Haiti’s surge in gang violence has led thousands to flee the capital

PORT-AU-PRINCE, Haiti — More than 53,000 people have fled Haiti’s capital in less than three weeks, the vast majority to escape unrelenting gang violence, according to a United Nations report released Tuesday.
More than 60% are headed to Haiti’s rural southern region, which worries U.N. officials.
“Our humanitarian colleagues emphasized that these departments do not have sufficient infrastructure, and host communities do not have sufficient resources, to cope with the large number of people fleeing Port-au-Prince,” said U.N. spokesman Stephane Dujarric.
The southern region already hosts more than 116,000 Haitians who previously left Port-au-Prince, according to the report by the U.N.’s International Organization for Migration.
Haiti struggles with poverty, a legacy of colonialism, and European and U.S. interference. But experts blame the latest violence in part on street gangs’ use by rulers.
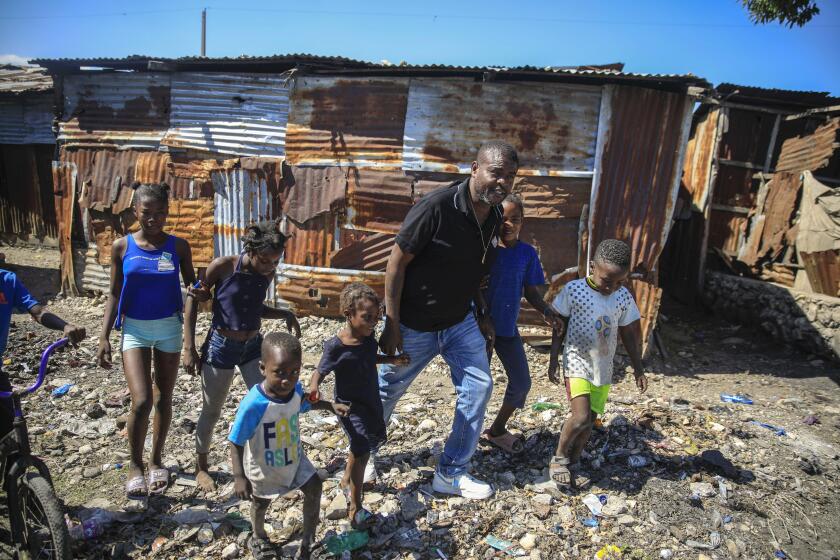
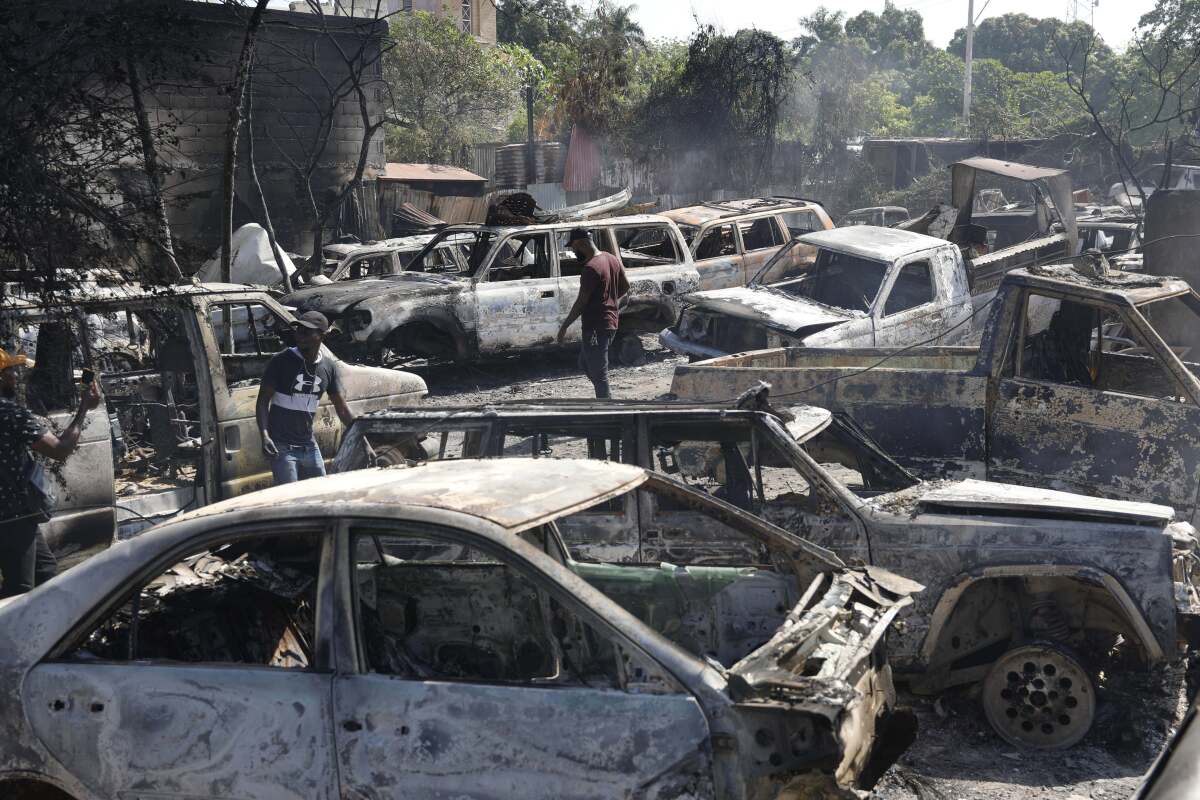
The exodus from the capital of some 3 million people began shortly after powerful gangs launched a series of attacks on government institutions at the end of February. Gunmen have burned police stations, opened fire on the main international airport that remains closed and stormed Haiti’s two biggest prisons, releasing more than 4,000 inmates.
