Biden says Israel shouldn’t press into Rafah without ‘credible’ plan to protect civilians

- Share via
RAFAH, Gaza Strip — Israel should not conduct a military operation in the densely populated Gaza border town of Rafah without a “credible and executable” plan to protect civilians, U.S. President Biden told Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on Sunday, the White House said.
It was the most forceful language yet from the president on the possible operation. Biden, who last week called Israel’s military response in Gaza “over the top,” also called for “urgent and specific” steps to strengthen humanitarian assistance to Palestinians in the region.
The two leaders spoke after two Egyptian officials and a Western diplomat said Egypt threatened to suspend its peace treaty with Israel if Israeli troops are sent into Rafah, where Egypt fears fighting could push Palestinians into the Sinai Peninsula and force the closure of besieged Gaza’s main aid supply route.
In addition, the pair discussed continued negotiations on the release of all hostages. Israel’s Channel 13 television said the conversation lasted 45 minutes.
The threat to suspend the Camp David accords, a cornerstone of regional stability for nearly a half-century, came after Netanyahu said sending troops into Rafah was necessary to win the four-month war against the Palestinian militant group Hamas. He asserted that Hamas still has four battalions there.
Over half of Gaza’s population of 2.3 million have fled to Rafah to escape fighting in other areas, and they are packed into sprawling tent camps and United Nations-run shelters near the border. Egypt fears a mass influx of hundreds of thousands of Palestinian refugees who may never be allowed to return.
Netanyahu told “Fox News Sunday” that there’s “plenty of room north of Rafah for them to go to” after Israel’s offensive elsewhere in Gaza, and said Israel would direct evacuees with “flyers, with cellphones and with safe corridors and other things.”
The standoff between Israel and Egypt, two close U.S. allies, took shape as aid groups warned that an offensive in Rafah would worsen the catastrophic humanitarian situation in Gaza, where around 80% of residents have fled their homes and where the U.N. says a quarter of the population faces starvation.
A ground operation in Rafah could cut off one of the only avenues for delivering Gaza’s badly needed food and medical supplies. Forty-four trucks of aid entered Gaza on Sunday, said Wael Abu Omar, a spokesman for the Palestinian Crossings Authority. About 500 entered daily before the war.
Hamas’ Al-Aqsa television station quoted an unnamed Hamas official as saying that any invasion of Rafah would “blow up” talks mediated by the United States, Egypt and Qatar aimed at achieving a cease-fire and the release of Israeli hostages.
All three officials confirmed Egypt’s threats, speaking on condition of anonymity because they were not authorized to brief reporters on the sensitive negotiations. Qatar, Saudi Arabia and other countries have also warned of severe repercussions if Israel goes into Rafah.
“An Israeli offensive on Rafah would lead to an unspeakable humanitarian catastrophe and grave tensions with Egypt,” European Union foreign policy chief Josep Borrell wrote on X, formerly known as Twitter.
Human Rights Watch said in a statement that forced displacement is a war crime. “There is nowhere safe to go in Gaza,” refugee and migrant rights researcher Nadia Hardman said.
The White House, which has rushed arms to Israel and shielded it from international calls for a cease-fire, has warned that a Rafah ground operation would be a “disaster” for civilians.
Israel and Egypt fought five wars before signing the Camp David accords, a landmark peace treaty brokered by the U.S., in the late 1970s. It includes several provisions governing the deployment of forces on both sides of the heavily fortified border.
Egyptian officials fear that if the border is breached, the military would be unable to stop a tide of people fleeing into the Sinai Peninsula.
