Asylum seekers turned away from border bridges ahead of caravan
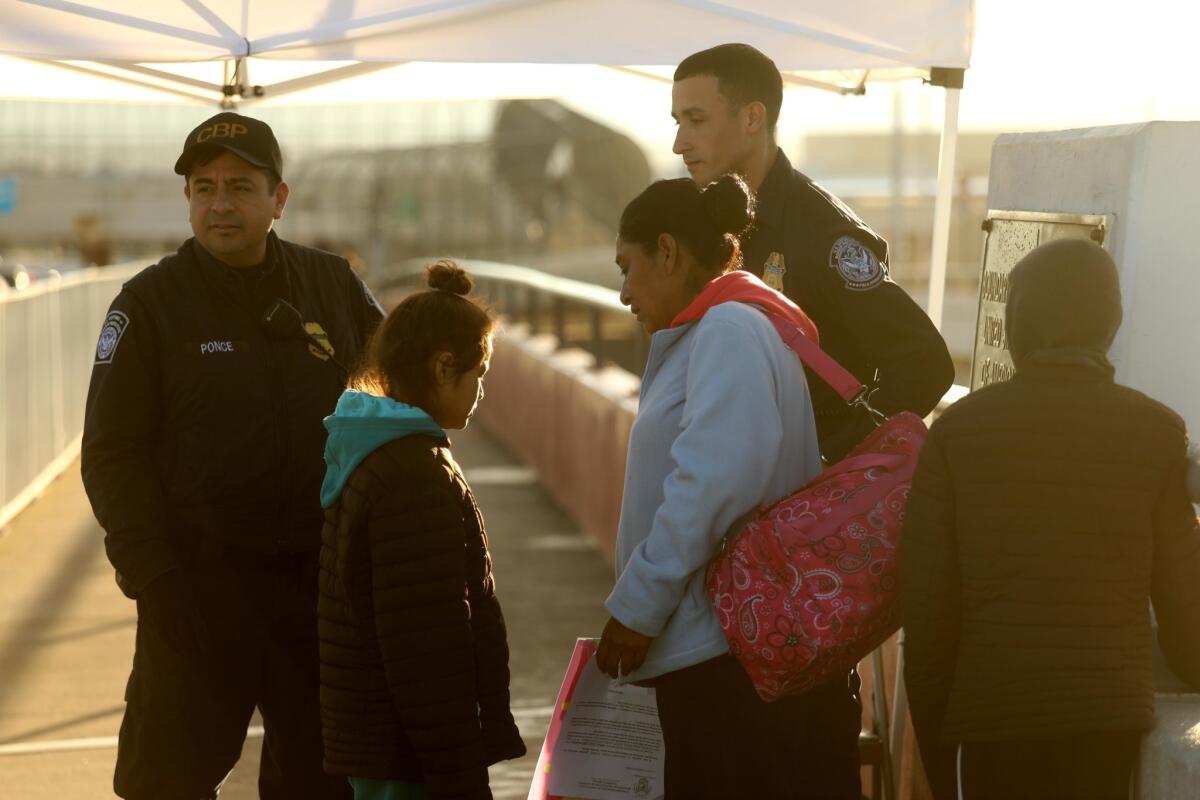

Reporting from El Paso — Migrants arriving at the U.S. border to seek asylum are routinely subjected to tactics that immigration rights advocates say are designed to drive them away in violation of their rights under federal law.
The tactics include forcing them to wait at the border indefinitely or sending them back into Mexico to join a backlogged list maintained by Mexican immigration officials.
The Trump administration says such measures are necessary because it is not equipped to deal with a large increase in the number of asylum seekers, many of them from Central America. Last year, U.S. immigration courts handled 120,000 asylum requests, a fourfold increase since 2013.
But immigrant advocates contend the government is violating the U.S. Immigration and Nationality Act, which says any foreigner who reaches the U.S. has the right to apply for asylum.
U.S. Customs and Border Protection “is violating the law and turning away asylum seekers on Texas bridges,” said Shaw Drake, an El Paso-based attorney with the Texas ACLU’s Border Rights Center.
He said forcing immigrants to join a long waiting list is tantamount to turning them away.
“To turn them away with some amorphous instructions is illegal,” he said.
The issue is likely to come to a head when a caravan of several thousand Central Americans now heading north through Mexico arrives at the U.S. border. Many are expected to claim asylum, which they can do based on fear of persecution due to their race, religion, nationality, social group or political opinion.
Trump, who has vowed to close the border, said in an interview Monday with conservative TV and radio host Laura Ingraham that the U.S. would allow migrants to file asylum claims but that they would be forced to live in “tent cities” while they await court rulings, a process that can take years.
