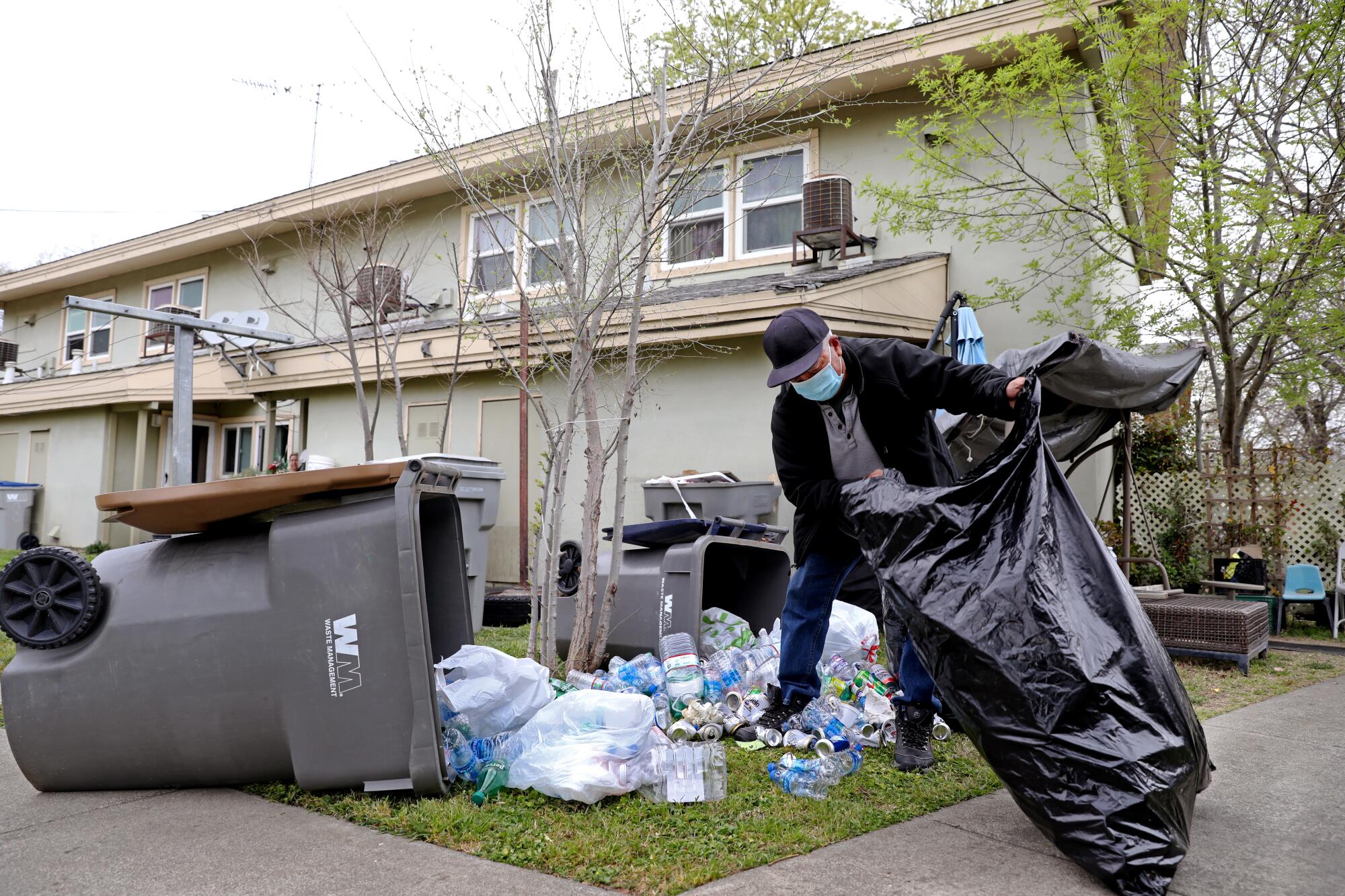

On a recent tour of the area, local officials said the investment needed to revitalize the blighted swaths of their community might have come if lawmakers had made good on their promise to steer the incentives only to struggling communities.