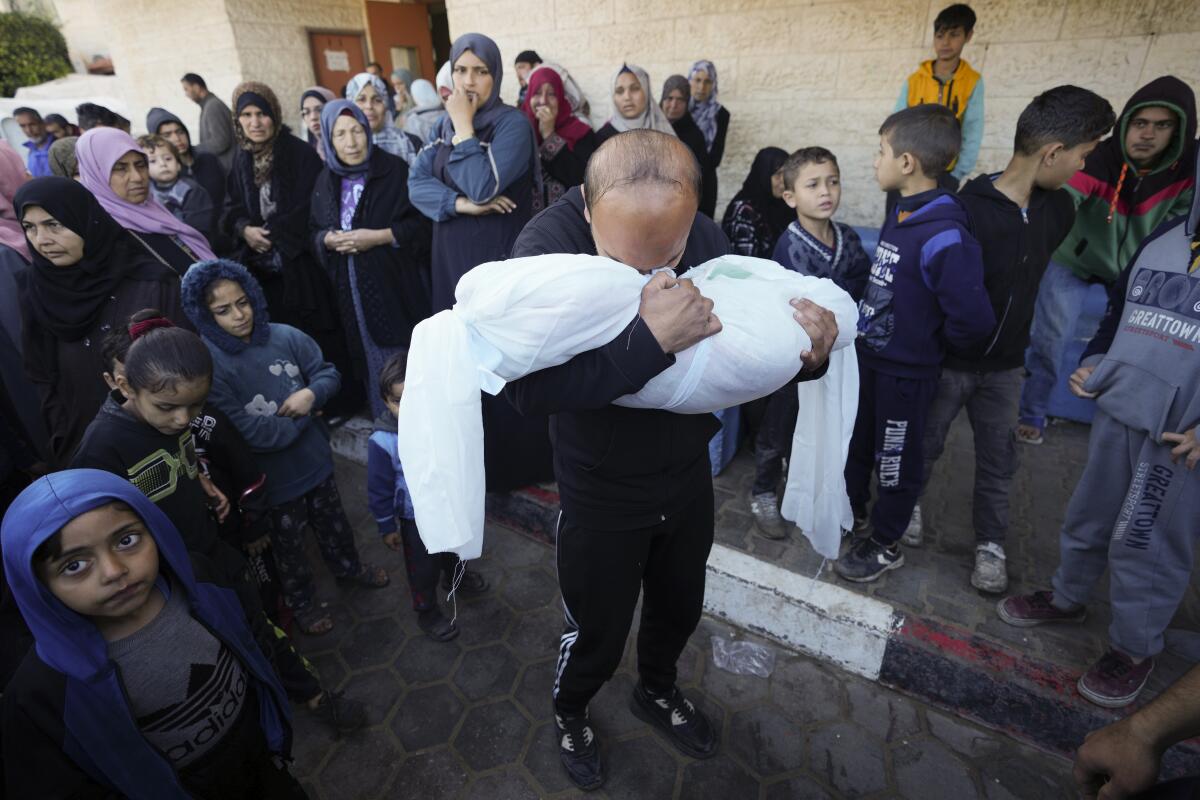
The United Nations says Rafah, normally home to fewer than 300,000 people, now hosts 1.4 million more who fled fighting elsewhere, and it is “severely overcrowded.”
Inside Rafah, some displaced people packed up again. Rafat and Fedaa Abu Haloub, who fled Beit Lahia in the north earlier in the war, placed their belongings on the back of a truck. “We don’t know where we can safely take him,” Fedaa said of their baby. “Every month we have to move, and with all the fear and missiles.”
An Israeli ground invasion of Rafah may force Palestinians to flee to Egypt, but “we hope Egyptians do not accept this situation and do not open the borders to deport us to Sinai because we do not want to leave,” said Om Mohammad Al-Ghemry, who was displaced from Nuseirat.
Israel has ordered much of Gaza’s population to flee south, with evacuation orders covering two-thirds of the territory, even as it regularly carries out airstrikes in all areas, including Rafah. Airstrikes on the town in recent days have killed dozens of Palestinians, including women and children.
Gaza’s Health Ministry said Sunday that the bodies of 112 people killed across the territory had been brought to hospitals in the last 24 hours, as well as 173 wounded people. The fatalities brought the death toll in the strip to 28,176 since the start of the war. The ministry does not distinguish between civilians and fighters but says most of those killed were women and children.
The war began with Hamas’ attack into southern Israel on Oct. 7, when Palestinian militants killed about 1,200 people, mostly civilians, and abducted around 250. More than 100 hostages were released in November during a weeklong cease-fire in exchange for 240 Palestinian prisoners. Some of the remaining hostages have died.
Hamas has said it won’t release any more unless Israel ends its offensive and withdraws from Gaza. It has also demanded the release of hundreds of Palestinian prisoners, including senior militants serving life sentences.
Netanyahu has ruled out both demands, saying Israel will fight on until “total victory” and the return of all the hostages.
Magdy reported from Cairo. Associated Press writer Colleen Long in Washington contributed to this report.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.