“We’re not going to build structures and spend all of this, you know, hundreds of millions of dollars,” Trump said. “We’re going to have tents. They’re going to be very nice and they’re going to wait and if they don’t get asylum, they get out… They don’t usually get asylum.”
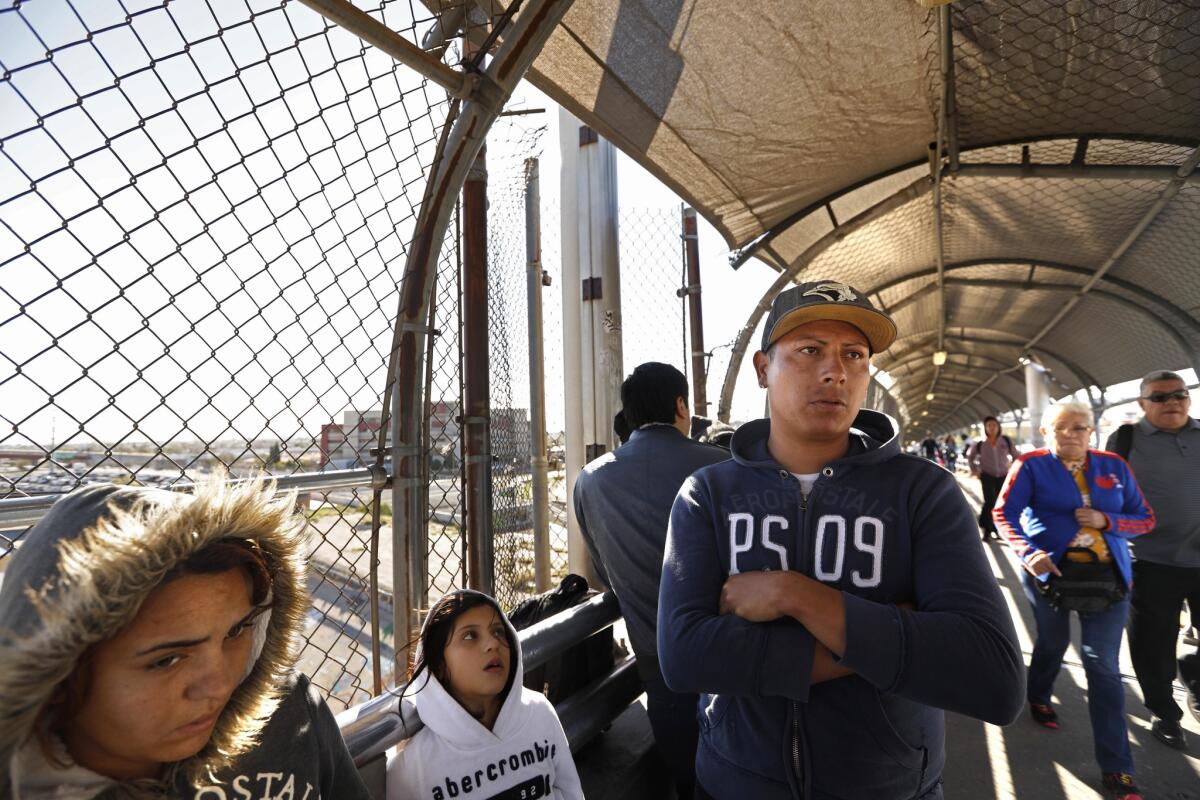

Last week, after 20 immigrants from Cuba, Honduras, Mexico and Russia arrived at the border bridge in El Paso, U.S. officers stationed in the middle of the bridge — the “limit line” — told them to wait. And so they did, some for days in the cold and rain. Others stayed at a nearby shelter.
“We’ll wait and see, night and day, because I don’t have anywhere to go,” said Alexander Narzilloev, 35, who was with his wife and sons, ages 3 and 6.
Narzilloev ran a construction supply business in Moscow but fled after he was extorted by local mafia and received death threats, including one from a man who called and said he knew where Narzilloev’s son attended kindergarten, he Narzilloev said.
The family had originally gone to the crossing in Calexico, Calif., where officers told them they didn’t have space. After waiting a week and spending what remained of their $8,000 savings on a hotel, Narzilloev and his family caught a bus to Ciudad Juarez, Mexico, in hopes of entering El Paso.
“I heard in the news Trump said close all the borders. Has it happened yet?” he said. “That’s supposed to be for illegals. We are legal.”
Last week, several House Democrats sent a letter to Homeland Security Secretary Kirstjen Nielsen requesting a briefing on why and how asylum seekers were being turned away. Sen. Tom Udall, a New Mexico Democrat, issued a statement calling for “fair and orderly processing of asylum seekers.”