There are 8,764 census tracts designated as Opportunity Zones nationwide. Only 16% of them attracted any projects in the gold rush for rich investors in the program’s first year, when the tax breaks were most lucrative, according to an April 2021 UC Berkeley report based on aggregate data from the IRS.
Nearly half the cash invested went to the richest 1% of Opportunity Zones — places that rarely fit the conventional definition of distressed. Data from the consulting firm Novogradac reveal California cities are getting more of that cash than anyplace else.
In Oakland, Opportunity Zone tax breaks are being used to build high-rise apartments on the waterfront; they’ll rent at market rate, far out of reach for most locals. The situation is the same in downtown Long Beach and in Los Angeles neighborhoods like Koreatown and Little Tokyo. In Portland, Ore., the tax break was used to build a Ritz Carlton hotel.
In January, Senate Finance Committee Chair Ron Wyden (D-Ore.) launched an investigation into several of these projects, including one in Palm Beach, Fla., where the incentive is being used to build a marina for “super-yachts.”


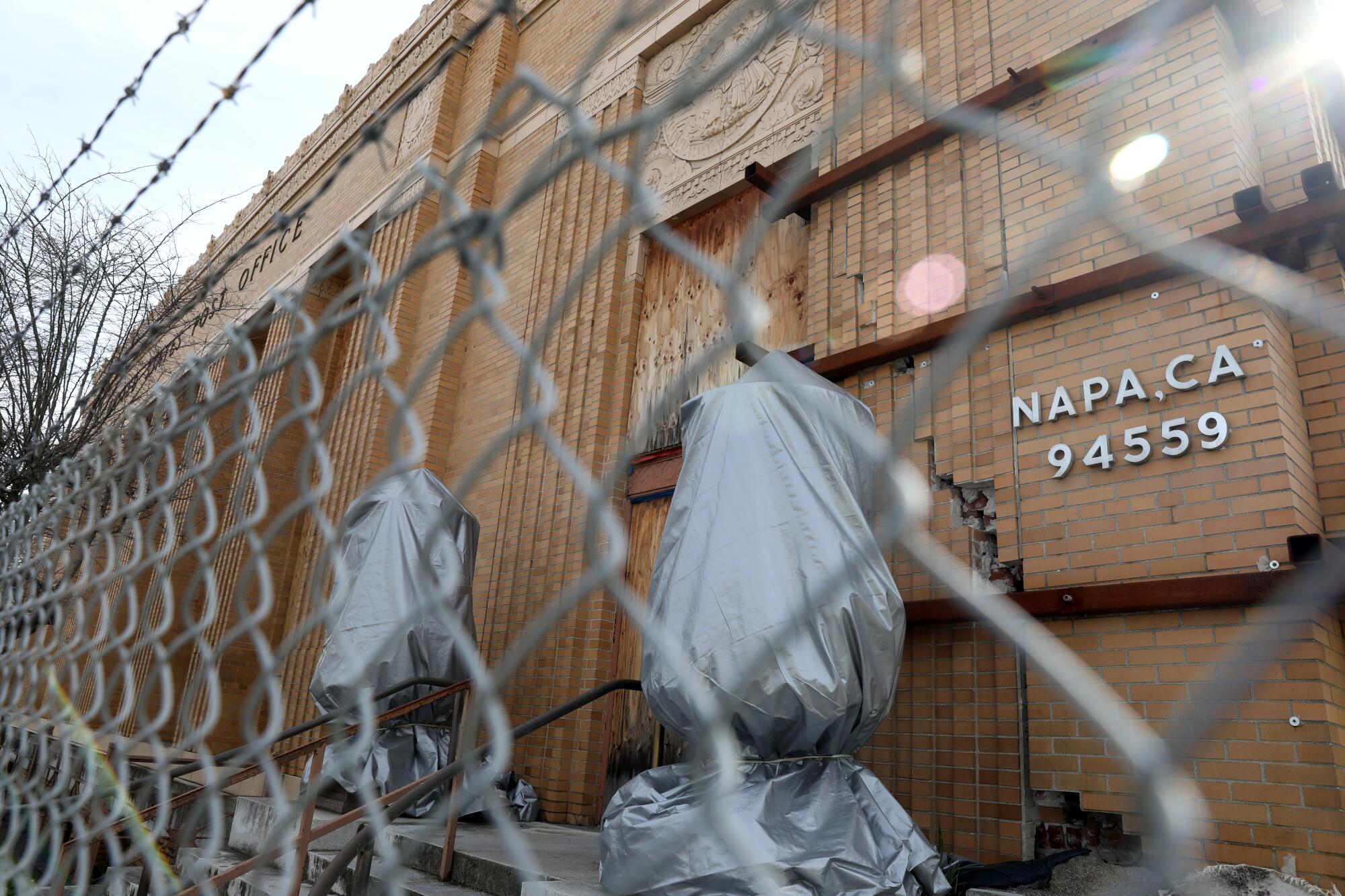
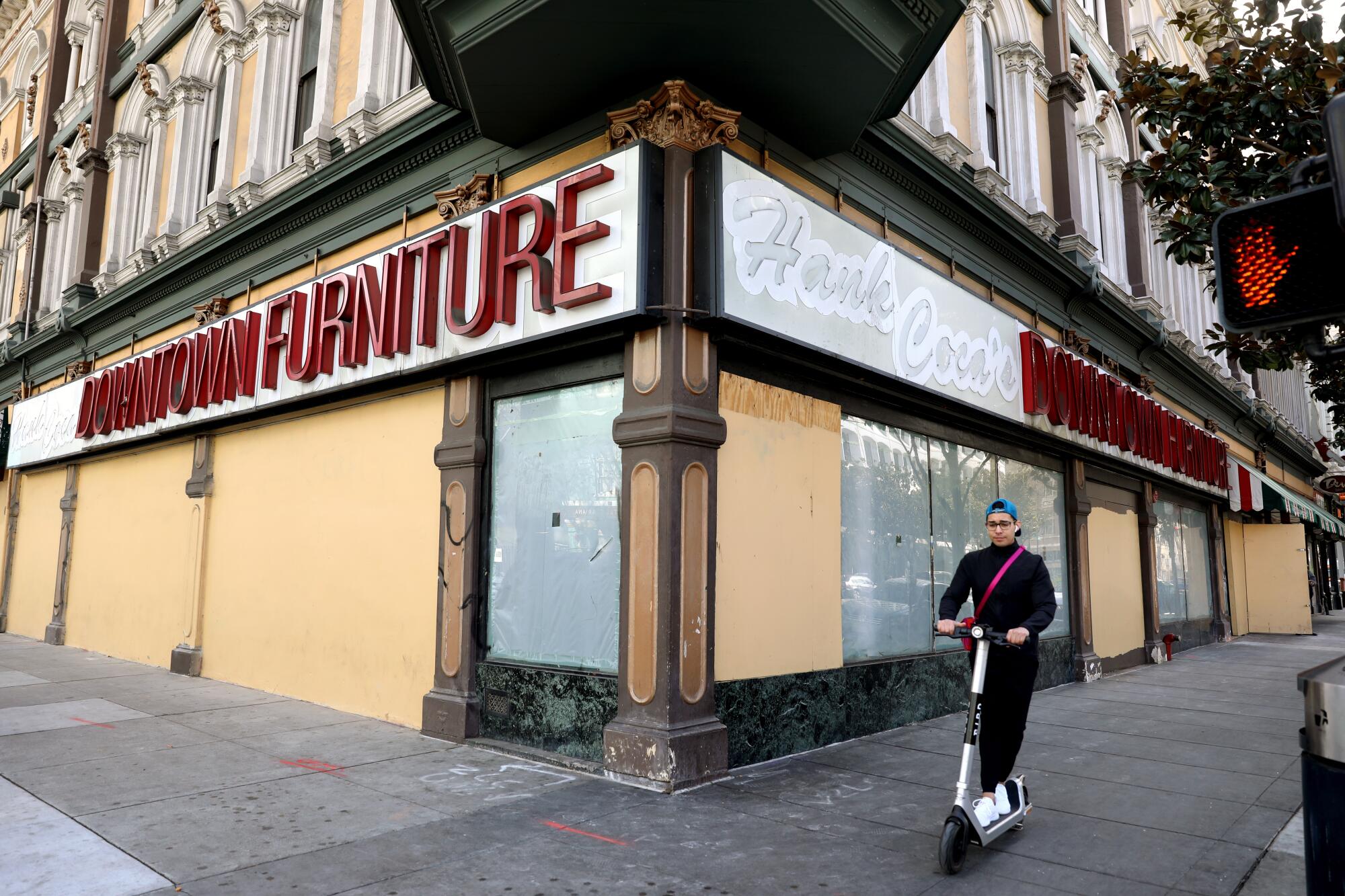
Back in Napa, the developer of the Gordon Building said the project will spur growth in a part of Northern California where underlying challenges of joblessness and housing affordability are obscured by the influx of wine vacationers. “We have some of the wealthiest in the country, and we have some of the poorest in the country,” Todd Zapolski said.
