Activists slam Johnson & Johnson for exporting COVID-19 vaccines from Africa

- Share via
JOHANNESBURG, South Africa — Health activists in Africa have slammed Johnson & Johnson for exporting COVID-19 vaccines produced in South Africa to countries in Europe, which have already immunized large numbers of their people and have even donated vaccines to needier countries.
The one-dose Johnson & Johnson vaccines were exported from South Africa, where they had been assembled, despite the pressing need for vaccines across Africa, where less than 3% of the continent’s 1.3 billion people have been fully vaccinated.
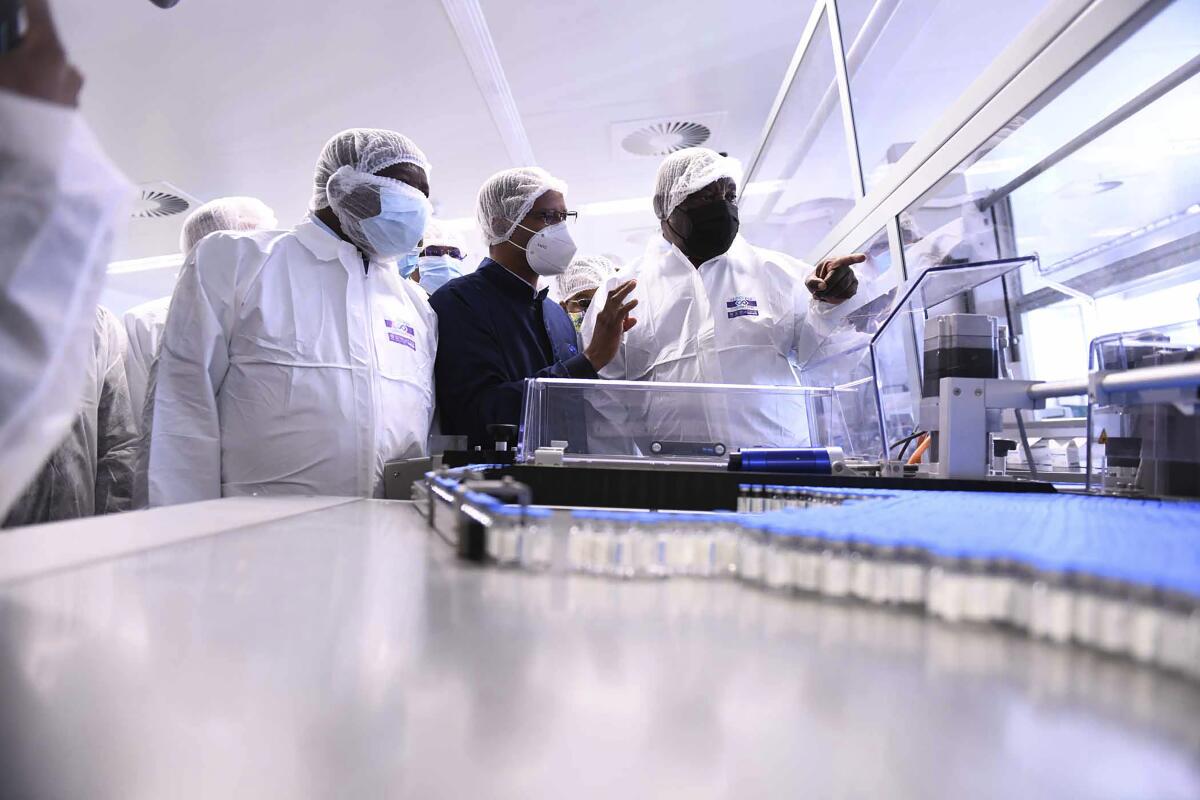
The South African activists Tuesday called for full disclosure of the South African government’s contracts with Johnson & Johnson and other vaccine manufacturers and threatened legal action to get the information. At a press briefing Tuesday, they reacted to revelations by the New York Times that millions of Johnson & Johnson doses produced by Aspen Pharmacare in the South African city of Gqeberha (formerly Port Elizabeth) are being exported to Europe.
The report also says that the South African government agreed to waive its right to ban exports to make sure that Johnson & Johnson could ship the vaccines abroad.
Aspen, a South African drug manufacturer, has a contract with Johnson & Johnson to assemble the ingredients of its COVID-19 vaccine, put it in vials and package it, a process called “fill and finish.” It was the first agreement for COVID-19 vaccines to be finished in Africa and was hailed by the African Union and the South African government as a boost for vaccine production and distribution in the continent.
The Aspen factory has the capacity to finish about 220 million Johnson & Johnson doses annually.
Nearly a dozen countries, most in Africa, still lack any COVID vaccine doses. They include Chad, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Eritrea and Tanzania.
“We believe that the conduct of Johnson & Johnson has been scandalous, immoral and unconstitutional,” Fatima Hassan of the Health Justice Initiative, an advocacy group in South Africa, said Tuesday.
The organization has already filed a request under South Africa’s Promotion of Access to Information Act to get access to the contracts, she said.
South Africa has vaccinated more than 2.1 million people with the Johnson & Johnson vaccine and has purchased 31 million doses, which are being delivered in large shipments from overseas and from the South African manufacturing plant. The rollout of the Johnson & Johnson vaccines has been delayed by delivery disruptions.
In addition to the Johnson & Johnson vaccines, South Africa is using the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. About 7% of South Africans are fully vaccinated and an additional 9% have received one dose. Overall, South Africa has given at least one vaccination does to more than 9.7 million people and is currently administering about 200,000 shots per day.
To fight future pandemics, nations in Africa, the Middle East and Latin America will need to build vaccine development capacity to suit regional needs.
Moses Muluba, from the Center for Health, Human Rights and Development in Uganda, said the distribution of vaccines produced in Africa to Europe shows glaring global inequity in the distribution of vaccines.
“In a country like Uganda where we have 44 million people, we have not even reached a target of 4 million vaccinations. Only 1.7 million have been vaccinated, but we cannot find vaccines in the market,” he said.
The vast majority of the world’s COVID-19 vaccine supply has already been bought up by rich countries, including the U.S., Canada and the European Union. While many of those countries have pledged to donate millions of vaccines to African countries, most of them won’t be delivered this year. And many are now planning booster shots for their own people.
“In this case, what does global solidarity mean? Vaccines made in South Africa were supposed to boost distribution to countries like ours, but that has not happened,” Muluba said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.