“Any attempts to deny these families and individuals their right to seek asylum are wrong,” he said.
Is the U.S. really facing a border crisis? »
The Trump administration has tried a variety of approaches to deter people from trying to reach the United States — most controversially a “zero tolerance” policy of criminally charging every adult migrant who crosses the border illegally, separating parents from their children.
The policy resulted in 2,654 children being separated and widespread outrage before Trump canceled it in June.
The administration still wants to detain families indefinitely and has been battling immigrant advocates in hopes of overturning a federal judge’s 1997 order that requires children be held for no longer than 20 days. Federal prosecutors have also fought to narrow the definition of political asylum.
But the government has been flummoxed by what Kevin McAleenan, commissioner of Customs and Border Protection, calls the “asylum gap”: the inability to stop people from making false claims for asylum and living legally in the U.S. for years while their cases proceed.
Immigrant advocates say the new tactics at the border are aimed at discouraging asylum claims. The ACLU of Texas noted Tuesday that Customs and Border Protection, the largest federal law enforcement agency, with a staff and budget doubled in the last 20 years, processed 1.1 million fewer people at the southern border last year than it did in 2000.
Instead of expanding capacity to process asylum seekers at border crossings, officials have forced them to wait. The method varies from crossing to crossing.
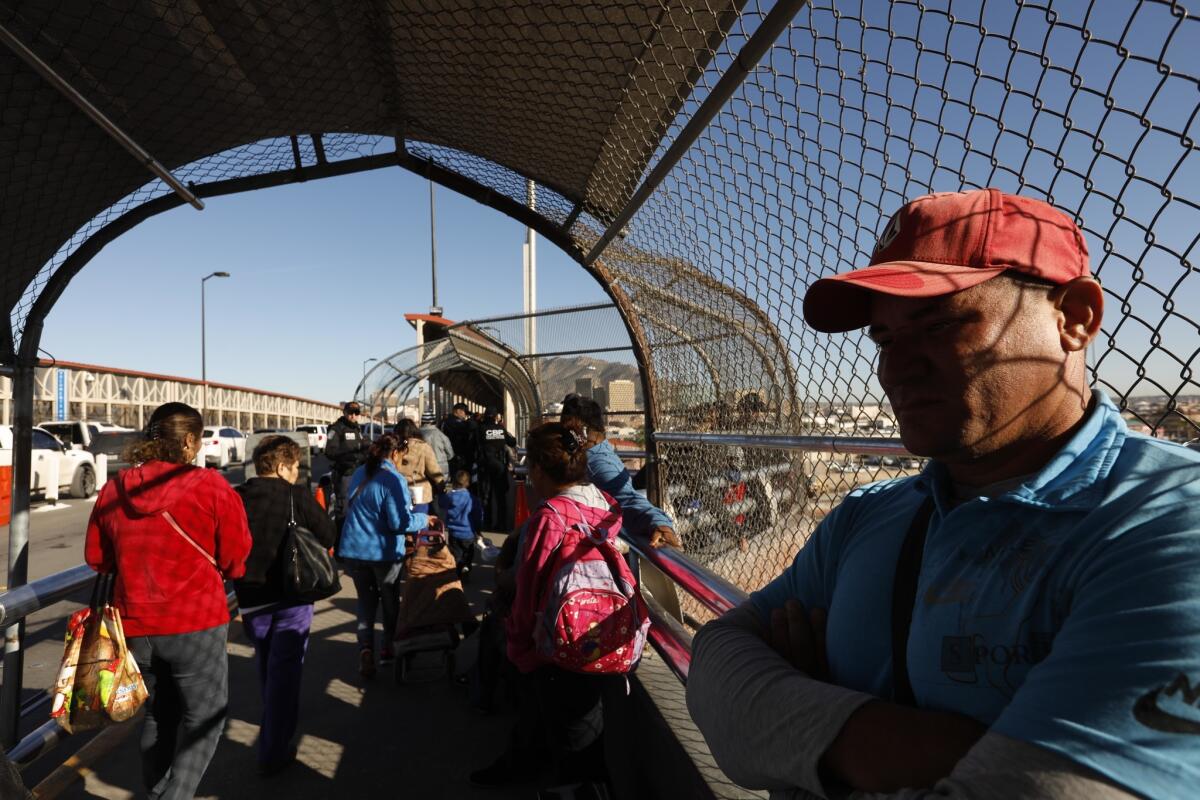

In El Paso, customs officers have told immigrants to return in a few hours, or simply “later.” The San Ysidro crossing in San Diego has been using a process called “metering,” in which asylum seekers have had to make appointments through Mexican immigration officials.
