California’s slide from coronavirus success to danger zone began Memorial Day
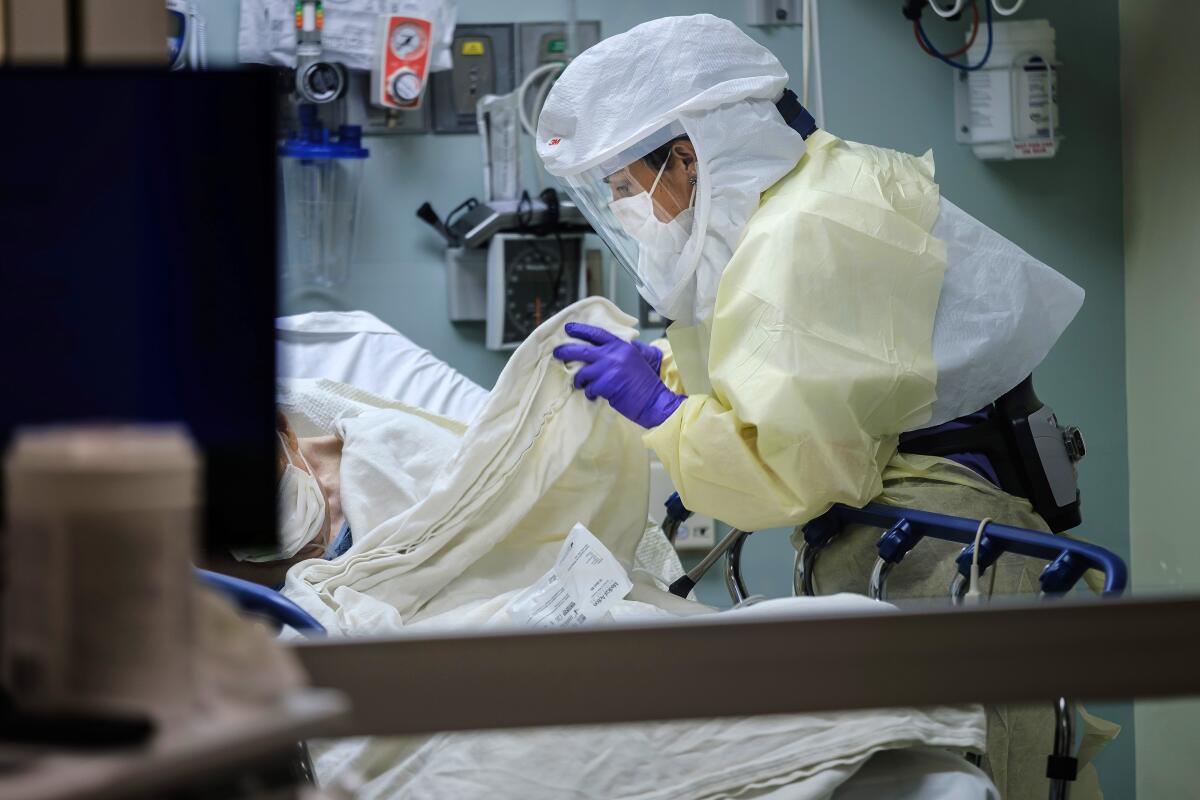
The seeds of the latest surge in coronavirus cases in California appear to have been planted around Memorial Day.
People had been pent up in their homes; businesses shuttered for months amid the stay-at-home order began to open. And as the reopening accelerated, a lot of people were ready to get out.
The beckon of summer rituals followed — day trips to the beach, Memorial Day barbecues, graduation celebrations, Father’s Day gatherings. Around the same time, historic protests began, triggered by outrage over the death in Minneapolis of George Floyd while in police custody, which sparked unprecedented demonstrations across the nation, including in the streets of California.
Many parks, beaches and trials will be open, but officials are urging people to keep their distance and not overcrowd these outdoor spaces.
It would take a few weeks of incubation. But it’s now clear that Memorial Day was the beginning of California’s turn from coronavirus success story to cautionary tale. A Los Angeles Times analysis has found that new coronavirus hospitalizations in California began accelerating around June 15 at a rate not seen since early April.
Statewide, the daily number of people in hospitals with a confirmed infection of the coronavirus has jumped more than 50% from when it had been stable in mid-April, The Times analysis found. Several counties said hospitals are near capacity — Riverside County reported 99% of its normal supply of beds in intensive care units occupied — while others including Los Angeles County say such conditions may be weeks away.
And officials and experts say the worst is still yet to come. It can take two weeks for the virus to incubate in the body, and an additional week or two after that to result in the hospitalization of severely ill people. That means more people may have gotten exposed to the virus around the week of Memorial Day or shortly thereafter, said Dr. Robert Kim-Farley, a medical epidemiologist and infectious-diseases expert at the UCLA Fielding School of Public Health.
But the behavior that is causing the rapid spread is continuing. Businesses haven’t been adhering to health orders to wear masks in public and stay away from crowded situations. About half of the restaurants and bars visited by Los Angeles County inspectors over the weekend were not complying with the new mask rules, and officials have seen examples of overcrowding in public spaces.
Gov. Gavin Newsom’s move to shut down bars in L.A. County and other hot spots might help, but those establishments represent only a small part of the problem.
“I’ve had an explosion of new outbreaks in workplaces. One that got shut down this past weekend, it had over 115 infections,” said Barbara Ferrer, public health director for Los Angeles County, which surpassed 100,000 cumulative cases and 3,330 total deaths on Monday. “And we’ve had numerous examples of outbreaks happening because families are getting together with extended family members and friends to celebrate weddings, things they had postponed, and again, created higher risk, and there was transmission.”
