The battle is not over: Rising coronavirus infections seen worldwide

- Share via
BERLIN — Renewed lockdown measures in a German region where hundreds of COVID-19 cases sprung up at a slaughterhouse and news that the world’s top-ranked tennis player had been infected provided a stark reminder to Europeans on Tuesday that the pandemic was far from gone.
Meanwhile, Britain, which has recorded the most coronavirus-related deaths in Europe, pressed on with its easing of the lockdown by confirming that restaurants, bars, hair salons and cinemas could reopen on July 4.
By contrast, Germany was reimposing some lockdown restrictions in North Rhine-Westphalia state after more than 1,550 people tested positive for the coronavirus at the Toennies slaughterhouse in Rheda-Wiedenbrueck, and thousands more workers and family members were put into quarantine to try to halt the outbreak.
On Tuesday, North Rhine-Westphalia Gov. Armin Laschet said people in Guetersloh and parts of a neighboring county would now face the same restrictions that Germany saw in March and April, including curbs on social gatherings and bar closures.
“The purpose is to calm the situation,” Laschet said, “to expand testing to establish whether or not the virus has spread beyond the employees of Toennies.”
Laschet expressed frustration at the company’s handling of the outbreak, saying authorities had to order Toennies to release the names of its employees.
“The readiness to cooperate could have been greater,” he said.
Union officials have blamed poor working and living conditions that migrant workers face under a loosely regulated subcontractor.
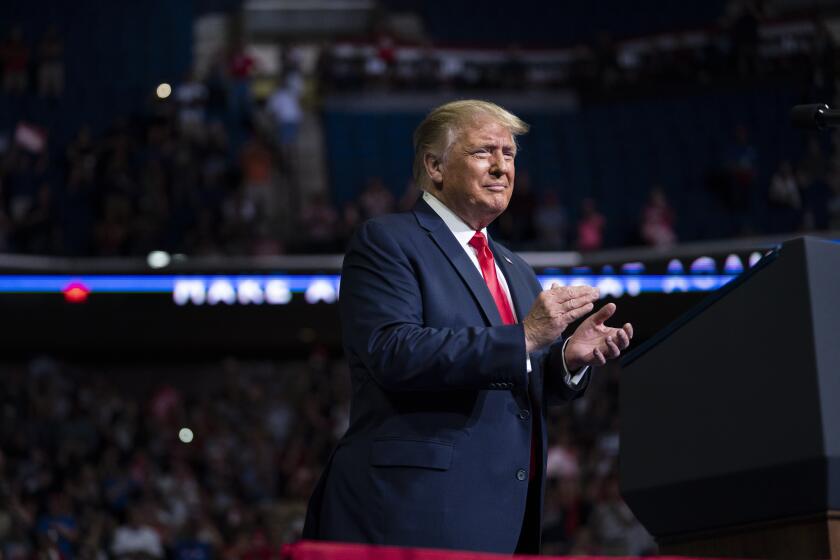
As Trump seeks a return to normal, his administration has considered rolling back emergency declarations that are key to states’ coronavirus responses.
Word of Novak Djokovic’s infection again illustrated that there was little room for complacency in doing what was necessary to beat back the disease. The world’s No. 1 tennis player said he and his wife contracted the coronavirus after he played in a series of exhibition matches he organized in Serbia and Croatia with zero social distancing.
The announcement by Djokovic, who stands third in men’s tennis history with 17 Grand Slam titles, has put into question the wisdom of a full-fledged return of tennis, including the U.S. Open in August.
The Serb tennis star is the fourth player to test positive for the illness after participating in the matches held in Belgrade and Zadar, Croatia.
“Unfortunately, this virus is still present, and it is a new reality that we are still learning to cope and live with,” Djokovic said in a statement released Tuesday.
In Britain, Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced a major rollback of lockdown measures, which will let millions in England back into pubs, cinemas, churches and hair salons starting July 4. The move came amid strong pressure from businesses to ease social distancing rules.