In a federal class-action lawsuit filed last year that’s still pending, Los Angeles- and Tijuana-based Al Otro Lado and other advocacy groups argued on behalf of more than a dozen immigrants that the policy violates international law and the right to due process.
The Office of Inspector General at the U.S. Department of Homeland Security recently reported that the practice of metering may have increased illegal border crossings.
During a visit to San Ysidro last week, McAleenan praised metering and said it’s likely to expand to other crossings if there’s a “significant increase in arrivals” in coming weeks.
He said the process didn’t amount to turning away immigrants because “they can stay in line if they want.”
“If somebody arrives and they have a claim, we are providing access,” he said, adding that some officers have been investigated, disciplined and retrained after turning away asylum seekers.
Other allegations were unsubstantiated, he said.
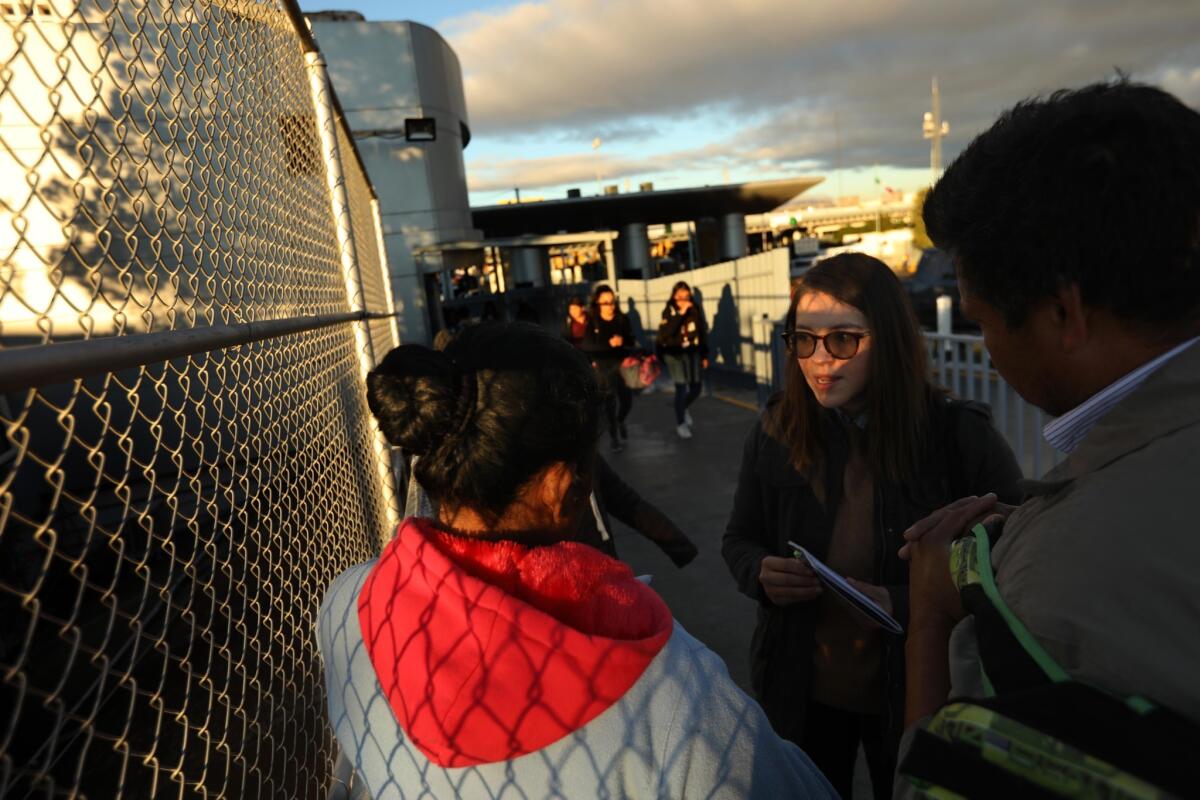

Workers from the nonprofit Hope Border Institute visit El Paso bridges to document cases of asylum seekers being turned away. On Oct. 24, they found Pedro Morales, 21, and girlfriend Janet Macola, 19.
The two said they fled Cuba after authorities halted their attempt to open a beauty salon and threatened to throw Morales in jail. Now they were seeking asylum.
So was a family of four from the southern Mexican state of Guerrero. They said that their area had become a ghost town, controlled by a mayor in league with organized crime, and that they were too scared to be quoted by name.
The Cuban couple and the Mexican family approached U.S. officers at the center of the bridge and were told the same thing: “It’s full right now.”
The asylum seekers lingered on the bridge.
“What can we do?” the Mexican mother said.
Out of money and options, they would wait.
molly.hennessy-fiske@latimes.com
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.