A farmers activist is beaten to death, and the video goes viral. How tensions over land are tearing at Myanmar

- Share via


Kneeling in the dirt, blood leaching from his scalp, Htay Aung pleaded with the mob that had just thrashed him with sugar cane stalks and bamboo poles.
“Oh my God,” he gasped. “Please stop. Please stop.”
The 47-year-old activist knew his assailants. They were his neighbors, some his distant relatives. He had married a woman from their ethnic community and lived with her in this village — until a personal tragedy opened a rift in the family and impelled them to leave.
Htay Aung believed the farmers were occupying his land illegally and had petitioned authorities asking for its return. He showed up with two other men the morning of Oct. 28 and began snapping cellphone pictures as the villagers tended the sugar cane crop they’d planted on the property.
The farmers had warned him not to take photos. One grabbed his cellphone while another pulled out his own and, as the violence escalated, pressed record.
The video would soon spread on Facebook. It shows the slight, shaggy-haired Htay Aung doubled over in the red dirt moments after the beating, a dozen farmers looking on. He reaches into his mouth, seemingly for loose teeth, then retches and sits back in a stupor with his head bowed.
Four days later, he was dead.
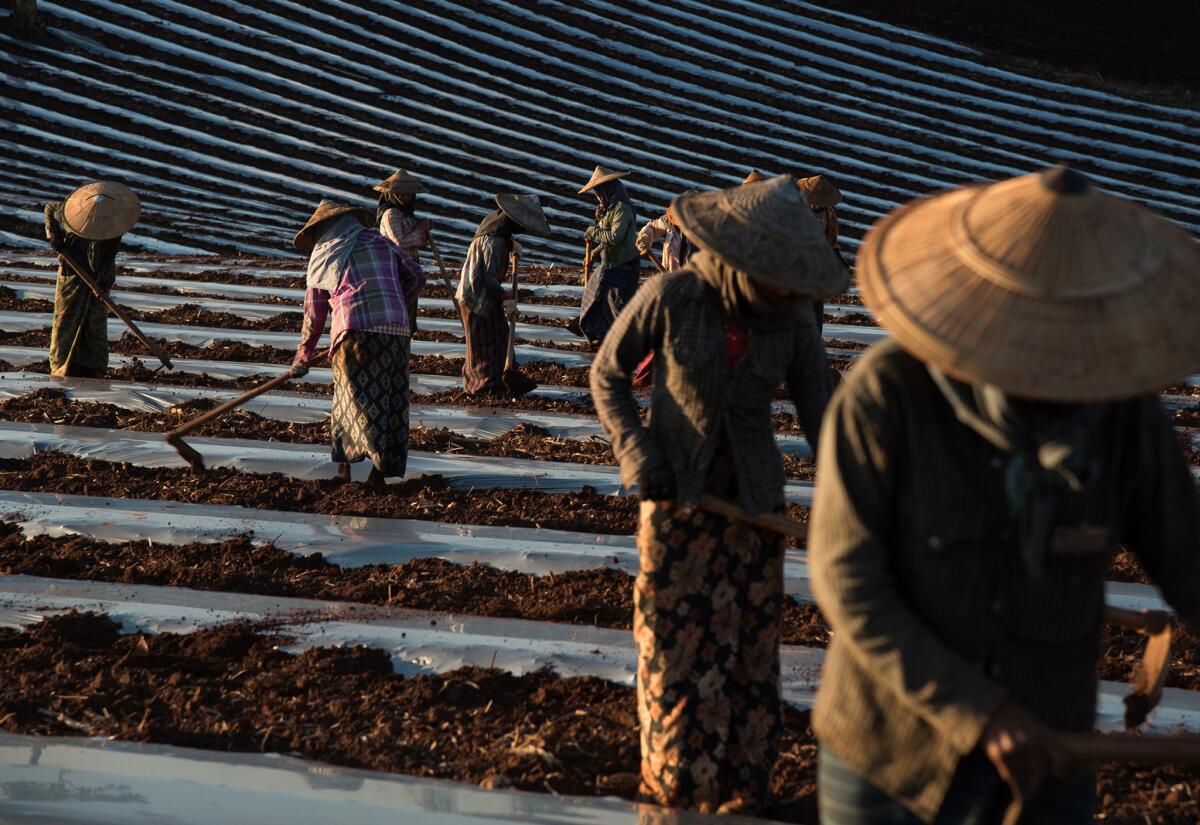
In Myanmar, a lush Southeast Asian nation where 70% of the population makes a living from agriculture, a slow transition from half a century of military rule has reopened old grievances over army seizures of land. The disputes pit farmers against the government, influential business interests, foreign investors — and often each other.