The landmark building was badly damaged in the 2014 South Napa earthquake, and Zapolski said repairing it was possible only because of the Opportunity Zone sweetener.
“We couldn’t make it work unless we had that incentive,” he said. “That gave us the extra oomph for investors to say, all right … we’ll take the risk.”
Parker declined to be interviewed, but the leader of the think tank he created took issue with scathing reviews of the program from community leaders, advocates and lawmakers who once saw promise in it. John Lettieri, president and chief executive of the Economic Innovation Group, said layering too many rules and restrictions onto the incentive would chase away investors.
“The trick is to get them to redeploy their capital without having to jump through bureaucratic hoops that would make it hard to access and leave communities in the same place they have been,” he said. “We were trying to create an incentive that can be relevant enough to a wide array of communities nationwide.”
States had broad authority on where to locate their Opportunity Zones, Lettieri said, and some were not judicious in drawing the maps. He said California, which drew the zones into some of the nation’s most wealthy enclaves, was one of the worst offenders.
Climate credits sold to California polluters bring billions to landowners. But scientists ask if that’s an environmental investment or a Ponzi scheme.
California officials were not particularly invested in the federal program, which the Trump administration gave states scant time to shape or vet before they had to draw maps. The administration of then-Gov. Jerry Brown initially proposed an expedient process involving an algorithm. The federal rules were so permissive that the state’s draft maps included the campus of Stanford as an Opportunity Zone.

Stanford and some others were removed from the program, but other pricey ZIP Codes stayed in amid lobbying by local politicians, economic development agencies and builders.
But the state’s ambivalence about Opportunity Zones is clear in its refusal to match the federal tax break with a credit investors in the projects can also claim on their state taxes. Officials in Gov. Gavin Newsom’s administration signaled to developers they believe the tax break is a giveaway. New York lawmakers gave their own vote of no confidence after the tax break was put to use for luxury projects in some of New York City’s most expensive ZIP Codes. The tax shelter last year was stripped from New York’s tax code.
Even so, there are cases of truly distressed communities making use of the credit.
An organization called SoLa Impact says it is leveraging the incentive to buy run-down residential properties in underserved neighborhoods of South Los Angeles and rehabilitate them for low-income tenants.
