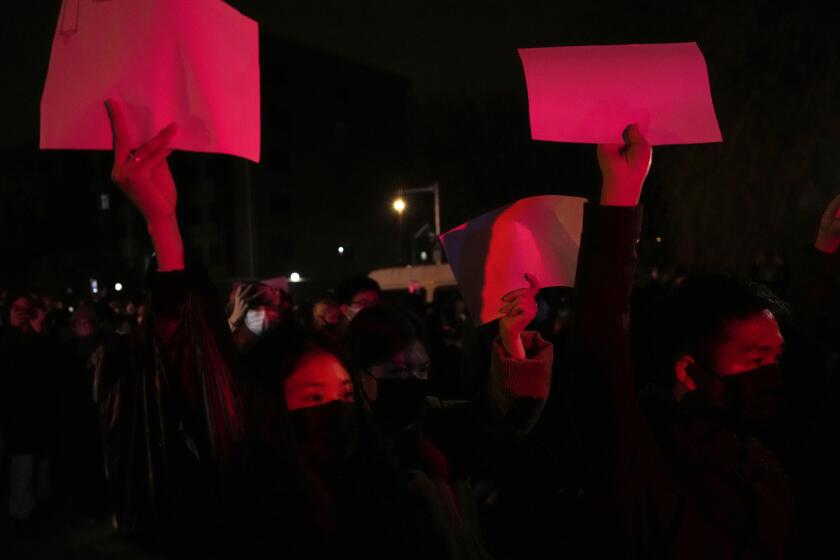China to drop some tracking of people’s travel as it relaxes anti-COVID measures

BEIJING — China planned to stop tracking some travel Monday, potentially reducing the likelihood people will be forced into quarantine after visiting COVID-19 hot spots, as part of an uncertain exit from the strict pandemic policies that helped fuel widespread protests.
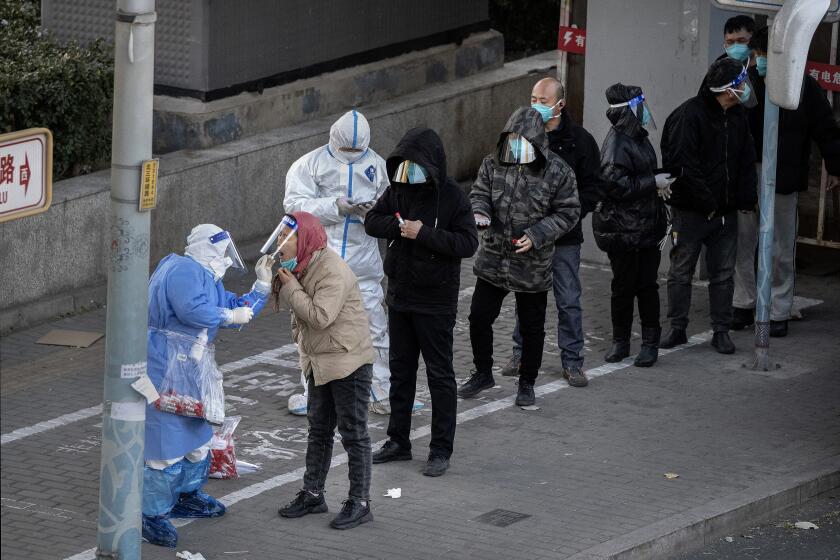
At midnight, the smartphone app that recorded a person’s travel between cities and provinces will be disabled. Another app used to restrict the movement of those who test positive or enter an area with a recent outbreak remains in effect. They’re part of a package of pandemic apps, some of which have also been used by local governments to suppress protests.
The move follows the government’s dramatic announcement last week that it was ending many of the strictest measures, following three years during which it enforced some of the world’s tightest coronavirus restrictions. That included near-constant mass testing, open-ended lockdowns and requirements that a clean bill of health be shown to access public areas.