The land battle is one of the crucial tests of a nation struggling to build democratic institutions while positioning itself as Asia’s new economic crossroads, a largely untapped source of mineral and agricultural wealth at the junction of India, China and Thailand.
Starting in the 1990s, the army confiscated millions of acres, uprooting farmers who had lived and worked on their small plots for generations. The generals built bases and infrastructure, started commercial enterprises that propped up their increasingly isolated dictatorship, sold concessions to crony developers — or left the land vacant and charged farmers rent to use it.
The seizures robbed countless citizens of Myanmar, formerly known as Burma, of their only tangible resource as the economy and education systems crumbled.
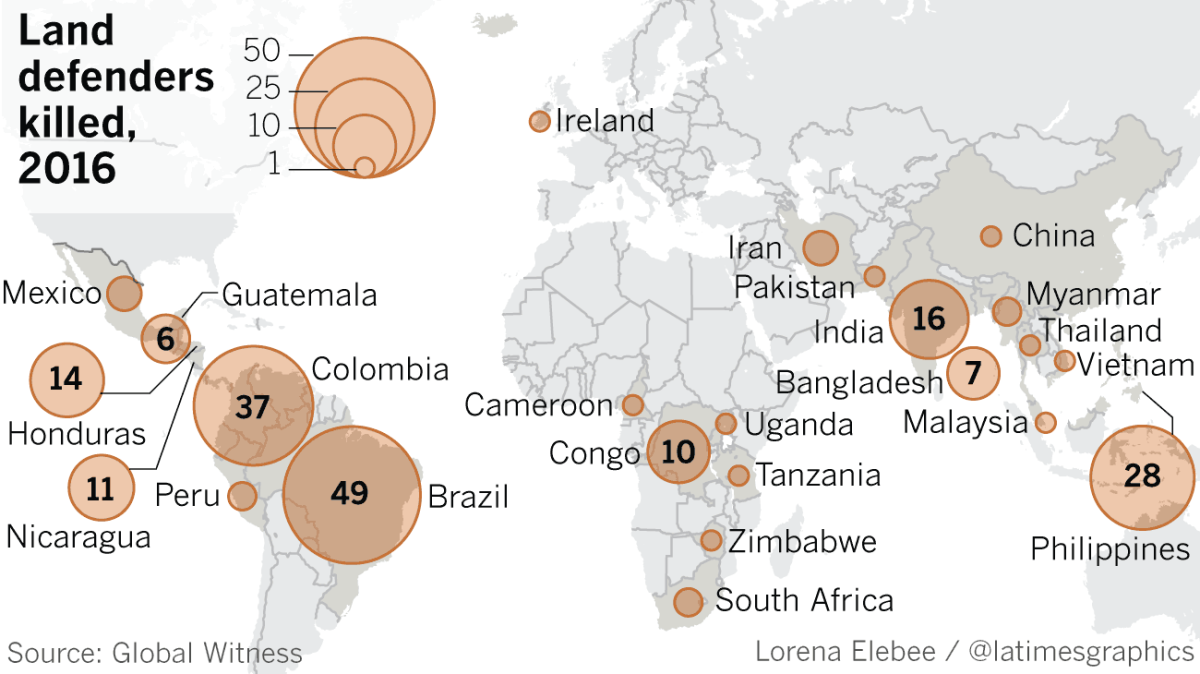
Green farmland gave way to giant rubber plantations. Waste from coal and tin mines fouled creeks and wells. Forests were denuded to produce teak and rosewood prized in China and other countries. Activists who opposed the land seizures were harassed, jailed or killed — joining hundreds of environmental defenders worldwide who have lost their lives in recent years.
Now, with the generals ceding some powers to a civilian government and introducing new land tenure laws in the hope of attracting investment, more farmers across Myanmar are trying to recover what was taken.
A sweeping victory by pro-democracy activist Aung San Suu Kyi’s party in parliamentary elections in November 2015 sparked a wave of petitions and protests calling for restitution. In less than five months, state media reported, the new government received more than 2,000 complaints involving land seizures, although very few have been resolved.
“There was a time when campaigning against land confiscation was unthinkable in Myanmar, but now there is more space for farmers, human rights defenders, activists, Buddhist monks and sometimes even politicians to campaign on land issues,” said Andrea Giorgetta, Asia director for the Paris-based International Federation for Human Rights.