No state has had a bigger impact on the direction of the United States than California, a prolific incubator and exporter of outside-the-box policies and ideas. This occasional series examines what that has meant for the state and the country, and how far Washington is willing to go to spread California’s agenda as the state’s own struggles threaten its standing as the nation’s think tank.
Before he was slain, Los Angeles rap star Nipsey Hussle had plans to use it to invest in businesses in Crenshaw. The Central Valley city of Merced is looking to the tax break to bring its downtown back to life.
The place boosters point to most often is across the country in Erie, Pa., a city that is emblematic of the Rust Belt’s economic collapse. Community leaders say the incentive is crucial to the development of 12 residential and retail projects that will reshape the downtown.
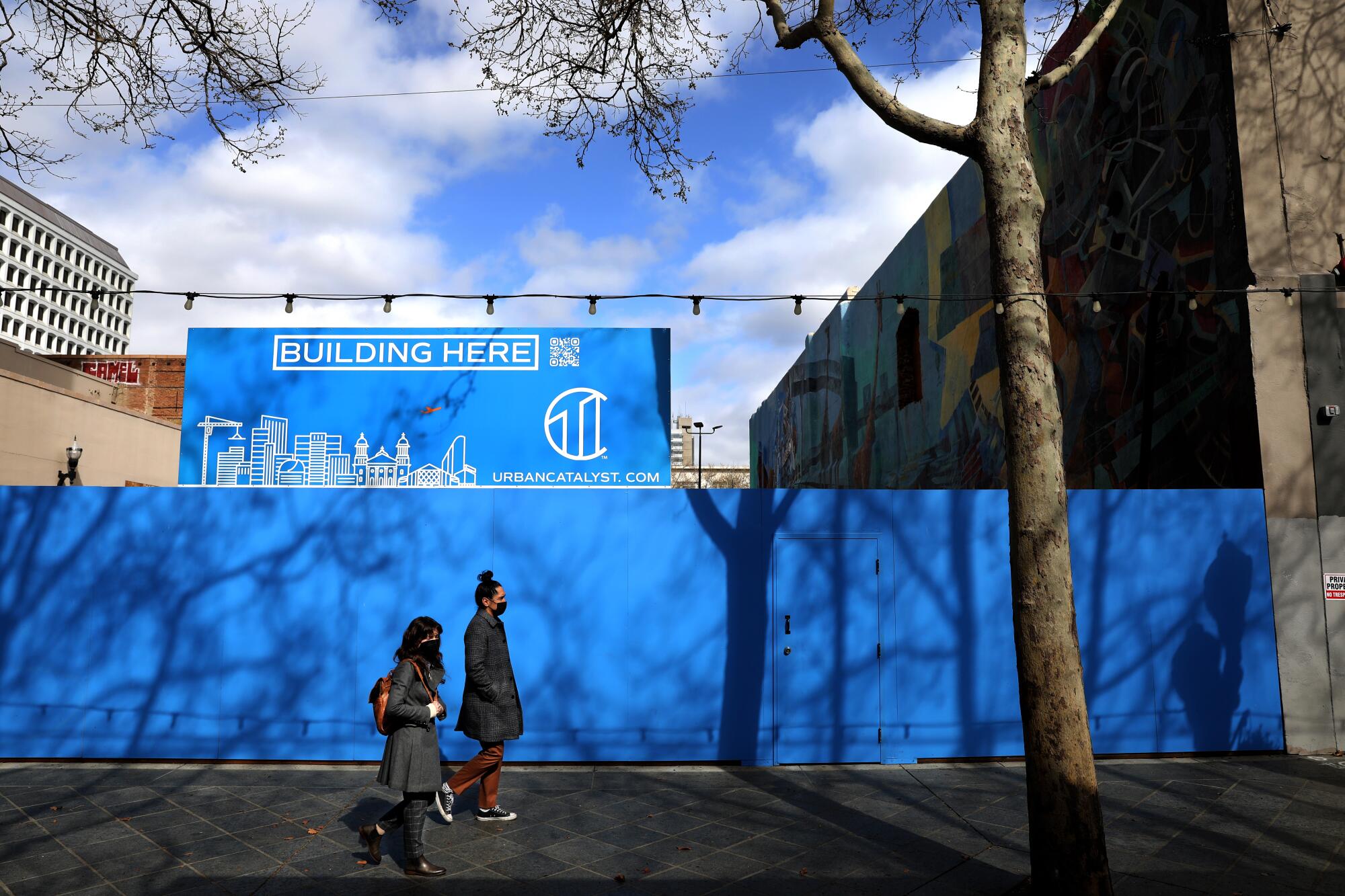
But for every dollar the federal government is investing in Erie through the tax break, it is spending several more in downtown San Jose, a place hardly hurting for capital. The Opportunity Zone there sits adjacent to the future home of a sprawling Google campus that is so big it will reshape the footprint of the downtown, bringing in thousands of highly paid tech workers.