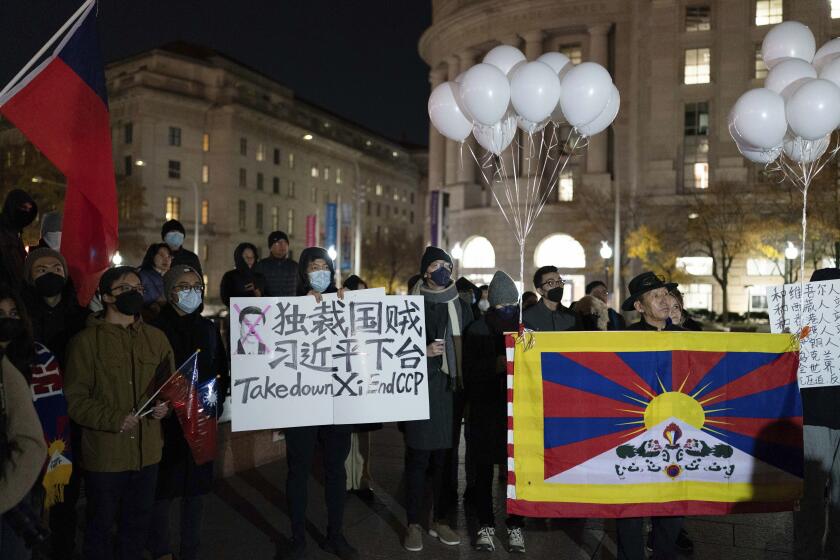
Last month in Beijing and several other cities, protests over the restrictions grew into calls for President Xi Jinping and the Communist Party to step down — a level of public dissent not seen in decades.
While met with relief, the relaxation has also sparked concerns about a new wave of infections potentially overwhelming healthcare resources in some areas.
The easing of measures means a sharp drop in testing, but cases still appear to be rising rapidly. China reported 8,500 new infections Monday, bringing the nation’s total to 365,312 — more than double the level Oct. 1. It has recorded 5,235 deaths — compared to 1.1 million in the United States.
First-time protesters in China grapple with how much agency they can wrest from an authoritarian government after the largest demonstrations since 1989.
China’s government-supplied figures have not been independently verified, and questions have been raised about whether the ruling Communist Party has sought to minimize numbers of cases and deaths.
Fever clinics at hospitals in Beijing received 22,000 patients Sunday — 16 times more than the previous week.
Following a rush last week to buy cold and flu medicine in many major Chinese cities, pharmacies in Hong Kong have reported a run on such medications by customers supplying relatives in mainland China, according to Lam Wai-man, chairman of the city’s pharmacy trade association. Hong Kong has already lifted most of its COVID restrictions.
“Everyone on the mainland wants to buy some pills to have in reserve at home,” Lam said.
Protesters in China are eager to see an easing of “zero-COVID” rules, but health experts warn that doing so could prompt a massive health emergency.
The uncertainty and apparent growing number of cases have forced the cancellation of events including foreign embassy holiday parties and next spring’s Formula One Chinese Grand Prix car race in Shanghai.
Xi’s government is still officially committed to stopping all coronavirus transmission, the last major country to try. But the latest moves suggest that the party will tolerate more cases without quarantines or shutting down travel or businesses as it winds down its “zero-COVID” strategy.
Facing a surge in COVID-19 cases, China is setting up more intensive care facilities and trying to strengthen hospitals’ ability to deal with severe cases. At the same time, part of the relaxation means that the government will allow those with mild symptoms to recuperate at home rather than being sent to field hospitals that have become notorious for overcrowding and poor hygiene.
Reports on the Chinese internet, which is tightly controlled by the government, sought to reassure a nervous public, stating that restrictions would continue to be dropped and that travel, indoor dining and other economic activity would soon be returning to pre-pandemic conditions.
An orderly end to the nation’s ostensible lockdown is China’s only path toward health or civil obedience.
China’s leaders had long praised “zero COVID” for keeping numbers of cases and deaths much lower than in other nations, but officials have recently begun to talk about the coronavirus as far less threatening and now say the most prevalent Omicron variety poses much less of a risk.
Amid the unpredictable messaging from Beijing, experts warn that there still is a chance the ruling party might reverse course and re-impose restrictions if a large-scale outbreak ensues.
Last week’s announcement allowed considerable room for local governments to assign their own regulations. Most restaurants in Beijing, for example, still require a negative test result obtained over the previous 48 hours, and rules are even stricter for government offices.
The change in policy comes after protests erupted Nov. 25, following the deaths of 10 people in a fire in the northwestern city of Urumqi. Many questioned whether COVID-19 restrictions impeded rescue and escape efforts. Authorities denied the allegation, but demonstrators gave voice to longstanding frustration in cities, such as Shanghai, that have endured severe lockdowns.
News Alerts
Get breaking news, investigations, analysis and more signature journalism from the Los Angeles Times in your inbox.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.
The party responded with a massive show of force, and an unknown number of people were arrested at the protests or in the days following.
The relaxation began shortly after — though the government had already announced its intention to begin opening up slowly, promising to reduce the cost and disruption after the economy shrank by 2.6% from the previous quarter in the three months ending in June.
Forecasters say the economy probably is shrinking in the current quarter. Imports tumbled 10.9% from a year ago in November in a sign of weak demand.
Some forecasters have cut their outlook for annual growth to below 3%, less than half of last year’s robust 8.1% expansion.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.