“Inevitably, that comes with increasing risks for defenders in an environment where protections afforded by legal frameworks and law enforcement agencies are still very weak.”
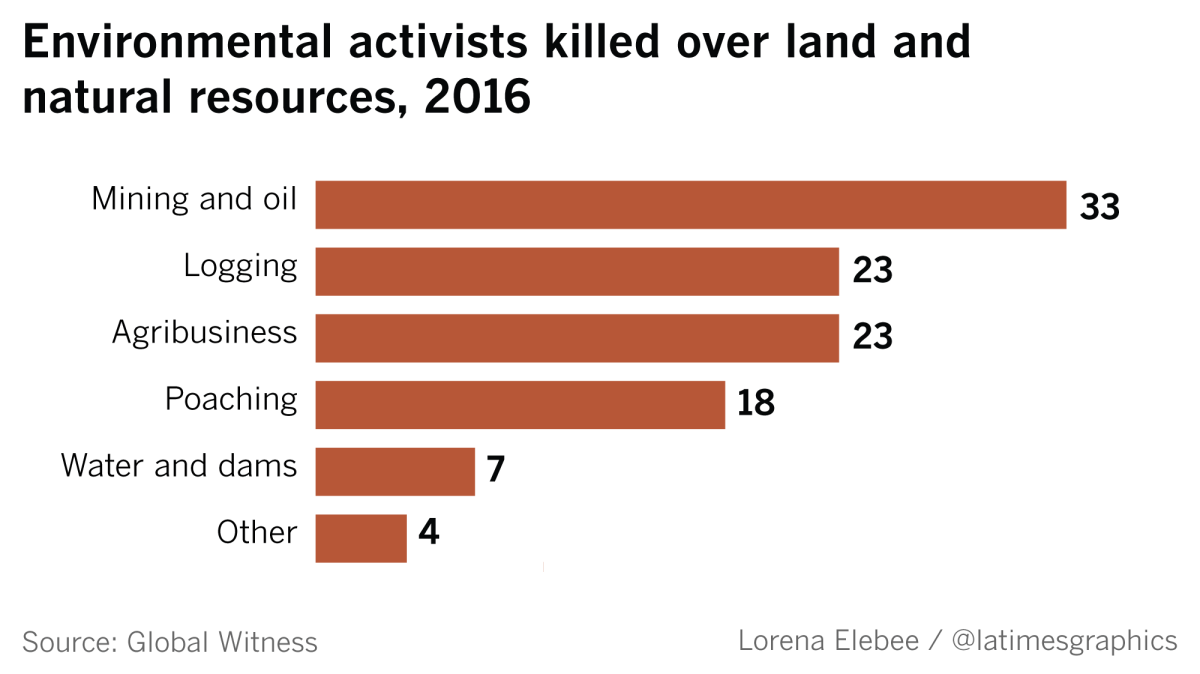
At least six people have been killed since 2015 for fighting land seizures or environmental exploitation in Myanmar, according to the nongovernmental organization Global Witness. They include a journalist who was found dead after writing a Facebook post listing the names of people apparently connected to illegal logging; a 22-year-old anti-mining activist who was stabbed at a fundraising event; and a farmers advocate who was shot in front of his house.
Htay Aung’s land battle was just beginning. Weeks before the attack, he wrote to a committee established by the government last year to resolve land grab cases. His letter called for the return of 346 acres seized from 31 households in Inn Wine Pahel, in rural eastern Myanmar.
In the hills of southern Shan state, three hours by road from Mandalay, the hamlet of Inn Wine Pahel is wet and verdant.
Yellow wildflowers and pale green stalks of sugar cane press up against winding dirt roads dappled with puddles. Under misty clouds, women in long patterned skirts walk along the fields balancing bamboo poles on their heads. The air smells of fresh rain and fertilizer.
“Everything grows here,” said Kyaw Tun, a village leader in his 60s.
Into this quiet land, in 1997, trooped army soldiers, who did not need to use force among a population worn down by decades of repression.
“They didn’t have to say anything,” recalled Myin Oo, a 36-year-old farmer who lost 5 acres in the land grab. “Everyone was just scared of them.”
The army briefly leased the land to an agribusiness company, then reallocated it in 2005 as the generals sought to make peace with an array of ethnic minority groups in Shan and other outlying states that had taken up arms to seek greater rights.