The latest maps and charts on the spread of COVID-19 in Los Angeles County, including cases, deaths, closures and restrictions.
Officials are looking with increased anxiety to the upcoming Fourth of July weekend, urging residents to only spend time in person with members of their households, avoid crowds and follow social distancing rules, while at the same time bracing for a surge in hospitalizations by people already exposed to the virus.
Los Angeles County announced beaches will close during the holiday weekend in hopes of reducing crowds.
It was clear from the outset that easing stay-at-home orders would result in a higher level of cases — but the rapid spread caught many by surprise.
Continuing to keep society shut down at such an extreme state for too long causes its own ill effects, whether it be more homelessness and deaths due to greater poverty or the effects of denying schoolchildren their in-person education, Kim-Farley said.
“It’s a luxury to shelter in place,” added Dr. Kirsten Bibbins-Domingo, chair of UC San Francisco’s Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics. “We have to think about how we open and minimize risk. We’re going to be living with this virus for a long time.”
But there is no textbook to figure out how to reopen California safely amid the world’s worst pandemic in a century, faced with a never-before-seen coronavirus.
The only way to figure out how to open is to do it gradually and dial things back if the disease spreads so fast it might overwhelm hospitals later. And that’s what’s happening now, Kim-Farley said.
“Now, we’re recognizing things are going up. So we’re dialing it back down again,” Kim-Farley said.
A Times analysis found that as of Monday, 5.9% of coronavirus test results received over the last week are positive. That’s a significant jump from the figure the previous week, when it was 4.9%. Younger people are making up a greater share of those that are infected, a sign they are beginning to socialize again.
The rate is even worse in Los Angeles County: As of Monday, the seven-day average of coronavirus tests being confirmed as positive was 8.4%. In late May, it was 4.6%.
Closing bars in hard-hit counties marked the state’s biggest step in ramping back reopening plans. But it warns more drastic restrictions could be coming.
“The bottom line is: We’re doing this because we have seen an increase in the spread of this virus,” Newsom said. “We need to take further steps and that’s exactly what we did this weekend.”
State officials say the consumption of alcohol in bars impairs judgment and leads to decreased use of face coverings and failing to keep socially distant from other people. The spaces are also raucous, often requiring people to speak in louder voices, which can lead to the spray of potentially infectious oral droplets while talking.
As of Monday, 14 California counties have seen increases in hospitalizations that have exceeded 10% in the last three days, according to The Times’ California coronavirus tracker. They affect the state’s most populated regions: Southern California, the San Francisco Bay Area, San Diego County and the Central Valley.
The latest maps and charts on the spread of COVID-19 in Los Angeles County, including cases, deaths, closures and restrictions.
Kim-Farley, a former senior health official with L.A. County and the national Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, said there are three protagonists — individuals, businesses and county governments — who each need to do their part to limit the spread of the disease.
Not only do government officials need to analyze data for worrisome trends, but individuals must wear face coverings and stay six feet away from other people, and business owners need to keep their establishments from getting crowded and regularly disinfect high-touch surfaces.
It’s possible too many Californians responded to the reopenings of businesses as a license to resume life as they did before the pandemic arrived, Kim-Farley said. Californians never endured the trauma New Yorkers did of seeing their hospital system get overloaded by COVID-19 patients in the spring.
“It may be that they’re no longer as conscious about masking and physical distancing,” Kim-Farley said.
Some residents are revolting against rules forcing them to wear masks in public, creating new coronavirus dangers
Another factor is that the political discord in the U.S. and California over the response to the pandemic, such as political fights over using face masks, is hurting our ability to control the epidemic, experts say. Countries that have had a unified public response to broad pandemic control measures, such as New Zealand and Taiwan, have kept the virus from spiraling out of control, experts say.
The pandemic could have triggered the sense of unifying around a common enemy in the U.S.
“Unfortunately, we’ve made it such that it’s become very divisive and become very politicized,” Kim-Farley said.
Health experts say it will take businesses, individual and local governments all working together to make sure there is not a new surge.
A Los Angeles taco chain said Sunday it was forced to temporarily close two locations after a mounting onslaught of harassment from customers angered by the business’ “no mask, no service” policy.
Experts say they hope society will learn from the spike.
Dr. Otto Yang, professor of medicine and associate chief of infectious diseases at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, said he thought L.A. County reopened too quickly.
“For a lot of the things that really work to reduce transmission — like contact tracing and even masks — depend on your starting at a low [disease] control level,” Yang said. “It’s back to the fire analogy: If the fire isn’t down to just smoldering embers, but if there’s still active pockets of fire, then backing off will let stuff flare up very quickly.”
With the benefit of hindsight, it’s now clear that officials should have made more enforcement of social distancing and masking a higher priority. Earlier implementation of a mask-wearing order would’ve helped, too.
At this point, Yang said he doesn’t think the public would tolerate a return to the springtime stay-at-home order. So officials will instead need to focus on more targeted approaches, such as the shutting down of bars and prioritizing the highest-risk activities.
Los Angeles County public health officials on Saturday reported a continued rise in new coronavirus cases and hospitalizations, saying the increase came at “a critical moment” in the county’s reopening.
Times staff writers Maura Dolan, Laura Newberry and Taryn Luna contributed to this report.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.



