They will be able to stroll to a glistening residential tower getting built with the incentive, where 1,000-square-foot apartments will rent for $4,250 per month. The developer, Urban Catalyst, is not required to set aside anything for affordable housing beyond what the city requires for any other project. The building will have an infinity pool.
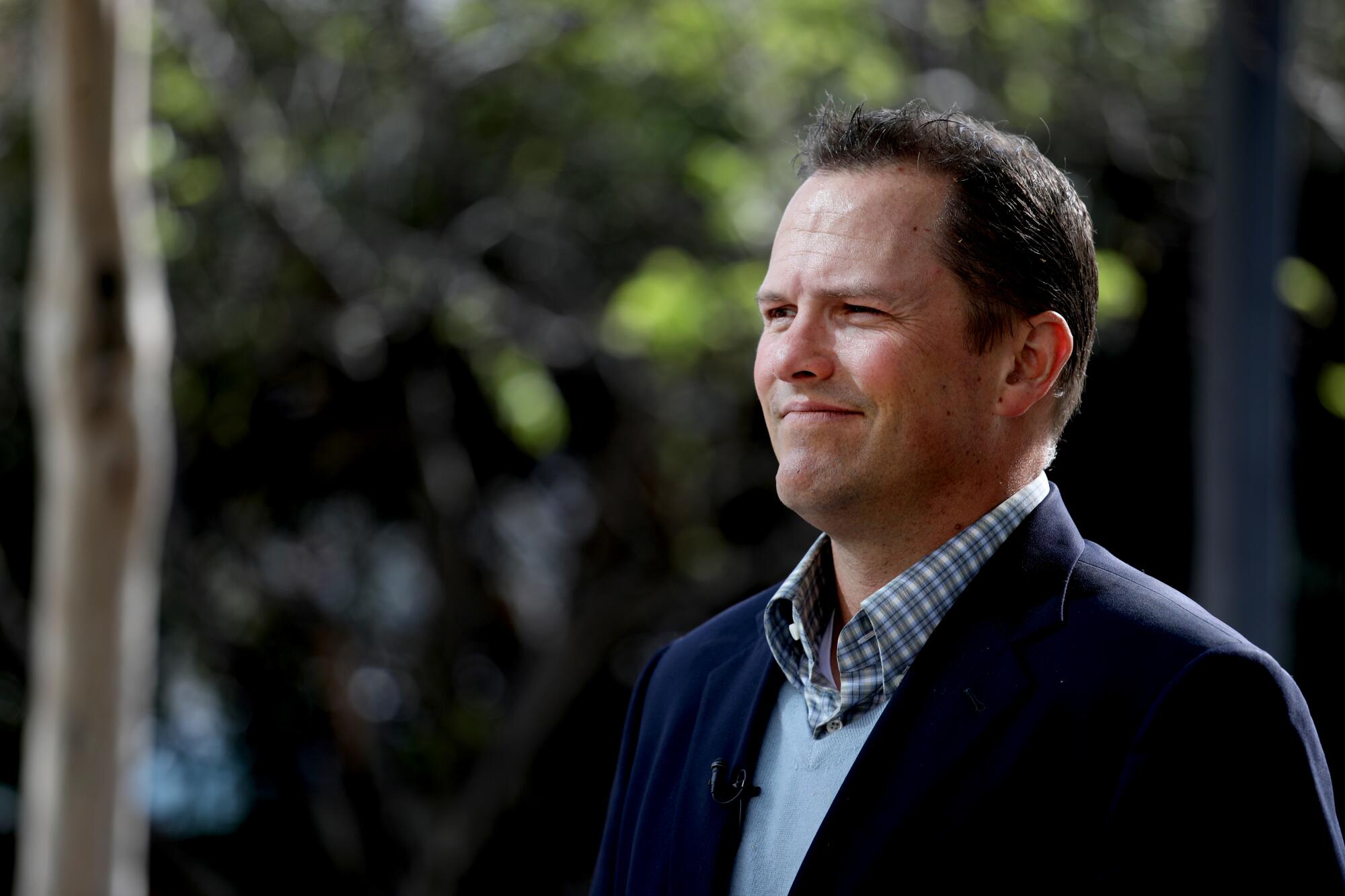


On a tour of San Jose’s Opportunity Zone building boom, Urban Catalyst founder Erik Hayden walked journalists through the construction of another stylish structure getting renovated with the tax break, with soaring ceilings and windows the size of movie screens. It will be home to a swank indoor miniature golf course and cocktail bar inspired by Burning Man. The complex will also house a venue for ax throwing and craft beer drinking.
Asked how such projects fit into the program’s goal of uplifting left-behind communities, Hayden points to properties downtown that remain vacant and boarded up, as the rapid gentrification and flood of investment in this community hopscotches across blocks. “It feels to me like a left-behind community,” he said. “We’re building a variety of different things, all of which are needed by downtown.”
It is hard to reconcile these luxury buildings in San Jose with the stated vision of Parker and that of the lawmaker who was the lead champion for the tax break, Sen. Tim Scott of South Carolina, the Senate’s only Black Republican.
When Scott was invited to the White House in 2017 and asked by Trump how to make amends for the president’s remark that “there were very fine people on both sides” of the violent white supremacist rally in Charlottesville, Va., Scott secured Trump’s endorsement for Opportunity Zones.