One was the Palaung, tea farmers whose traditional homeland lies about 30 miles north of Inn Wine Pahel, on the other side of a range of low green hills. The army had reached a cease-fire agreement with the group’s armed wing, the Palaung State Liberation Army, and granted 120 members farming rights on the land.
They created a settlement just outside Inn Wine Pahel and named it Palaung Gone; there, they set about cultivating sugar cane, sesame and rice just a few hundred yards from Myin Oo’s house.
The people of Inn Wine Pahel were members of a smaller ethnic group, the Danu, which had no militia — and therefore no standing with the army. Myin Oo and his wife went from growing their own potatoes and sugar cane to working as laborers on the farms of larger landholders, earning just a few dollars a day to support their three children.
The Danu resented what they saw as the army rewarding an insurgent group. They would later learn that the army, known as the Tatmadaw, had forged a relationship with the PSLA, training some former insurgents and recruiting them into a pro-government militia to fight other ethnic armies in Shan.
“That is classic Tatmadaw,” said Jennifer Franco, a Myanmar expert at the Transnational Institute, a research organization based in the Netherlands. “They are so good at divide-and-rule, and setting up people-to-people conflict that serves their interests.”
At first, residents of the two villages attended each other’s weddings and observed Buddhist festivals together. At the end of the long rainy season, Palaung Gone villagers brought new robes to the monks of Inn Wine Pahel, an annual rite of giving thanks to the keepers of the faith.
Among the Palaung Gone residents were Htay Aung and his wife, Myint Sein. They had moved in 2014 from Htay Aung’s ancestral home in Mogok, a valley in northern Myanmar famed for mines that bear some of the world’s most expensive blood-red rubies.
His family had little land in Mogok, where companies linked to army generals had taken over many of the lucrative mining areas, and the couple struggled to raise their six children. So they came to work alongside Myint Sein’s siblings in Palaung Gone.
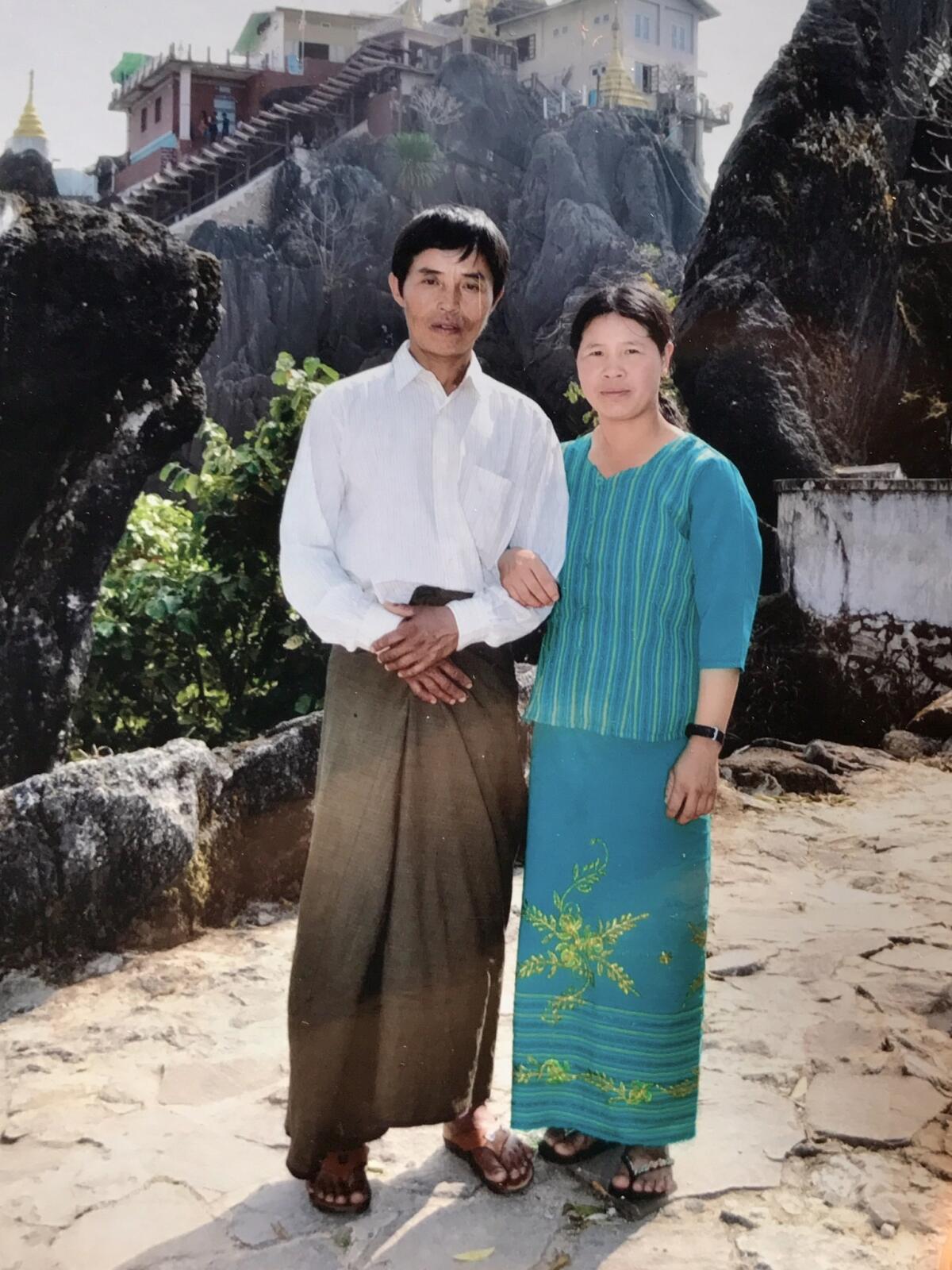

“We had enough to educate the children and save a little bit every month,” said Myint Sein, a petite woman 11 years her husband’s junior.
Then, in 2015, their simple life was destroyed.
One morning, while Htay Aung was at work in the fields, Myint Sein’s sister took the couple’s eldest son, 9-year-old Htet Thar Aung, into town on a motorcycle. They were traveling near a sugar cane factory when a truck collided with the motorbike. Htet Thar Aung was thrown to the ground and died of his injuries.
Htay Aung blamed his sister-in-law for the death. “He never forgave her,” Myint Sein said.
Htay Aung stopped associating with other families and participating in meetings. In a small, ethnically homogeneous village, such gestures ripped at the social fabric. Palaung leaders decided he should be removed.