Although gyms, pools, spas and tattoo parlors will remain shut, Johnson told lawmakers “our long national hibernation” was coming to an end.
Pubs and restaurants wanted the government to cut its social distancing requirements in half, to 3 feet, between people indoors, and said many businesses wouldn’t be able to survive without the change.
But some scientists worried the move was too hasty, especially since measures like a track-and-trace system to stamp out outbreaks isn’t yet in place.
“This is far too premature,” said David King, a former chief scientific advisor to the government. “To come out of (lockdown) too early is extremely risky.”
The World Health Organization says the pandemic is still in its ascendancy.
“The epidemic is now peaking or moving toward a peak in a number of large countries,” said Dr. Michael Ryan, WHO’s emergencies chief.
South Africa braced for an anticipated surge of COVID-19 cases by opening a large field hospital with 3,300 beds in a converted car-manufacturing plant.
The field hospital has been constructed in the city of East London in the Eastern Cape province, one of the country’s centers of the disease. South Africa has now reported 101,590 coronavirus cases, including 1,991 deaths.
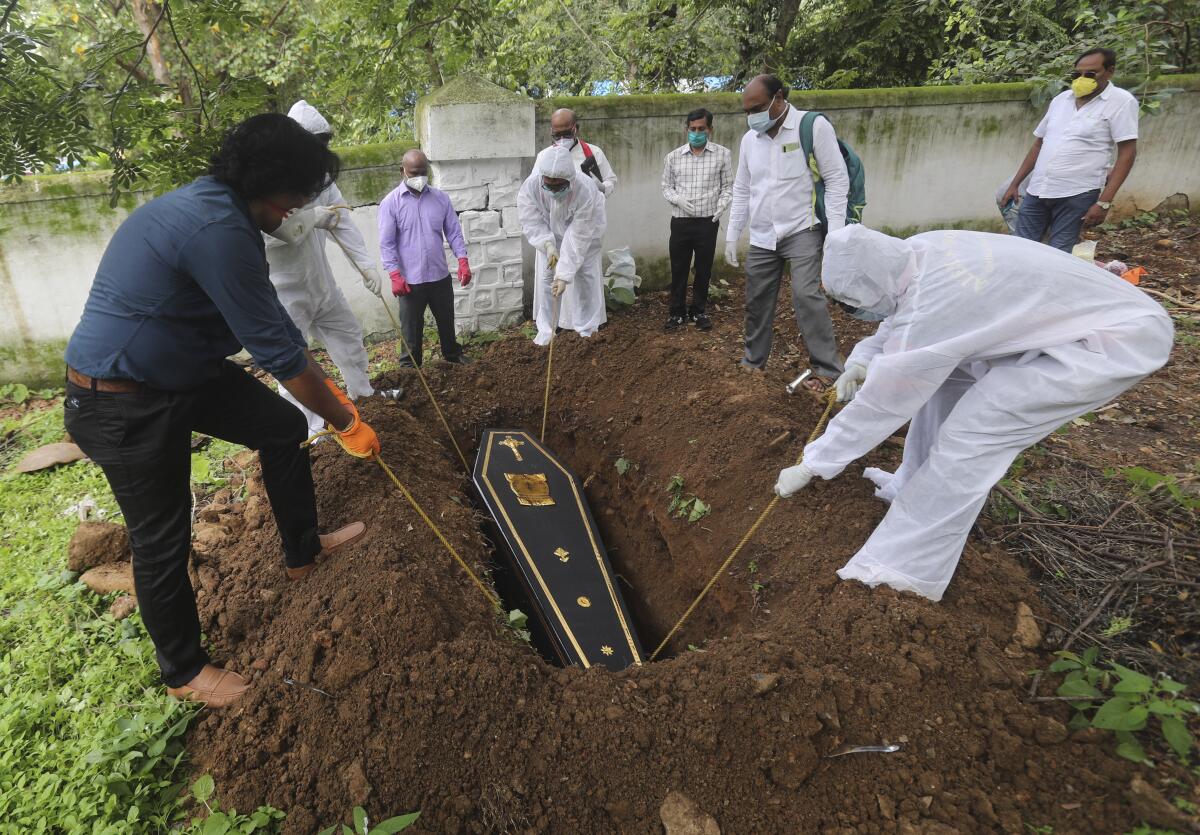
India has been recording about 15,000 new infections each day, and some states Tuesday were considering fresh lockdown measures to try to halt the spread of the virus among the country’s 1.3 billion people. The government had lifted a nationwide lockdown to restart the ailing economy and give hope to millions of hungry, unemployed day laborers.