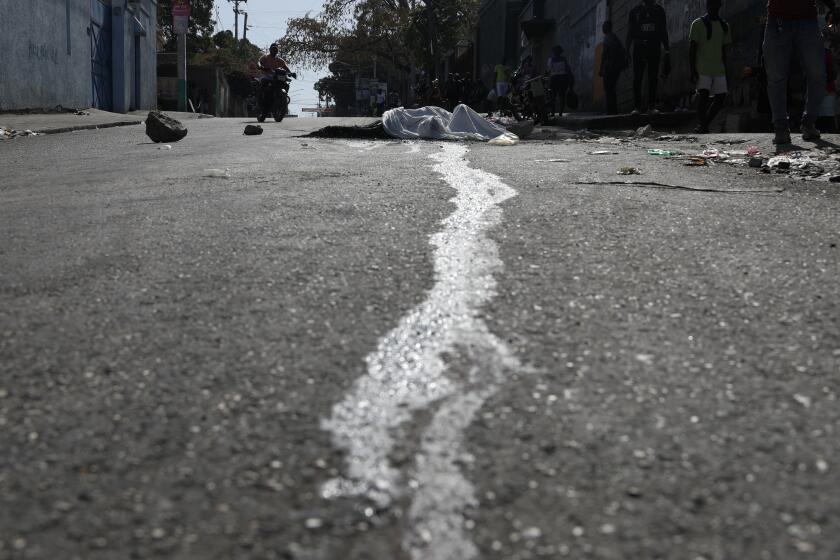
More than 1,500 people have been reported killed through March 22, and another 17,000 have been left homeless, according to the U.N.
Among the rare travelers trying to head north instead of south from the capital were Marjorie Michelle-Jean, a 42-year-old street vendor, and her two children, ages 4 and 7.
“I want to see them alive,” she said, explaining that stray bullets keep hitting the tin roof of their home. Last week, they tried twice to travel to her hometown of Mirebalais in central Haiti but were forced to turn back because of roadblocks.
Some 1.4 million Haitians are on the verge of famine, and more than 4 million require food aid, sometimes eating only once a day or not at all
“I will definitely try again,” she said. “It’s absolutely not safe in Port-au-Prince.”
Of the 53,125 people who fled Port-au-Prince from March 8-27, nearly 70% already had been forced to abandon their homes and were living with relatives or in crowded and unsanitary makeshift shelters across the capital, the U.N. found.
More than 90% of Haitians leaving the capital have been crowding into buses, risking travel through gang-controlled territory where gang rapes have been reported and gunmen have been known to open fire on public transport.
The violence forced Prime Minister Ariel Henry to announce last month that he would resign once a transitional presidential council is created. Henry was in Kenya to push for the U.N.-backed deployment of a police force from the East African country when the attacks began, and he remains locked out of Haiti.
As gangs rampage through Haiti’s capital, more than 33,000 people have fled in 13 days, report finds
U.N. officials say more than 33,000 people have fled Haiti’s capital in a span of nearly two weeks as gangs continue to pillage homes and attack state institutions.
The transitional council, which will be responsible for choosing a new prime minister and council of ministers, has yet to be formally established.
Meanwhile, the mass migration from Port-au-Prince is expected to continue.
But Gary Dorval, 29, who was among a handful of people joining a demonstration on Tuesday, said he wants to stay until a new government is installed: “I want to be part of the change.”
Sanon writes for the Associated Press. AP reporters Dánica Coto in San Juan, Puerto Rico, and Edith M. Lederer at the United Nations contributed.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.