The senator recounts in his book, “Opportunity Knocks,” how he made the pitch, telling Trump “that we must find fresh ways to alleviate the terrible poverty that is the source of so many of our ills — including the plague of racism.” Scott remains a proponent of the program, saying in a House hearing in November that the tens of billions invested in Opportunity Zone projects are, by the program’s definition, going to “low-income, high-poverty, racially diverse areas.”

He pointed to new businesses in Columbia, S.C., an affordable housing development in Rockhill, N.C., and local enthusiasm for the program in Stockton. He acknowledged, though, that accurately measuring the tax shelter’s success is impossible, because there are no disclosure rules that allow taxpayers to learn “exactly what people are doing with the resources and the benefits and the incentives.” Scott says he wants more disclosure.
Those who have soured on the tax break say they have seen enough to know it is doing little to bring the country closer to Scott’s lofty goal of alleviating poverty and racism. But it is, they say, helping a lot of wealthy investors and developers of luxury properties.
One need only peruse the Lake Tahoe real estate ads for evidence.
Among the listings is an 8-acre property directly across the street from Heavenly Mountain Resort ski area. The price tag is $52 million. One selling point: The city has already greenlighted the property for a hotel or condos, shops and a large event space.
Another selling point: It is in an Opportunity Zone.
More to Read
Sign up for This Evening's Big Stories
Catch up on the day with the 7 biggest L.A. Times stories in your inbox every weekday evening.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.