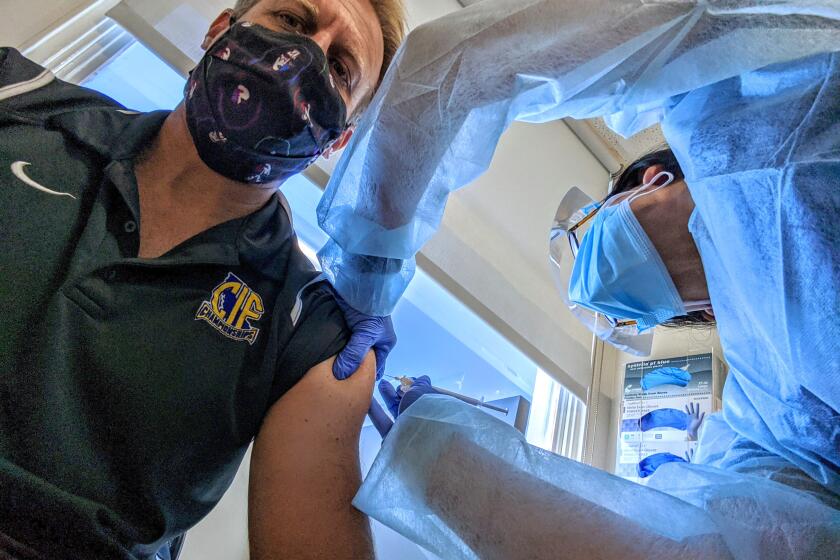
Despite COVID-19 vaccine successes, volunteers still needed for testing

Two COVID-19 vaccines might be nearing the finish line, but scientists caution it’s critical that enough people volunteer to help finish studying other vaccine candidates in the U.S. and around the world.
Moderna Inc. and competitor Pfizer Inc. recently announced preliminary results showing their vaccines appeared to be 95% and 90% effective, at least for short-term protection against COVID-19.
If those early results hold up — and U.S. regulators agree the shots are safe — emergency use of small, rationed supplies could start in late December. Other countries with contracts for early doses would undertake their own reviews.
But multiple vaccines will be needed to meet global demand and help end the pandemic. And that’s raising concern that the clinical trials that still need to sign up thousands of volunteers could run short if people decide to wait for an already OK’d option instead.
Father and daughter partook in a vaccine trial at Kaiser hospital. On Monday, Pfizer announced its success
“We don’t want to see that happen,” said Dr. James Cutrell, an infectious disease expert at UT Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Supplies aside, other COVID-19 vaccines under development may work differently in different populations, Cutrell said, and “we likely will benefit from having a menu of vaccine options.”
“We still need volunteers,” stressed Dr. Francis Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health. He urged Americans to sign up for clinical trials.
Additionally, participants in the Moderna and Pfizer studies who originally received dummy shots will almost certainly be offered the real vaccine if the U.S. Food and Drug Administration allows emergency use. But no one knows how long protection will last, meaning those studies also must continue to track recipients somehow.
“It’s one thing to be effective two months after your last vaccination and another thing to be effective a year” later, said Dr. Jesse Goodman of Georgetown University, a former director of the FDA’s vaccine division. “It’s going to be really important to complete these clinical trials and the trials of the other vaccines so we can make comparisons.”
Coronavirus vaccines developed by Moderna and Pfizer show highly promising preliminary results in large-scale clinical testing. But key questions remain.
The promising Moderna and Pfizer news bodes well for some of their competitors, said Dr. Anthony Fauci, the U.S. government’s top infectious disease expert whose team at NIH helped develop the Moderna candidate.
Those shots target the “spike” protein that studs the surface of the coronavirus, and the early results prove that’s enough to generate “a protective response,” Fauci said. “Conceptually this looks good” for other spike-focused vaccines made in different ways.
Here’s a scorecard of the front-runners in the global vaccine race:
Genetic code vaccines
The Moderna-NIH vaccine and the candidate developed by Pfizer and its German partner BioNTech aren’t made with the coronavirus itself, so there’s no chance anyone could catch it from the shots.
Instead, the vaccines are made with a brand-new technology that injects a piece of genetic code for the coronavirus’ spike protein. That messenger RNA, or mRNA, instructs the body to make some harmless spike protein — enough to prime the immune system to react if it later encounters the real virus.
The global race for a coronavirus vaccine involves a few basic approaches. Some have been around for decades, others are being tried for the first time.
Currently, there are no licensed mRNA vaccines for people, so scientists had no idea whether or how well the COVID-19 candidates might work.
Both manufacturers are working to scale up production in factories in the U.S. and Europe. They can’t simply partner with other vaccine companies to take on some of the work because the technology is so different than the way most of today’s shots are made.
“It is not a very easy or quick swap,” said Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel.
Trojan horse vaccines
These target the coronavirus spike protein in another way: They use a different, harmless virus to carry the spike gene into the body. Once again, the body produces some spike protein and primes the immune system to recognize it.
Britain’s Oxford University and AstraZeneca are making their version of this “viral vector” vaccine with a cold virus, or adenovirus, that normally infects chimpanzees. Studies of tens of thousands of people are underway in the U.K., U.S. and several other countries.
Johnson & Johnson is using a human adenovirus for its vaccine candidate. It’s the only option in advanced U.S. testing aiming to show whether a single dose, rather than two, would be enough.
China’s government authorized emergency use of CanSino Biologics’ adenovirus shots in the military ahead of any final testing. Russia likewise began offering an adenovirus vaccine ahead of late-stage tests.
Protein vaccines
Novavax makes its vaccine candidate by growing harmless copies of the coronavirus spike protein in the laboratory and packaging them into virus-sized nanoparticles.
There are protein-based vaccines against other diseases, so the technology is not as novel as that of some of its competitors. Novavax has begun a large final-stage study in Britain, and is set soon to begin another in the U.S.
‘Killed’ vaccines
Spike-focused vaccines aren’t the only option. Making vaccines by growing a disease-causing virus and then killing it is a tried-and-true approach — it’s the way Jonas Salk’s famed polio shots were made.
China has three so-called “inactivated” COVID-19 vaccine candidates in final testing in several countries, and has allowed emergency use in some people ahead of the results. An Indian company is testing its own inactivated candidate.
Safely brewing and then killing the virus takes longer than newer technologies. But inactivated vaccines give the body a sneak peek at the coronavirus itself rather than just that single spike protein.