Htay Aung reacted calmly, recalled his brother-in-law, Kyaw San. “He said he would go and live in Inn Wine Pahel,” he said. “That’s when our problems started.”
In May 2016, the family moved a few hundred yards away to the edge of Inn Wine Pahel, into a one-room house with a sloped tin roof and walls made of cane. Htay Aung and Myint Sein worked in the sugar cane fields, each earning $3 a day. From their doorstep, they could see the house of the prosperous Palaung Gone village chief, a sturdy concrete dwelling with a new Toyota truck parked outside.
Across the Myanmar countryside, unrest was bubbling. Unions, first allowed by the military rulers in 2011, were forming to teach farmers technical skills and press land claims. As the government made slow progress in hearing cases, protests on seized land broke out in several states, with dozens of farmers and activists arrested.
Unlike most of his new neighbors, Htay Aung had studied well into high school. Books had been one way to escape the risks of working in the ruby mines. Now, digesting reports in newspapers and on Facebook, Htay Aung sought to rally his new neighbors.
He began inviting farmers to his house to lecture them about agricultural practices that could improve crop yields and read from union treatises posted online. His favorite topic was human rights.
“He told the villagers not to be afraid,” said San San Aye, a local leader of the National Peasants Union, founded in 2016. “He told them that they were the natives on this land and they should organize to get it back.”
San San Aye is a voluble middle-aged woman with long black hair and face streaked with thanaka, a yellow-white traditional makeup made from tree bark. Her family has been locked in a battle over land seized from them by a former army officer. This summer, her husband, Sein Na, spent three months in jail on charges of trespassing during a protest.
From a small grocery overlooking her former land, San San Aye has been managing dozens of land cases, filing documents in crinkled plastic bags and making weekly trips to the courthouse in Naungcho township on a motorcycle. The Inn Wine Pahel villagers had a strong claim, she said, because they had lived there for generations and possessed tax receipts from the 1980s showing they were cultivating crops before the army arrived.
Though he wasn’t native to the area, Htay Aung struck San San Aye as honest and dedicated. If the villagers had their land restored, he stood to gain a plot — the only one he would ever own. She asked him to collect evidence.
Over several days in the spring, Htay Aung, Myin Oo and others walked the perimeter of Palaung Gone with a length of rope, carefully measuring the 346 acres. But when they tried to take pictures, the Palaung villagers chased them away and cautioned them not to return.