India’s huge virus caseload is highlighting the country’s unequal society, where private hospitals cater to the rich while public hospitals are so overwhelmed that many people fear to enter them.
In Pakistan, the government is determined to buoy the frail economy by opening up the country even if overcrowded hospitals are turning away patients. New cases have also been rising steeply in Mexico, Colombia and Indonesia.
Concerns over the spread of the virus prompted Saudi Arabia’s unprecedented decision to limit the number of people performing the hajj pilgrimage this year to only a few thousand. The pilgrimage usually draws up to 2.5 million Muslims from all over the world.
Saudi Arabia has one of the highest infection rates in the Middle East, with more than 161,000 confirmed cases so far, including 1,307 deaths.
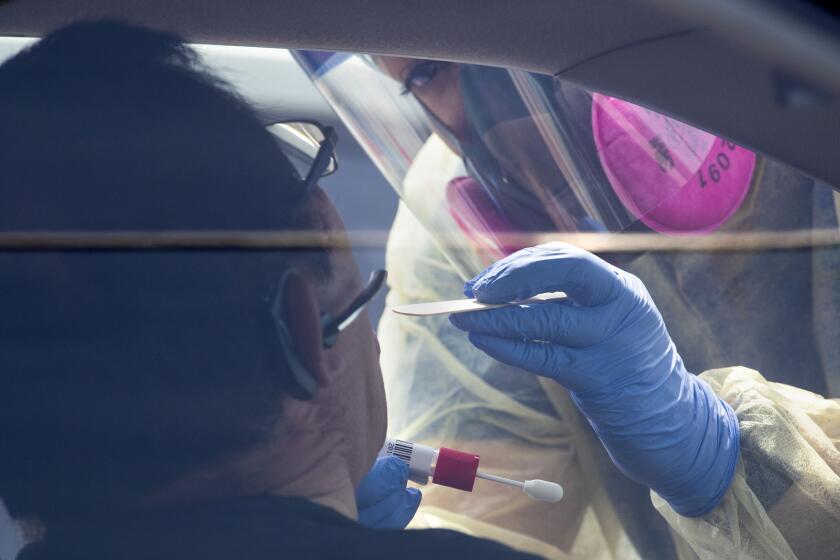
In the U.S., rapid increases in cases across the South and West are raising fears that progress against the virus is slipping away.
The United States has the most infections and deaths by far in the world, with 2.3 million cases and over 120,000 confirmed virus-related deaths, according to a tally by Johns Hopkins University.
Across the state, the positivity rate among those tested for coronavirus has risen from 4.5% to 4.8%, and the number of hospitalizations is up 16%.
Dr. Anthony Fauci, the government’s top infectious disease expert, was testifying before a House committee just days after President Trump told an Oklahoma rally that he had asked officials to slow down testing because too many positive cases were turning up.
Worldwide, more than 9 million people have been infected, and more than 472,000 have died, according to the Johns Hopkins tally. Experts say the true numbers are much higher because of limited testing and cases in which patients had no symptoms.
WHO Director-General Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said it took more than three months for the world to see 1 million confirmed infections but just eight days to see the most recent 1 million cases.
“The greatest threat we face now is not the virus itself. It’s the lack of global solidarity and global leadership,” he said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.