“They used to be fighters, so we’re scared of them,” Myin Oo said. “But Htay Aung did not want to stop. He said that if someone has been a victim, they should fight back.”
The whole land management of the country is under the control of the military.
— Saw Alex Htoo, Myanmar land rights activist
A local administrator called a meeting of the two villages on Oct. 28 to discuss the case. Htay Aung was walking down the hill to Palaung Gone when he began taking pictures again.
A mob quickly formed, said Myin Oo, who was trailing behind. Before he and another farmer could intervene, the Palaung villagers had knocked Htay Aung to the ground. They kicked and punched him for several minutes, then began beating him with sticks.
“He shouted back at them, ‘Don’t do this,’ but they didn’t care,” Myin Oo said.
The local administrator arrived to find Htay Aung lying motionless on the ground and summoned the police. Htay Aung was taken to a hospital an hour away, but doctors said his injuries were life-threatening and sent him to Mandalay in an ambulance.
Myint Sein rode with him, holding his hand.
Three Palaung villagers — Kyaw Swin Thet, Ko Naw Ngin and Aik Kyaw — were arrested that afternoon but released after a few hours.
Htay Aung lay in a coma for 72 hours before doctors in Mandalay said they could not save him. He was pronounced dead Nov. 1.
A few days later, after the video surfaced online, the three Palaung villagers were rearrested. They are jailed in Naungcho and awaiting trial for murder, which carries a maximum life sentence. None has enlisted a lawyer, and police would not make any of the accused available for an interview.
In Palaung Gone, the defendants garnered as much sympathy as Htay Aung.
“I’m sorry for my brother-in-law, and I’m sorry for the people who were arrested,” said brother-in-law Kyaw San. “But he was making a lot of problems here. He has no farm, he has no land, he has nothing. You see the poor condition of his house. We were given the land legally, and still he was raising his voice everywhere against us.”
Every week, family members of the defendants visit them in jail, a police official in Naungcho said. Sometimes they are allowed to bring them food, cooked by other Palaung families.
A month after Htay Aung’s death, neither Kyaw San nor any other Palaung villager had spoken to his widow.
“Bus drivers face accidents; fishermen drown,” Kyaw San said, shrugging. “It is part of Buddha’s teachings that everyone will face death.”
In April 2017, one year after the government formed the Central Review Committee on Confiscated Farmlands and Other Lands, state media reported that the committee had reviewed 10,891 cases and resolved 2,057 by returning the land to original inhabitants.
But activists say that nearly all the returned land was vacant or unused. Despite promises by Suu Kyi’s government to uphold farmers’ rights, the committee has not transferred land being used by farmers or businesses. “The success rate has been very low,” said Joseph Wah, a human rights activist in Myanmar who has studied land issues. “Only land where there is nothing going on at the moment has been possible for villagers to claim.”
Some question the review committee’s independence. “The whole land management of the country is under the control of the military,” said Saw Alex Htoo, a member of the secretariat of Land in Our Hands, a consortium of Myanmar farmers and human rights groups.
In January, Myanmar’s parliament is expected to approve changes to a land acquisition law that activists say would criminalize attempts to challenge land seizures. The government has also failed to revisit laws passed during military rule that privilege businesses and allow authorities to seize any land that isn’t being cultivated, ignoring traditional farming practices under which many farmers leave plots fallow for periods of time to allow soil to regenerate.
Saw Alex Htoo said the government is caught up in a “gold rush” for Myanmar’s land and is catering to investors from China, Thailand and other countries as it seeks to rebuild the economy.
“If you look at social justice, this is not fair,” he said. “There will be more protests, people will continue to fight for land rights and there will be more political instability. The laws are favoring investment too much instead of protecting the native communities and marginalized people.”
Without Htay Aung, the future of the Inn Wine Pahel case is uncertain. Villagers say they are still gathering evidence, but express little hope for a resolution. Since his death, no one has dared set foot in Palaung Gone.
“We had put our hope in the new government, but we haven’t seen any change,” Myin Oo said. “We didn’t know anything about the laws. That is why we are grateful to Htay Aung. He was very brave.”
This story was reported with a grant from the United Nations Foundation.
Follow @SBengali on Twitter for more news from South Asia
ALSO
He defended the sacred lands of Mexico’s Tarahumara people. Then a gunman cut him down
'They should be thought of as heroes': Why killings of environmental activists are rising globally
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.








